Let’s think of Tubifex worms as the chameleons of the aquatic world. They adjust their behaviors based on the temperature, food availability, and even the water quality around them. That’s pretty impressive when you consider these worms can be found in various habitats, from ponds to streams and even muddy bottoms of lakes. Through field studies, researchers have been able to observe these seasonal patterns firsthand, revealing a lot about their lifecycle and environmental adaptability.
What Are Tubifex Worms?
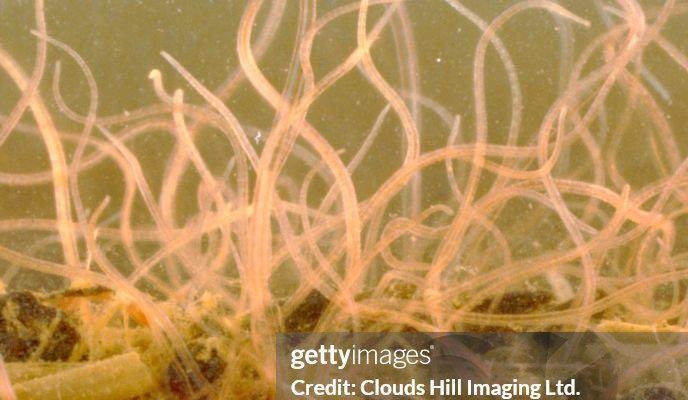
To kick things off, let’s get familiar with Tubifex worms. These small, segmented creatures belong to the annelid family, which makes them cousins to earthworms. Tubifex worms can reach lengths of about 10 to 15 cm and are typically found in environments rich in organic material, like mud or sediment. Their reddish-brown color often camouflages them in the muck, which is a clever trick to stay hidden from predators.
You might be wondering about their diet. Tubifex worms are scavengers, feeding on decomposing organic matter, bacteria, and algae. They play an essential role in the ecosystem by breaking down waste and helping to maintain the balance of nutrients in aquatic environments. So, they’re not just “wiggly things”—they contribute significantly to the health of their habitats.
In addition to their ecological role, Tubifex worms are interesting for researchers because they can indicate the health of the freshwater environment. When studying these worms, scientists can gain insights into pollution levels and overall ecosystem health.
Seasonal Changes in Temperature and Tubifex Behavior
One of the most significant factors influencing Tubifex worm behavior is temperature. Just like how we feel more energetic on a warm day, Tubifex worms become more active when temperatures rise during spring and summer. They tend to burrow deeper into the sediment during colder months, slowing their metabolism to survive the chill.
During warmer months, these worms often engage in reproductive activities, which means you might see more of them wriggling around. They can reproduce both sexually and asexually, depending on environmental conditions. As the temperatures rise, the increased availability of food also boosts their activity levels and reproductive success. Think of it like throwing a party—the more guests (food) you have, the more lively things get!
This seasonal fluctuation not only affects their activity but also their population density. Research shows that during warm months, Tubifex worms gather in large numbers, which helps them to compete for resources and increase survival rates.
Feeding Patterns and Food Availability
Food availability is crucial for the survival of Tubifex worms, and it fluctuates with the seasons. In spring, as waters warm and organic matter starts to break down, there’s usually an abundance of food. Tubifex worms take full advantage of this, ramping up their feeding and growth.
During summer, they continue to feast on the decomposing plant material and microorganisms in their environment. However, as autumn sets in and temperatures drop, the food supply can dwindle. This is when Tubifex worms switch gears. They may enter a sort of “survival mode,” consuming whatever organic matter they can find, even if it’s less than ideal.
It’s fascinating to see how these little worms adapt to changing food supplies. Some studies have noted that during leaner months, they can slow their metabolism and adjust their feeding habits to conserve energy. It’s like preparing for a long winter’s nap—keeping the supplies for leaner times.
Behavioral Adaptations to Water Quality
Water quality is another critical factor that influences Tubifex worms’ behavior throughout the seasons. When it comes to pollution, these worms can be sensitive indicators. If there’s an increase in contaminants—like heavy metals or excessive nutrients from runoff—they might not be as active.
In field studies, researchers have observed that during periods of poor water quality, Tubifex worms tend to become more reclusive. They can burrow deeper into the mud, where conditions may be more favorable. In contrast, when water quality improves, Tubifex worms become more visible and active.
This sensitivity isn’t just interesting; it also carries important implications for environmental monitoring. Scientists often study Tubifex worms to assess the health of freshwater ecosystems. If these worms are thriving, chances are the water quality is good. If not, it might be a signal for environmental concern.
Reproductive Patterns Throughout the Seasons
Reproductive activity in Tubifex worms is heavily tied to the seasons, particularly temperature and food availability. As I mentioned earlier, during the warmer months when food is plentiful, Tubifex worms are more likely to reproduce. They can do this in a couple of ways, either through sexual reproduction or by budding—essentially cloning themselves.
It’s not just about quantity; the conditions affect the quality of their offspring too. Higher temperatures and abundant resources lead to healthier worms, which means their offspring are more likely to thrive. Conversely, if they reproduce during lean times or in poor conditions, their young might struggle to survive.
It’s interesting to think about how these worms coordinate their breeding cycles with the environmental conditions. It’s almost like they have an internal calendar, ensuring their babies arrive when conditions are just right.
Field Studies on Tubifex Worms
Field studies have been pivotal in observing and understanding the seasonal behavior of Tubifex worms. Researchers often set up traps and observe these creatures in their natural habitats over different seasons. This method allows scientists to gather data on their populations, behavior, and adaptations.
One notable study examined Tubifex worm populations in a polluted river over a year. The findings showed that worm activity decreased significantly during certain months when pollution was high. Other studies have focused on temperature and seasonal shifts, revealing insights into when these worms thrive or become dormant.
These field studies are crucial for developing effective conservation strategies. They provide insights not only into the lives of Tubifex worms but also into the health of the ecosystems they inhabit. The data collected can help inform efforts to protect freshwater environments and their delicate balances.
The Importance of Understanding Tubifex Worm Behavior
You might be wondering why all this matters. Understanding the seasonal behavior patterns of Tubifex worms can help us gauge the health of freshwater ecosystems. Since they are sensitive to environmental changes, monitoring their activity can give insights into pollution levels and ecosystem dynamics.
Moreover, knowledge about Tubifex worms is important for various practical applications like aquaculture. Farmers and researchers can learn how to optimize conditions for worms, allowing them to thrive and contribute to nutrient cycling in aquatic systems.
So, it’s not just a matter of curiosity—understanding these little worms can lead to better environmental management and protection strategies. Every tiny creature plays a role, and Tubifex worms are no exception.
In conclusion, Tubifex worms are fascinating little creatures whose behaviors ebb and flow with the seasons. Their adaptability to temperature, food availability, and water quality showcases the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems. By studying them, we not only learn about their lives but also gain insights into the health of our environment. So, the next time you think of worms, remember there’s a whole world of underwater dynamics at play!