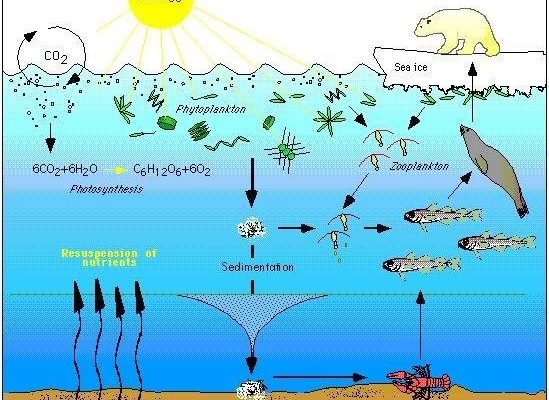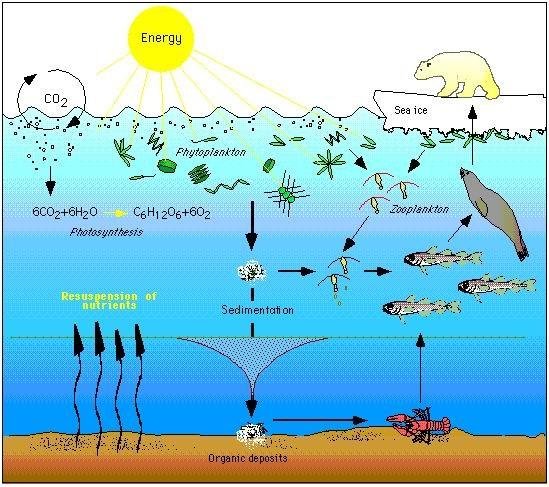
Imagine the snapper as a kind of ocean canary. Just like canaries in coal mines alert miners to danger, snapper can signal when something’s amiss in the ocean. As temperatures rise and environmental conditions change, snapper face new challenges that could affect their survival. Understanding these impacts can help us recognize the broader shifts happening in our oceans and why they matter to all of us.
Understanding Snapper Habitats
Snapper, particularly species like the red snapper, thrive in warm, shallow waters. These areas are typically rich in nutrients and support a diverse ecosystem. You might find them lurking around reefs, rocky structures, and in sandy areas on the continental shelf. Imagine these fish as the social butterflies of the ocean—gathering in schools, darting through coral formations, and feeding on smaller fish and crustaceans.
As climate change kicks in, we see rising sea temperatures and changes in ocean chemistry. The waters are warming at an alarming rate, disrupting the delicate balance of these habitats. Think of it like turning up the heat in an oven. At some point, it’s just too hot, and things start to burn—or in the snapper’s case, simply can’t survive.
These temperature changes not only affect the snapper directly by altering their habitats but also impact the food they rely on. The phytoplankton and smaller fish that snapper feed on are equally sensitive to temperature shifts, and any disruption in their populations can lead to a domino effect.
Impact of Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is another sneaky side effect of climate change that’s making life tough for snapper. When we burn fossil fuels, carbon dioxide (CO2) is released into the atmosphere. Some of that CO2 is absorbed by the oceans, causing the water to become more acidic. You might be wondering, “Why should I care about that?” Well, it turns out that increased acidity can harm the delicate structures made by marine life.
Coral reefs, which are essential habitats for snapper, are especially affected. When the water turns more acidic, it becomes harder for corals to build their calcium carbonate structures. It’s like trying to stack building blocks while someone keeps knocking them down. Over time, this can lead to weaker reefs, reducing the habitat and shelter that snapper need to thrive.
Additionally, changes in water chemistry can weaken or disrupt the sensory systems of snapper. They rely on these senses to find food and evade predators. Less efficient hunting means fewer snappers—and that’s a problem for both the fish and the fishermen who depend on them.
Changes in Migration Patterns
Fish are not lazy swimmers; they often migrate to find optimal living conditions. Snapper are no exception. As ocean temperatures rise, they might shift their migration patterns in search of cooler waters. You could think of this like people moving to a new city for a better job or living situation.
However, this is not as simple as packing up and leaving. Migration patterns are intricate, involving not just the snapper but their prey and predators too. A change in one species can ripple through the entire ecosystem. If snapper move to cooler waters, it can lead to overpopulation in one area while leaving others drained of resources. This can create tension among local fishermen and communities reliant on them for income and food.
Moreover, if snapper don’t migrate fast enough, they may find themselves in waters that are unsuitable for breeding or feeding. It’s a tricky balancing act, and unfortunately, the scales are tipped against them.
The Role of Overfishing
While climate change is a significant challenge for snapper, overfishing is another massive hurdle that compounds the problem. Think of the ocean as a large buffet. If too many people come in and take too much food, the buffet won’t last long. Similarly, overfishing disrupts snapper populations, making recovery even tougher under changing conditions.
Overfishing can deplete snapper numbers to critical levels, which means they cannot reproduce fast enough to sustain their populations. This issue is further exacerbated by climate change, as fewer fish mean less genetic diversity, making it harder for the species to adapt to new conditions.
In some regions, regulations and fishing limits are in place to help protect snapper populations, but compliance is inconsistent. Fishermen face tough choices: balancing their livelihoods with the health of the oceans. It’s a tough situation, and without effective management, the future of snapper could be in jeopardy.
Adaptations and Resilience
Despite all these challenges, nature has a way of surprising us with resilience. Snapper have some remarkable adaptability traits. For instance, they can adjust their spawning times in response to changing environmental conditions. When temperatures rise, some snapper might choose to spawn earlier or later than usual, hoping to catch the best conditions for their young.
This flexibility can be a game changer, but it only works up to a point. If changes happen too quickly or drastically, even the most adaptable species can struggle. Imagine trying to change your lifestyle overnight; it’s not easy for anyone!
It’s also vital to note that conservation efforts can help give snapper a fighting chance. Creating marine protected areas and enforcing sustainable fishing practices allows snapper populations to rebound. It’s like giving them a safe space to thrive and reproduce without the pressures of overfishing or habitat destruction.
The Bigger Picture: Why Snapper Matter
You might be thinking, “Why does all this matter to me?” Well, snapper are more than just a fish; they’re indicators of ocean health and biodiversity. Healthy snapper populations signal robust ecosystems, which benefit countless other marine species, from the tiniest shrimp to the largest whales.
Furthermore, snapper are essential to many coastal communities. They contribute to livelihoods through fishing and tourism. Protecting snapper means not just looking after a species, but also safeguarding cultural practices and economies.
Ultimately, understanding how climate change affects the snapper is crucial for developing effective strategies for marine conservation. It’s all interconnected, and as we work to protect the snapper, we’re also taking steps to secure a healthier planet for future generations.
In closing, the challenges faced by snapper due to climate change illustrate a pressing need for collective action. From individuals making sustainable choices to policymakers enforcing better regulations, everyone has a role to play. The ocean—and its inhabitants—depend on it. By understanding and addressing these issues, we can help ensure a sustainable future for snapper and the broader marine ecosystem. So, let’s keep the conversation going and take steps toward a healthier ocean together!