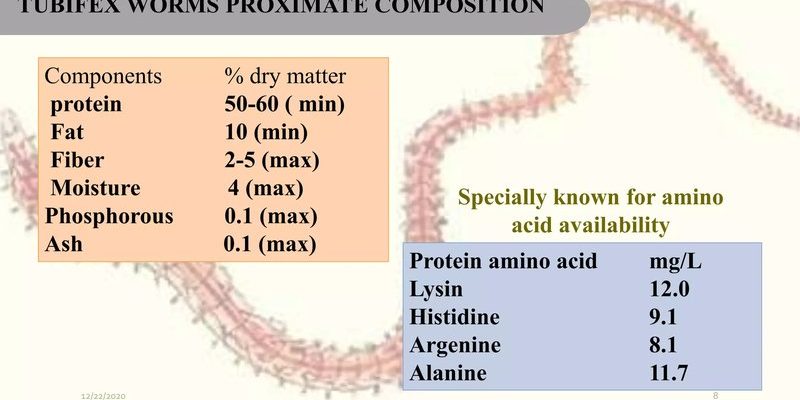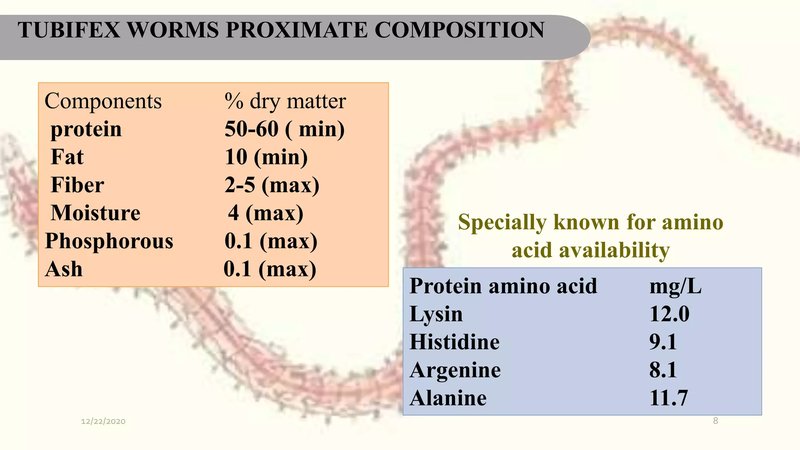
If you’ve ever looked closely at Tubifex worms, you might have noticed how they seem to effortlessly filter their food. They use a combination of physical structures and clever adaptations to build their meals. By understanding their feeding mechanism step-by-step, we can appreciate these often-overlooked organisms a lot more. Ready to dive in? Let’s explore how these worms work their magic.
Understanding Tubifex Worms
Before we break down their feeding mechanism, it’s important to know who Tubifex worms really are. These worms belong to the family Tubificidae and are often found in freshwater habitats. They can grow up to four inches long, depending on their environment and food availability.
You might picture them as long, thin tubes of jelly, which isn’t far off. There are even different species of Tubifex worms, but they all have a few common characteristics. For instance, they have a segmented body that allows them to move through sediments easily. Their bright coloration, often red or pink, helps them stand out in murky waters, even if they blend in with their surroundings.
Another interesting trait is their ability to tolerate low oxygen levels. This adaptability is crucial since they often live in ecosystems with fluctuating oxygen supplies. It’s almost like they have a built-in survival guide for living in challenging environments.
The Role of the Head Structure
Let’s start with the head of the Tubifex worm. At the front end, they have a specialized structure that plays a huge role in their feeding. This part is called the prostomium. Think of it as their mouth and sensory organ combined. The prostomium helps the worm sense organic particles in the water and the sediment.
When they’re ready to eat, Tubifex worms extend their prostomium into the sediment, looking for tasty morsels. They mainly feed on decomposing plant materials, bacteria, and tiny organic particles. This scavenging approach helps recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem, which is vital for the health of aquatic habitats.
This is where their head structure shines. The flexible prostomium can extend and retract, allowing the worm to explore its environment for food efficiently. Imagine it as a hungry snake poking its head around to find food in a pile of leaves.
Using the Mucus for Feeding
Here’s where it gets really interesting: Tubifex worms use mucus to help them eat! Yes, you read that right. These worms secrete a slimy substance that helps them capture food particles. Imagine trying to grab a handful of grease with your bare hands—pretty tricky, right? Mucus acts like a sticky trap for the tiny bits of sediment they want to consume.
As the worm moves through the sediment, it uses the mucus to stick to organic matter. After trapping the food, they pull it into their body. The mucus not only helps catch food but also aids in their movement through the muddy environments they inhabit. It’s like a two-for-one deal for these clever critters!
Plus, this mucus serves another purpose. It protects them from potential predators. Being slimy can make them less appealing or harder to grab for fish or other aquatic animals that might want to snack on them.
Digestive System Breakdown
Once the Tubifex worm catches its food, it needs a way to digest it, right? That’s where their digestive system comes into play. After the food is consumed, it travels down a tube-like structure called the gut. This organ does most of the work and is essential for breaking down those nutrients.
Let’s break it down a bit further. The gut is designed to process the food slowly so the worm can absorb as many nutrients as possible. Think of it as a slow cooker: the longer you let it simmer, the better the flavors blend, and the tastier the dish becomes.
The waste from this digestion is expelled through the anus at the other end of their body, completing the cycle. This process not only provides energy for the worm but ultimately returns nutrients back into the aquatic ecosystem.
Feeding in Different Environments
Tubifex worms are adaptable, and their feeding strategies can vary based on their environments. In nutrient-rich areas, they thrive and can grow quickly. But in poorer areas, they have to work a bit harder to find food.
In cleaner water, you might find them struggling to find enough organic matter to eat. In contrast, in heavily populated areas with decaying plant material, they flourish. This flexibility allows them to survive in various habitats, from ponds to polluted environments.
You might be wondering how this affects their overall behavior. Well, when they find a suitable feeding ground, they can form large colonies, working together to break down organic litter and improve the health of their ecosystem. It’s a team effort that benefits everyone in their habitat.
The Importance of Tubifex Worms in Ecology
Now that we’ve explored their feeding mechanism, let’s talk about why Tubifex worms matter. These little guys are not just scavengers; they’re essential players in their ecosystems. By breaking down organic material, they recycle nutrients, making them available for other organisms in the food web.
Their presence can indicate the health of a freshwater ecosystem. If Tubifex worms are thriving, it often means the water is rich in nutrients. But a sudden decline in their population can signal problems, such as pollution or habitat degradation.
Additionally, they serve as food for fish and other aquatic creatures. In a way, they’re like the backbone of the food chain in their environments. By providing nourishment to higher-level consumers, they help maintain the balance of aquatic life.
Final Thoughts on Tubifex Worms
So, there you have it! The feeding mechanism of Tubifex worms is a fascinating example of nature’s ingenuity. From their unique head structure to their clever use of mucus and efficient digestive systems, these worms play a crucial role in maintaining the health of aquatic ecosystems.
Next time you think about worms, remember that Tubifex worms are more than just simple creatures; they are vital players in recycling nutrients and supporting biodiversity. By understanding how they eat and their importance in the ecosystem, we can appreciate the intricate relationships that exist in our natural world.