Marine polychaetes are more than just the ocean’s workhorses; they play vital roles in ecosystems as scavengers, predators, and prey. Let’s dive deep into their life cycle, from the delicate beginnings to their complex adult behavior, and explore the unique traits that make these worms special. Whether you’re a marine biology enthusiast or just curious about the ocean’s residents, it’s time to unravel the mysteries behind the life of polychaetes!
What are Marine Polychaetes?
Before we jump into their life cycle, let’s get to know marine polychaetes a little better. These worms belong to the class Polychaeta, a diverse group primarily found in oceanic environments. Unlike their earthworm cousins, polychaetes have numerous bristles called setae along their body segments, which help them move and anchor in their habitat. You might encounter them in various environments, from coral reefs to deep-sea sediments.
What truly sets polychaetes apart is their body structure. They’re typically elongated, segmented, and come in a variety of colors and sizes. Some are small and unassuming, while others can be quite large and vividly colored. Imagine them as the quirky artists of the sea, with each species bringing its own flair to the underwater canvas.
These worms have adapted to thrive in many niches of the marine ecosystem. They can be scavengers or predators, feeding on organic matter or smaller creatures. Their flexibility in diet and habitat makes them key players in maintaining the balance of marine life.
The Stages of the Polychaete Life Cycle
Marine polychaetes undergo a fascinating series of stages in their life cycle. Understanding these stages helps us appreciate how they grow and adapt to their environments. There are generally two main phases: the larval stage and the adult stage.
1. Fertilization and Larval Development
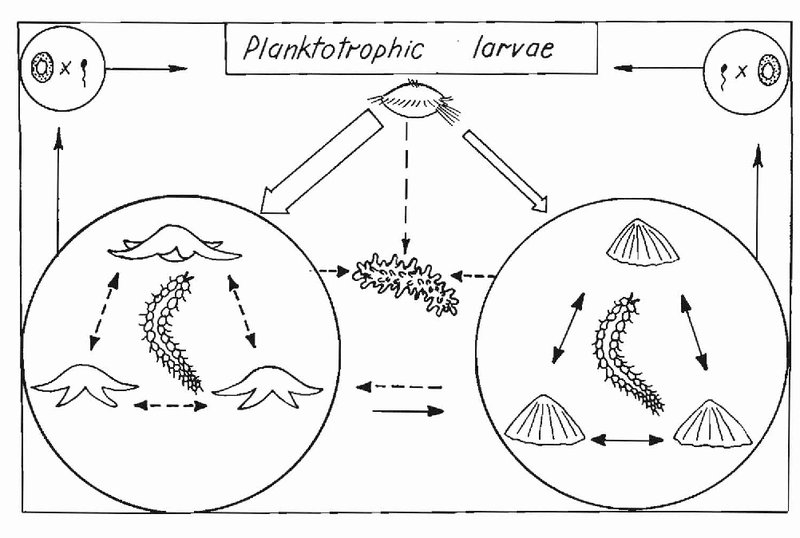
The life of a polychaete begins with fertilization. When conditions are right, adult polychaetes release their eggs and sperm into the water. Here’s the thing: the journey starts with a large number of eggs, but only a few will survive to adulthood. The fertilized eggs develop into free-swimming larvae called trochophore larvae.
These tiny larvae are a marvel of nature. They’re equipped with cilia—tiny hair-like structures—that help them swim through the water. During this stage, they drift with ocean currents, feeding on plankton and other small particles. It’s a bit like a toddler trying to navigate a bustling playground, surrounded by other larvae and colorful marine life.
As they grow, trochophore larvae undergo metamorphosis, transforming into more complex forms called metatrochophore larvae. This change allows them to start settling down on the ocean floor, where the next phase of their life begins.
2. Settling and Adult Development
Once the larvae settle on the seafloor, they begin to develop into juvenile polychaetes. This phase is crucial because it marks the transition from floating free in the water to living among the rocks, sediment, or coral. You might be wondering, how do they choose where to settle? Well, it often depends on environmental factors like food availability and habitat type.
As they transition into adults, polychaetes undergo segmentation, where their bodies become more defined and complex. They start to develop their characteristic setae and parapodia—fleshy appendages that help with locomotion and respiration. Honestly, watching a polychaete wriggle and move around is like witnessing a small dancer perform on the ocean floor, gracefully navigating its surroundings.
This adult stage can last for many years, depending on the species and environmental conditions. Polychaetes can live in various habitats, from shallow coastal waters to deep-sea environments, making them incredibly adaptable.
Behavioral Traits of Marine Polychaetes
Now that we’ve explored their life cycle, let’s dive into some of the interesting behaviors exhibited by marine polychaetes. These creatures are not just passive inhabitants of the ocean; they’re active participants in their ecosystems.
1. Feeding Habits
Marine polychaetes have diverse feeding strategies, which often depend on their habitat. Some are filter feeders, using their tentacle-like structures to capture plankton and organic matter from the water. Others are predators, actively hunting smaller marine animals. You might think of them as the vacuum cleaners of the ocean floor, cleaning up detritus and recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Filtration can be quite impressive, with certain species extending their tentacles to create a feeding structure—imagine an underwater version of a flower blooming to catch sunlight. Predatory polychaetes, on the other hand, often have powerful jaws to capture prey. It’s like watching a nature documentary unfold right before your eyes!
2. Reproduction and Social Structures
Reproduction in marine polychaetes can be quite fascinating. Many species are known to reproduce through a process called epitoky, where a portion of the worm’s body transforms to form a reproductive segment. This special segment is often more colorful and equipped for swimming to spawn. It’s as if they don their best outfits for a gala before heading off to create the next generation.
Interestingly, some polychaetes can also reproduce asexually through budding or fragmentation. This means that if a worm loses a part of its body, it can grow a new one, essentially cloning itself! This resilience captures the idea that nature has its tricks and tools for survival.
The Role of Polychaetes in Marine Ecosystems
Marine polychaetes are often overlooked, but they play essential roles in their ecosystems. As scavengers, they help break down organic matter, recycling nutrients that nourish other marine life. They also provide a food source for various fish and invertebrates, creating a bridge in the food web.
1. Nutrient Cycling
By consuming detritus and feeding on decomposing matter, polychaetes help in the natural process of nutrient cycling. They break down complex organic materials, turning them into simpler forms that can be used by other organisms. It’s a bit like composting in our gardens, where decomposers create fertile soil for new plants to grow.
2. Biodiversity Indicators
Marine polychaetes can serve as indicators of ecosystem health. Changes in their populations or behaviors often signal shifts in environmental conditions, pollution levels, or habitat degradation. Monitoring these creatures can provide valuable insights for marine conservation efforts.
The Importance of Conservation
As with many marine creatures, marine polychaetes face threats from human activities, including pollution, habitat loss, and climate change. Preserving their habitats is crucial for maintaining the balance of ocean ecosystems.
1. Protecting Habitats
By conserving marine environments—like coral reefs, estuaries, and seagrass beds—we can support polychaete populations. Sustainable practices in fishing and coastal development are essential for ensuring these fascinating creatures continue to thrive.
2. Research and Awareness
Increased awareness of marine polychaetes, their life cycle, and their role in ecosystems can foster support for conservation efforts. Promoting research and education will help us understand the intricate web of life in the ocean and the importance of each species—no matter how small.
In conclusion, the life cycle of marine polychaetes unfolds like a captivating story filled with drama and transformation. From their early larval stages drifting through the ocean to becoming vital components of marine ecosystems, these worms remind us of the complexity and beauty of life beneath the waves. So, the next time you think about ocean creatures, don’t forget to include the remarkable polychaetes in your reflections. They truly deserve a spot in our underwater tales!