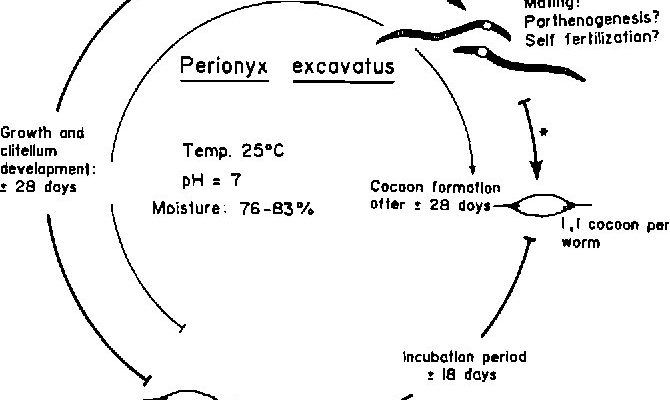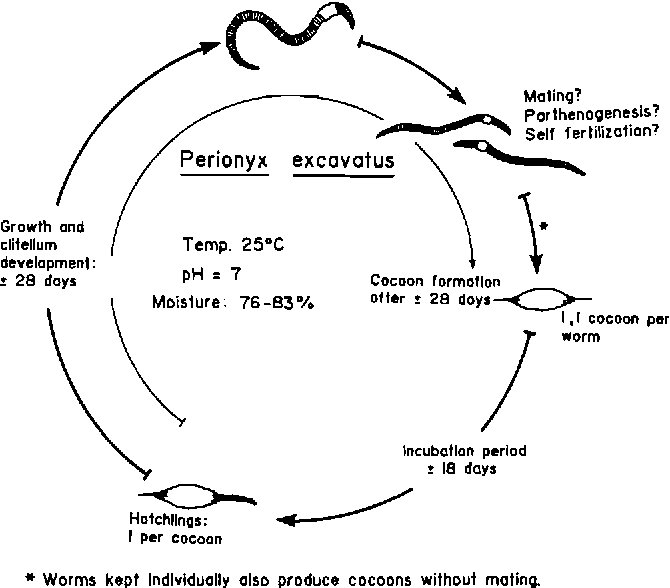
Imagine the Eisenia hortensis as a small superhero in the soil, tirelessly working to break down organic matter and improve soil health. Their life cycle isn’t just about surviving but thriving and contributing to a balanced ecosystem. Understanding the various stages and behaviors of these worms can help you appreciate their role and maybe even inspire you to start composting or gardening.
Let’s dive into the captivating world of the Eisenia hortensis and explore its life cycle—from tiny eggs to mature worms—and uncover the remarkable behaviors that define these little soil champions.
The Life Cycle Stages of Eisenia Hortensis
The life cycle of Eisenia hortensis can be broken down into several distinct stages. Each stage has its processes and characteristics, much like a movie with different acts. Here’s a closer look at each one.
1. Egg Stage
The first stage in the life cycle of the Eisenia hortensis starts with its eggs. After mating, which usually involves two worms exchanging sperm, each female produces a cocoon that contains several eggs. Each cocoon can hold up to 20 eggs! They’re about the size of a tiny pinhead and are often yellowish or translucent.
Once laid, these cocoons are typically buried in the soil where warmth and moisture are optimal. This environment is key for the eggs to develop. Within two to three weeks, depending on temperature and moisture, the eggs hatch into tiny worms. Can you imagine being born into a world full of soil and life?
2. Juvenile Stage
After hatching, the baby worms, called juveniles, emerge. At this point, they are incredibly small—often only a few centimeters long. They look quite different from the mature worms we’ll get to know later. This stage is crucial since it’s when they begin to feed on organic matter and start to grow.
During this period, the juveniles will typically stay close to where they hatched. They consume decaying plant material and microorganisms in the soil. Their bodies go through numerous changes as they develop. It’s like watching a caterpillar grow into a butterfly, but in this case, it’s all about growth underground.
3. Adult Stage
After several weeks of feeding and growing, the Eisenia hortensis reaches the adult stage. This is when they usually reach about 10 to 15 centimeters long. But here’s the interesting part: these worms are not just bigger—they’re also more active. Adult worms are known for their burrowing behavior, which helps aerate the soil and allows water to penetrate more effectively.
During this stage, they also become sexually mature. This means they can start the cycle all over again! They can live for several years, continuing to help maintain soil fertility while reproducing and contributing to their ecosystem.
Behavioral Traits of Eisenia Hortensis
Understanding the behavior of Eisenia hortensis provides valuable insight into why they’re so beneficial to gardening and composting. Their actions play a crucial role in soil health and plant growth. Let’s break down a few of their most notable behaviors.
Burrowing
Eisenia hortensis are natural burrowers, digging extensive networks of tunnels in the soil. This behavior is not just instinctual; it serves several important functions. For one, it allows them to access food sources more efficiently. As they burrow, they break down organic materials, which contribute to nutrient cycling.
Additionally, their burrowing helps aerate the soil. This improves water infiltration and promotes better root growth for plants. So, when you see these little guys wriggling in your garden, you can feel good knowing they’re probably doing a lot of heavy lifting underground!
Feeding Habits
These worms are not picky eaters; in fact, they have quite the appetite for organic matter! Eisenia hortensis primarily consume decomposing leaves, vegetable scraps, and other plant material. Their feeding habits help break down organic matter, turning it into nutrient-rich worm castings, which are like nature’s fertilizer.
One of the cool things about these worms is their ability to process food quickly. They can consume their body weight in food every day. This means that in a well-maintained compost bin, Eisenia hortensis can effectively recycle a lot of organic waste, reducing the burden on landfills!
Social Behavior
While you might think of worms as solitary creatures, Eisenia hortensis display some social behavior. They tend to cluster in groups, especially when they find a rich source of food. This is particularly noticeable in composting systems, where you might see them gathering around decomposing matter.
Interestingly, they can also engage in some form of communication through their skin, using chemical signals to attract others to food sources or warn against danger. Talk about teamwork!
The Role of Eisenia Hortensis in Ecosystems
Eisenia hortensis plays a significant role in the ecosystem, acting as nature’s recyclers. Their activities have far-reaching effects on soil health and plant growth for both gardens and natural environments. Let’s delve into why they matter so much.
Soil Fertility
One of the most significant contributions of the Eisenia hortensis is their role in enhancing soil fertility. As they decompose organic matter, they produce worm castings, which are rich in nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Research shows that these castings can increase crop yields and improve the overall health of the soil.
By aerating the soil and mixing it with nutrients, these worms create an environment where plants can thrive. So, if you’re gardening, having a healthy population of Eisenia hortensis is like having a secret team of soil health experts on your side!
Composting Heroes
Another important aspect is their role in composting. Eisenia hortensis is often used in vermicomposting systems, where they help break down kitchen scraps and yard waste efficiently. These processes can reduce waste and create rich compost, making them champions in sustainability.
Their ability to digest a variety of organic materials means they can help divert food waste from landfills, reducing methane emissions—a significant contributor to climate change. It’s amazing how such small organisms can have such a big impact!
Environmental Indicators
Finally, the presence of Eisenia hortensis can also serve as an indicator of soil health. Healthy populations of these worms often signal good soil conditions, while a decline can suggest issues like soil contamination or poor management practices. They act as a barometer for the ecosystem’s overall health.
If you start seeing fewer Eisenia hortensis in your garden, it might be time to assess your soil management practices. You might be unwittingly harming your garden’s hidden superheroes!
In summary, the life cycle of Eisenia hortensis is a fascinating journey that highlights the important roles these worms play in our ecosystems. From their early beginnings as eggs to their impactful adult lives, they contribute to soil health, nutrient cycling, and waste reduction.
Next time you’re out in the garden or preparing compost, take a moment to appreciate the hard work these worm superheroes do beneath our feet. Understanding their life cycle and behaviors not only helps us cultivate better gardens but also fosters a deeper respect for the intricate web of life that surrounds us. So let’s champion the Eisenia hortensis and all the amazing things they do for our world!