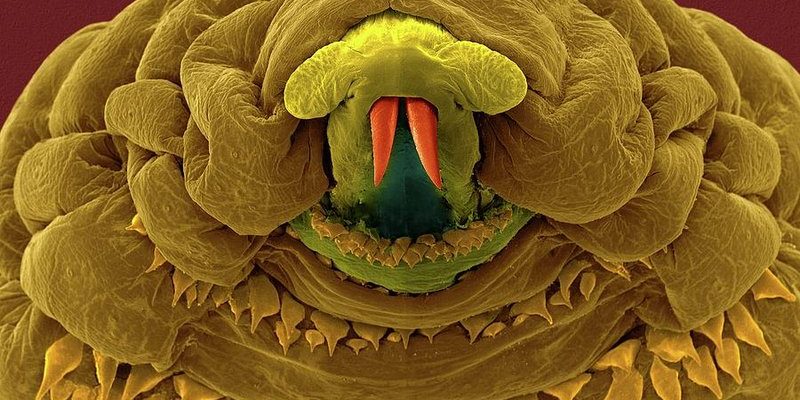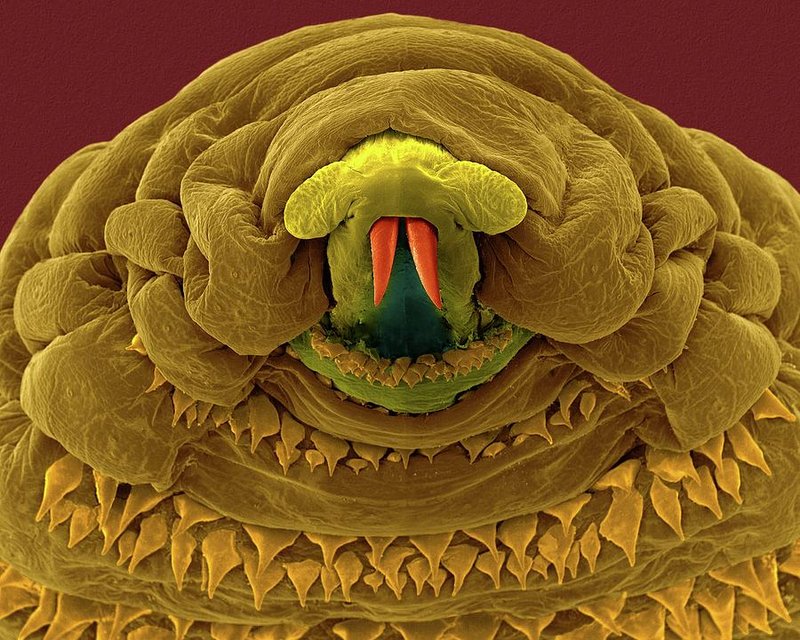
Understanding botfly larvae isn’t just about knowing what they are; it’s also about how they impact their environment. In research studies, scientists have unraveled their fascinating roles, from how they affect host animals to their influence on soil health. So, let’s dive deeper into the world of botfly larvae and explore the ecosystem roles they play.
What Are Botfly Larvae?
Botfly larvae are the young stage of botflies, which are a type of fly found mainly in tropical and subtropical regions. These tiny creatures start their lives as eggs laid on the skin or fur of animals, particularly mammals. Once the eggs hatch, the larvae burrow into the host’s skin, where they develop over several weeks. You might be thinking, “Wow, that sounds a bit creepy!” And it is! But this life cycle has fascinating implications for the environment.
The nature of their parasitism can lead to some interesting dynamics in the ecosystems they inhabit. For instance, the presence of botfly larvae can indicate a healthy population of host animals. In a way, these larvae are like nature’s little health check-ups for wildlife! By studying where and how they thrive, researchers can gather important data about the health of various species and their habitats.
The Life Cycle of Botfly Larvae
The life cycle of botfly larvae is a neat example of nature’s complexity. It begins when a female botfly lays her eggs on a host animal, such as a cow or a human. The eggs hatch, and the larvae penetrate the skin, where they live for several weeks. During this time, they feed on the host’s tissue, which might sound alarming, but it’s a natural part of their growth.
As the larvae grow, they create a hole in the skin to breathe. This hole is not just a nuisance; it can even attract other insects that can help in the decomposition process once the larvae eventually fall out and become pupae. The cycle continues as these pupae develop into adult botflies, ready to lay their eggs once again. This intricate cycle is a beautiful example of how life perpetuates itself, even in the most unexpected forms.
The Ecological Impact of Botfly Larvae
You might be surprised to learn that botfly larvae play a role beyond just being parasites. Their presence in an ecosystem can affect various components of that ecosystem. For instance, when they invade a host, they can change the behavior of that animal. The discomfort and injury caused by the larvae may make the host more vulnerable to predators or affect its ability to reproduce.
On the flip side, as botfly larvae develop, they contribute to nutrient cycling. When they leave the host, they return to the environment, where their decomposition helps enrich the soil. This process is essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems. So, while botfly larvae might seem like a pest to some, they also contribute to the natural balance.
Research Insights on Botfly Larvae
Recent studies have shed light on botfly larvae and their roles in the ecosystem. Researchers are using various methods, from field studies to lab experiments, to understand how these creatures interact with their environment. For example, studies have shown that the density of botfly larvae can be linked to the health of certain wildlife populations. More larvae may indicate that a particular host species is thriving, while fewer may signal issues.
Additionally, researchers are investigating how botfly larvae impact the microbial communities in the soil. When they exit their hosts, they can leave behind a nutrient-rich legacy, promoting beneficial bacteria and fungi that support plant growth. This interconnectedness illustrates just how vital even the smallest creatures can be in maintaining ecological balance.
Botfly Larvae and Biodiversity
Biodiversity is crucial for healthy ecosystems, and botfly larvae are part of that picture. Their interactions with various host species help maintain a balance that supports a wide range of life. In areas with higher biodiversity, you might find a greater variety of botfly species, each adapted to different hosts and environments.
Furthermore, the presence of botfly larvae can influence competition among species. For instance, if one host species is heavily infested, it might struggle against competitors for resources. This could lead to shifts in population dynamics, affecting predator and prey relationships. It’s a delicate dance that highlights the interconnectedness of life.
Conservation Considerations
Understanding the role of botfly larvae in ecosystems has important implications for conservation efforts. As habitats change due to climate change, urbanization, and other factors, the dynamics of host species—and consequently the botfly populations—can shift as well. This might lead to a decline in biodiversity, which could hurt the ecosystem’s overall health.
Conservationists are now looking at how these larvae can serve as bioindicators for ecosystem health. By monitoring botfly populations, we can gain insights into the broader environmental changes occurring around us. This information can guide efforts to protect habitats and ensure that the delicate balance of life continues.
While botfly larvae might not be the most charming creatures in the animal kingdom, their roles in ecosystems are undeniably important. From influencing host behaviors to enriching the soil, these little larvae are key players in the natural world. Research studies on botfly larvae have uncovered fascinating insights into their life cycles and interactions, reminding us of the intricate webs of life we’re all part of.
So next time you hear about botflies, remember there’s more to them than meets the eye. They’re part of a complex ecosystem, and every creature, no matter how small or seemingly bothersome, plays a role in the grand tapestry of life. By understanding these roles, we can appreciate the beauty and complexity of the world around us a little more.