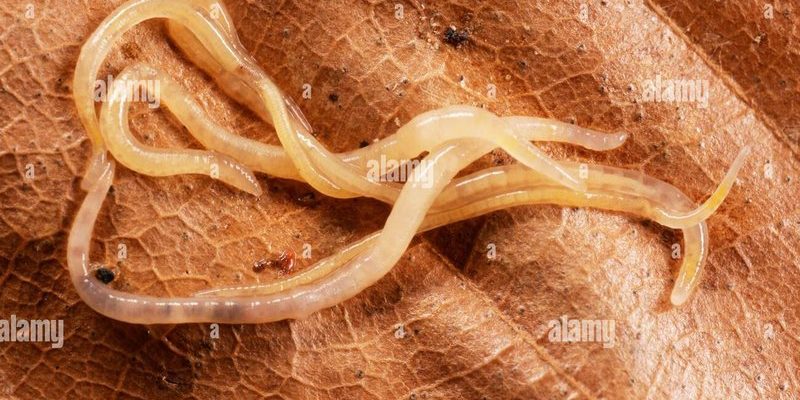
You might be wondering why we’d use these tiny worms instead of more visible indicators like plants or larger animals. Well, enchytraeids are sensitive to changes in their environment, making them excellent bioindicators. They respond to pollutants, soil composition, and moisture in ways that can reveal the underlying health of an ecosystem. In this article, we’ll dig into how enchytraeids can act as messengers about environmental conditions, why they matter, and how they’re used in monitoring efforts.
What are Enchytraeids?
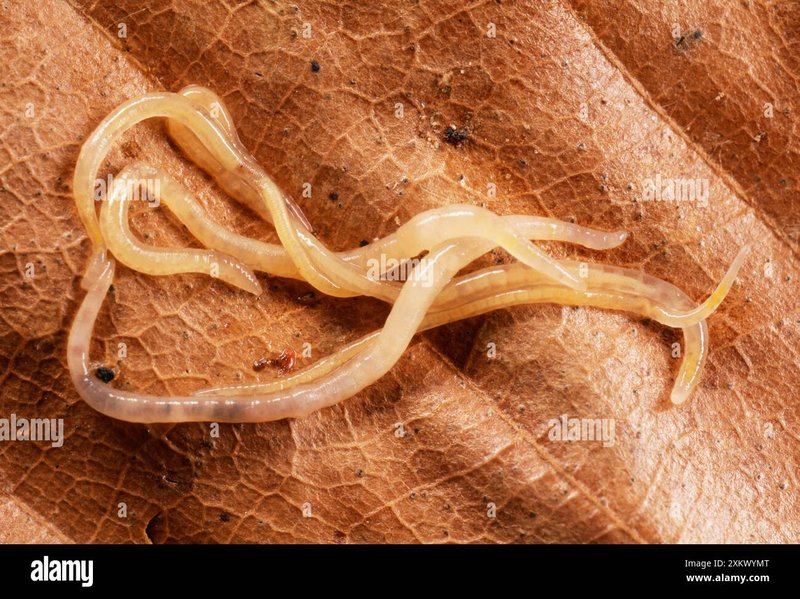
Enchytraeids are small, white worms that live in the soil. They belong to a group of organisms known as oligochaetes, which are relatives of earthworms. Usually less than an inch long, these worms thrive in moist environments, often found in rich organic matter. Because they’re so small, you might overlook them, but they play a crucial role in breaking down organic materials and cycling nutrients back into the soil.
Their presence indicates healthy soil. If you scoop up a handful of dirt and find several of these little guys wriggling around, that’s usually a good sign! They contribute to soil aeration, improve drainage, and help facilitate plant growth by enhancing soil fertility.
Enchytraeids also reproduce quickly, which makes them even more useful for monitoring purposes. You can observe changes in their population density over time, providing a quick snapshot of soil health or environmental changes.
Why Use Enchytraeids for Environmental Monitoring?
There are plenty of reasons to consider using enchytraeids in environmental monitoring. First, they have a high sensitivity to changes in their environment. When soil quality changes due to pollution or other factors, you can often see that reflected in enchytraeid populations. This sensitivity makes them a reliable indicator of soil health.
Additionally, studying enchytraeids can be cost-effective. Rather than expensive and time-consuming tests, monitoring these small worms allows researchers and environmentalists to quickly gauge soil health with relatively low effort. This means that even community projects or smaller organizations can use them as part of their environmental assessments.
Finally, enchytraeids are part of a larger ecosystem of organisms. By tracking their populations, we gain insights into the overall health of the soil ecosystem, which impacts plants, animals, and even humans. Ensuring healthy soil helps maintain biodiversity and a sustainable environment.
How Do Enchytraeids Serve as Bioindicators?
Enchytraeids act as bioindicators by responding to environmental stressors like pollutants. For instance, when heavy metals or pesticides seep into the soil, these worms may show a decline in population or changes in behavior. Researchers can then use this information to assess the level of contamination in a given area.
You might be curious about how this actually works in practice. Environmental scientists conduct studies by sampling soil from various sites. They’ll collect and analyze the enchytraeid population, which can then reveal exposure levels to contaminants. A drop in their numbers can signal the presence of harmful substances, allowing for targeted clean-up efforts.
Overall, the interactions between enchytraeids and their environment provide valuable data. By understanding how these worms respond to different conditions, researchers can develop better conservation strategies and improve soil health.
Enchytraeids vs. Other Bioindicators
While enchytraeids are fantastic bioindicators, they’re not the only game in town. Other organisms, like earthworms, insects, and even plants, can also indicate soil health. However, each indicator has its pros and cons.
For example, earthworms are larger and easier to spot, but they often live deeper in the soil and may react more slowly to changes. In contrast, enchytraeids are surface-dwellers, making them more responsive to short-term environmental shifts. Their quick reproduction rates also mean they can rebound faster after improvements in soil quality.
On the other hand, insects can serve as excellent bioindicators, but they can be more variable in their responses based on life cycles and other factors. By using a combination of these indicators, environmental scientists can get a more comprehensive picture of soil health.
The Process of Using Enchytraeids in Monitoring
Using enchytraeids for environmental monitoring involves several steps. First, scientists select specific sites for sampling. These sites could be industrial areas, urban gardens, or natural habitats. Each site presents unique challenges and conditions that contribute to soil health.
Next, they’ll take soil samples, often using a cylindrical sampler. This process needs to be done carefully to avoid disturbing the worms too much. Once collected, the soil is screened to separate the enchytraeids from the rest of the soil and organic matter. This allows researchers to count their numbers and identify any species present.
After counting and identifying the worms, scientists analyze the data. They’ll look for patterns or changes in population densities and compare these to historical data or different sites. This analysis is crucial for assessing soil health and can lead to actionable insights about the environment.
Challenges in Using Enchytraeids for Monitoring
While using enchytraeids for environmental monitoring sounds straightforward, there are challenges. One major issue is the potential for inconsistencies in data collection. Factors like sampling techniques or seasonal variations can affect results. Researchers need to standardize methods to ensure reliable data.
Another challenge is understanding the full range of environmental factors that might influence enchytraeid populations. Pollution isn’t the only factor; moisture levels, temperature, and organic matter availability can all play significant roles. This means researchers have to consider multiple variables when interpreting the data.
Lastly, public awareness and understanding of these tiny creatures are often lacking. Many people are unaware of the importance of enchytraeids, which makes it difficult to advocate for their role in environmental monitoring. Education and outreach are key to raising awareness about their significance.
The Future of Enchytraeid Research
The future looks promising for enchytraeid research in environmental monitoring. As we face increasing environmental challenges, the need for effective and affordable monitoring solutions like these little worms is more critical than ever. Ongoing research aims to refine sampling techniques, enhance our understanding of their biology, and better integrate their use into environmental assessments.
You might also see greater collaboration among researchers, government agencies, and community groups to promote the use of enchytraeids in monitoring initiatives. With more attention on soil health, there’s potential for these worms to contribute significantly to global sustainability efforts.
In conclusion, enchytraeids offer a unique perspective on environmental monitoring and bioindication. Their sensitive response to changes in soil health makes them invaluable allies in the fight for a cleaner, healthier environment. By understanding and utilizing these tiny worms, we can gather important insights that ultimately lead to better conservation practices and a healthier planet for future generations.

