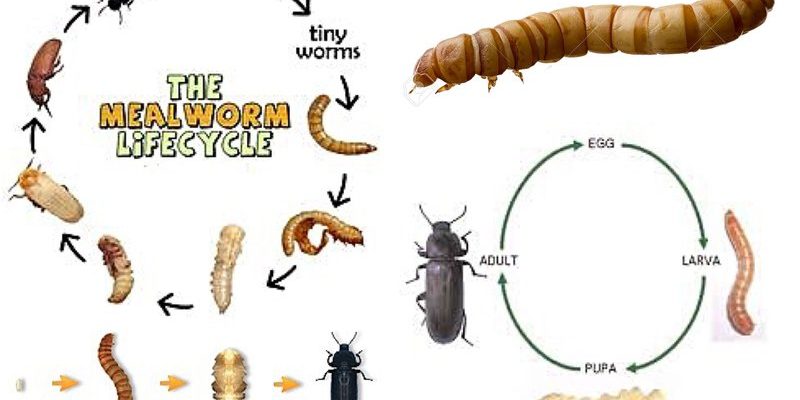
Wolf worms, also known as larvae of the **Dermatobia hominis**, depend on other animals to grow. This is where things get interesting. Depending on whether they latch onto mammals, birds, or even reptiles, their development timelines will vary. Let’s explore these unique timelines and how they relate to the host species.
What Are Wolf Worms?
Wolf worms are the larvae of the **botfly**, a unique type of fly known for its unusual reproductive strategies. After being laid, these larvae need a host to survive and grow. Once they enter the host’s skin, they go through different stages of development.
Here’s the thing: not all hosts provide the same environment. Factors like body temperature, immune system responses, and even skin thickness can influence how quickly these larvae grow. So, let’s break down how these factors play into the development timeline, depending on the host.
Wolf Worms in Mammals
When wolf worms infect mammals, they often choose larger animals like **cattle** or even **humans**. The development cycle for wolf worms in mammals can last anywhere from 4 to 10 weeks.
– **Initial Infection:** After the larvae enter the skin, they can cause irritation. You might notice a swelling or bump where they’ve entered. This is normal.
– **Feeding Stage:** During this stage, they feed on the host’s tissues. It’s a bit like them having a buffet of nutrients! This stage can last several weeks, allowing them to grow sufficiently before they mature.
– **Pupation:** After several weeks of feeding, they emerge from the host’s skin to pupate. This is when they turn into adult flies and begin the cycle all over again.
Mammals are often preferred because of their considerable mass, which provides a robust environment for growth.
Wolf Worms in Birds
Birds present a different scenario for wolf worms. The development timeline for these larvae in birds typically ranges from 3 to 6 weeks. Birds have a faster metabolism than mammals, leading to quicker development.
– **Entry Point:** Similar to mammals, wolf worms will enter through the skin. However, because birds usually have thinner skin, the larvae can settle in without much hassle.
– **Growth Phase:** While feeding, wolf worms can cause discomfort to the host, often leading to health complications. Birds may show signs of restlessness or unusual behavior due to irritation from the larvae.
– **Emergence:** Once fully grown, the larvae will exit the bird’s skin and find a safe spot to pupate.
Birds might not provide as robust a feeding environment as mammals, but their rapid metabolism creates a unique challenge for these larvae.
Wolf Worms in Reptiles
When it comes to reptiles, wolf worms are less common, but they do still occur. The development timeline in reptiles like snakes and lizards tends to be slower, often taking around 6 to 12 weeks.
– **Entry & Adaptation:** Reptiles have tough, scaly skin, which can be a barrier for wolf worms. This means they often take longer to penetrate and get settled.
– **Feeding and Growth:** In this stage, their growth can be hindered by the host’s natural defenses. Since reptiles may not provide the same nutritional value as mammals or birds, the larvae might grow slower.
– **Pupation and Emergence:** After enough time, the wolf worms can emerge, but the overall cycle may last longer compared to mammals and birds.
Interestingly, the slower development can sometimes provide an advantage, as fewer predators may be around for the less common hosts.
Impact of Environmental Factors
Aside from the host species, environmental factors can also affect the development of wolf worms. For instance, temperature and humidity levels can either speed up or slow down their growth.
– **Temperature:** Warmer environments usually lead to faster development. Think of it like baking cookies. The warmer the oven, the quicker they cook!
– **Humidity:** High humidity levels can also support larvae growth, providing a conducive environment for feeding and development.
Surprisingly, the right external conditions can be just as important as the host itself when it comes to the success of wolf worm development.
Why Understanding Development Timelines Matters
So, why should we care about the development timelines of wolf worms by host species? Understanding these timelines can help in various ways:
– **Veterinary Health:** Knowing how these larvae develop can assist veterinarians in diagnosing and treating infestations.
– **Wildlife Management:** Wildlife biologists can use this knowledge to manage animal populations and their health.
– **Human Health Awareness:** Since wolf worms can infect humans, being aware of the timelines could lead to better preventive measures.
Ultimately, understanding the timelines can lead to healthier environments for both animals and humans alike.
Exploring the wolf worm’s development timelines by host species reveals the intricate connections in nature. These tiny larvae may seem daunting, but they serve a purpose in the grand scheme of ecosystems. Whether they’re feeding on mammals, birds, or reptiles, they remind us of the delicate balance in the animal kingdom.
By appreciating how different host species affect these timelines, we can create better strategies for managing wildlife and ensuring the health of both animals and humans. Understanding nature’s complexities is key to living harmoniously with the world around us. So, the next time you hear about wolf worms, you’ll know just how fascinating their life cycle truly is.