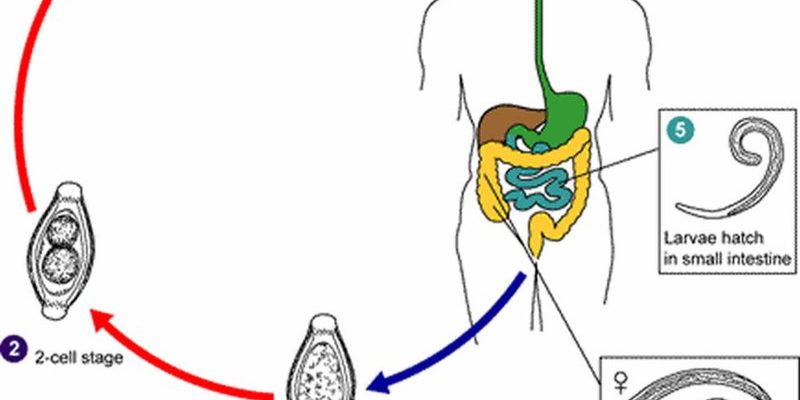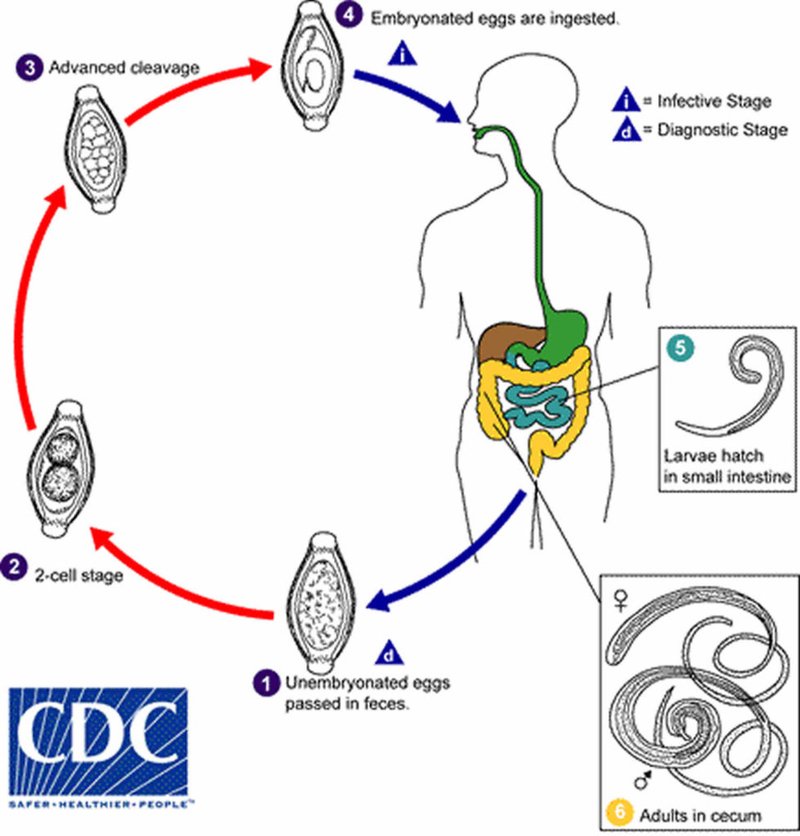
So, what exactly are whipworms? These small, whip-like creatures are parasitic roundworms that primarily reside in the intestines of their hosts, typically mammals, including humans. Yet, outside of their parasitic ways, they interact with the environment in fascinating ways. Let’s dive deeper and explore how they contribute to ecosystems, both in the soil and aquatic environments.
What Are Whipworms?
Whipworms belong to the genus *Trichuris*. These worms are named for their long, whip-like shape, which is quite distinctive. They can grow to about 2 to 8 centimeters in length. While humans can get infected by *Trichuris trichiura*, dogs and other mammals can also be hosts to different species of whipworms.
These parasites are often spread through contaminated soil or food. One interesting fact is that once whipworms find their way into a host’s intestine, they can live for several years. But here’s the catch: while they can cause gastrointestinal issues, they also play a crucial role in nutrient cycling.
You might be wondering how something that causes problems can also be beneficial. It all comes down to their life cycle and contributions to the ecosystem.
Whipworms in Soil Ecosystems
In soil ecosystems, whipworms contribute to nutrient cycling in several ways. Their presence helps in the breakdown of organic matter, which is essential for maintaining soil health. As they digest their host’s nutrients, they also excrete waste that can be rich in nitrogen and other important minerals. This waste becomes a natural fertilizer, promoting the growth of plants and other organisms.
Another aspect to consider is that whipworms can affect the populations of other microorganisms in the soil. For example, when whipworm populations are healthy, they can help control the growth of harmful bacteria and promote a more balanced ecosystem. Picture a small team of workers keeping an office organized—without them, things could get a bit out of hand.
Additionally, whipworms can influence soil structure. Their movements through the soil can create tiny air pockets, allowing water and nutrients to circulate more efficiently. This is crucial for plant roots, which need both air and moisture to thrive.
Whipworms in Aquatic Ecosystems
When it comes to aquatic ecosystems, whipworms also play their part. Some species have adapted to living in water, where they can impact the health of fish and other aquatic animals. Like their terrestrial cousins, these aquatic whipworms can help regulate populations of certain microorganisms, contributing to a healthier water environment.
In aquatic settings, whipworms can also enhance nutrient cycling. As they feed on detritus (that’s just a fancy word for decomposing organic matter), they help break it down into simpler forms that other organisms can use. Think of them as nature’s recyclers, turning waste into resources that sustain other life forms.
Another fascinating aspect is their interaction with larger aquatic animals. These worms may serve as a food source for certain fish or invertebrates. In this way, whipworms contribute to the food web, supporting the dietary needs of various species.
The Role of Whipworms in Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variety of life in a particular ecosystem, and whipworms contribute to this diversity both directly and indirectly. By maintaining healthy populations of microorganisms, they help support a rich tapestry of life in both soil and aquatic ecosystems. When whipworms are present, they can indicate a balanced ecosystem, suggesting that conditions are right for other forms of life.
In a way, whipworms remind us of the interconnectedness of all life forms. Just like in a well-functioning community where everyone has a role to play, whipworms have their place in the grand scheme of things. They may be small, but their impacts can be significant.
You might also find it interesting that some researchers are studying whipworms for potential medical benefits. Their unique biology could inspire new treatments or therapies, further demonstrating how even the tiniest creatures can have a big impact.
Impacts of Human Activity on Whipworm Populations
Human activities, such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change, can significantly affect whipworm populations and their ecological roles. When we disrupt their habitats, we alter the delicate balance in the ecosystems where they thrive. For instance, excessive use of fertilizers in agriculture can lead to nutrient overloads, potentially harming whipworm populations and other beneficial organisms.
Moreover, urban development often leads to the loss of natural habitats, putting pressure on whipworm species and their ability to fulfill their ecological roles. It’s essential to recognize how our actions can ripple through ecosystems, affecting even the smallest organisms.
Conversely, by promoting sustainable practices, we can help protect whipworm populations. Maintaining healthy soil and aquatic environments through responsible agriculture and conservation efforts ensures that these tiny gardeners continue their essential work.
Whipworms may not be the most glamorous creatures, but they hold a vital place in our ecosystems. From enriching soil to supporting aquatic life, these tiny worms contribute to the health and balance of nature in ways that are both fascinating and essential. It’s a reminder that every organism, no matter how small, plays a part in the intricate web of life.
As we delve into the world of ecosystems, let’s remember to appreciate the roles of even the tiniest players like whipworms. By respecting and protecting their habitats, we ensure not only their survival but also the well-being of our planet. After all, the health of our environment depends on a variety of life forms, working together harmoniously—much like every ingredient that goes into making that perfect cup of coffee.