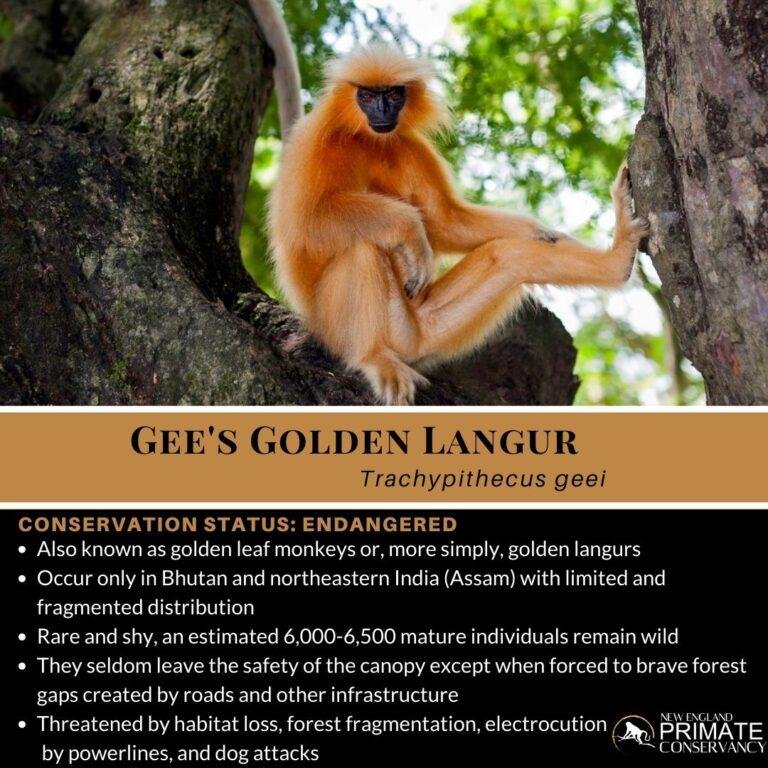
Let’s take a journey through the lush forests and rocky hills where langurs make their homes. Just like people prefer certain neighborhoods for their unique vibes, langurs have their own favorite spots influenced by climate, food sources, and safety from predators. So, grab a cup of coffee, and let’s explore the fascinating habitats and distribution of these incredible primates.
What Are Langurs?
Before we dive into their habitat, it’s helpful to know a bit more about langurs themselves. Langurs are primarily leaf-eating monkeys that belong to the family Cercopithecidae. They are characterized by their slender bodies, long tails, and expressive faces, which can range in color from black to a lighter brown or gray. There are several species of langurs, each adapted to their own environment.
For instance, the Northern Langur has a more pronounced facial structure and features a grayish-brown coat, while the Black-faced Langur sports a striking black face. They are social animals and usually live in groups, which helps them stay safe and find food more efficiently. Their social structure is as intricate as human communities, often led by an alpha male with several females and their young.
Their primary diet consists of leaves, fruits, and flowers, which they cleverly forage from trees. This means they require extensive forest areas to find enough food to sustain their groups. Here’s the thing: their habitat is not just about finding food; it’s also about safety. Langurs often choose locations with plenty of trees to escape from their predators.
Langur Distribution Across Asia
Langurs are mostly found in the tropical and subtropical forests of Asia. You might be wondering where exactly they live. Their distribution stretches from the northeastern parts of India, through Nepal, and down to the jungles of Southeast Asia. Here’s a brief overview:
- India: Home to several species, like the Indian Gray Langur.
- Nepal: The Nepalese Langur is often spotted in the Terai and hilly areas.
- Bangladesh: The Phayre’s Langur can be found in the northern forests.
- Thailand and Myanmar: These regions are rich in diversity, hosting various langur species.
- China: The Tibetan Black Langur is native to the southern areas.
Each of these regions offers unique environmental conditions. For example, the hot and humid climate of the tropical forests contrasts sharply with the cooler temperatures found in the Himalayan foothills. Langurs adapt to these conditions by changing their behavior and diet based on seasonal variations.
Types of Habitats Langurs Prefer
Langurs are quite versatile when it comes to their habitat preferences. They can be found in several types of environments, including:
- Tropical Rainforests: These lush forests provide a rich source of leaves and fruits.
- Dry Deciduous Forests: Some species thrive here, especially where there’s a mix of trees.
- Himalayan Foothills: They can also adapt to colder climates in the mountains, foraging for food in unique vegetation.
- Urban Areas: Surprisingly, some langurs have adapted to city life, often seen in parks where they forage for food.
Honestly, their adaptability is quite remarkable. In urban areas, langurs can often be seen interacting with humans, sometimes rummaging through trash or looking for food in parks. This adaptability showcases their intelligence and ability to thrive in a variety of settings.
The Importance of Habitat Conservation
With langurs relying on specific habitats, the need for habitat conservation cannot be overstated. Rapid urbanization, deforestation, and climate change are significant threats to their existence. Here’s why this matters:
1. Biodiversity: Langurs play a crucial role in maintaining the health of their ecosystems. By eating leaves and fruits, they help with seed dispersal, promoting plant growth.
2. Ecological Balance: Their feeding habits also influence the structure of forests, which can affect other wildlife. If langurs decline, it may lead to imbalances in their environments.
3. Cultural Significance: In many cultures, langurs are a symbol of nature’s beauty and resilience. Losing them could mean losing a part of our cultural heritage.
Conservation efforts are key in protecting these habitats. Organizations work to create wildlife sanctuaries and educate local communities about the importance of preserving ecosystems. It’s like tending to a garden; if we don’t take care of it, it won’t flourish.
Challenges Facing Langurs
Langurs face various challenges that put their survival at risk. Understanding these issues is essential for effective conservation. Here are some critical factors:
– Deforestation: Logging, agriculture, and urban expansion lead to habitat loss. When langurs lose their homes, they struggle to survive.
– Human-Wildlife Conflict: As humans encroach on their territory, conflicts arise. Langurs can be seen as pests, leading to retaliatory killings.
– Climate Change: Shifts in climate patterns affect food availability. Extreme weather events also disrupt their habitats.
Addressing these challenges requires a combined effort from governments, organizations, and individuals. After all, preserving the homes of langurs indirectly protects our planet’s health.
The Future of Langurs: Hope and Action
Despite these challenges, there is hope for langurs. Many conservation organizations and wildlife enthusiasts are committed to protecting them and their habitats. Here’s how you can help:
1. Support Conservation Efforts: Contributing to local and international organizations can make a big difference.
2. Educate Yourself and Others: Raising awareness about langurs and their habitat helps promote conservation.
3. Responsible Tourism: When visiting areas where langurs live, practice responsible tourism. Respect nature and wildlife.
Engagement and awareness are crucial. By fostering a culture of respect and care for these incredible animals, we can ensure they continue to thrive for generations.
In conclusion, langurs are more than just monkeys swinging through the trees—they are vital components of their ecosystems. Understanding their habitats and distribution sheds light on why conservation is crucial for their survival. Let’s celebrate and protect these fascinating primates and the rich environments they call home.

