Roundworms, scientifically known as nematodes, are incredibly diverse and adapt to various environments. They can be found in soil, freshwater, and even in extreme conditions. While they might be small, their impact on ecosystems is huge, making their life cycle all the more interesting. So, grab a cup of coffee, and let’s dive into the remarkable journey of a roundworm, from its beginnings to its adult life and everything in between.
What Are Roundworms?
Roundworms are a type of nematode, characterized by their elongated, cylindrical bodies. They live in nearly every habitat, including marine, freshwater, and terrestrial environments. There are thousands of species, with some being beneficial and others harmful, especially in agriculture. Now, here’s something you might be wondering: why are they so important?
These tiny creatures play a crucial role in soil health and nutrient cycling. They help decompose organic matter, which enriches the soil and supports plant growth. So, even though they might not be the star of the show, roundworms are like the backstage crew in an ecosystem, keeping everything running smoothly.
The Stages of the Roundworm Life Cycle
The life cycle of a roundworm consists of several stages, each distinct but interconnected. It’s kind of like a video game where each level has specific challenges and enemies. Here’s a breakdown of those stages:
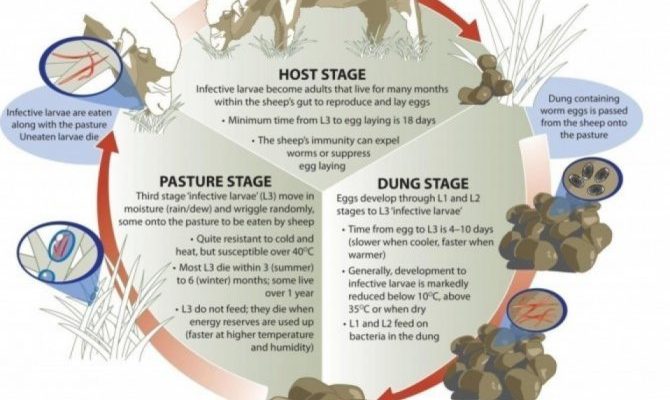
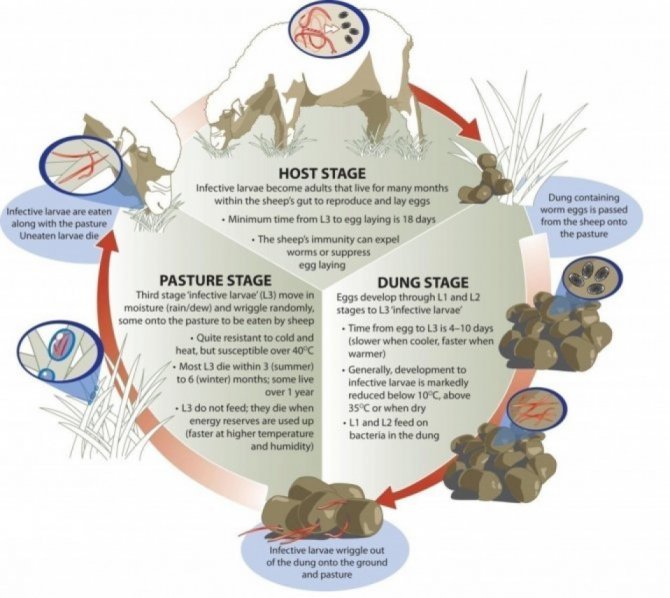
1. Egg Stage: It all starts with the roundworm laying eggs in its environment. Depending on the species, a female roundworm can produce thousands of eggs at once. These eggs are tough and can survive harsh conditions, waiting for the perfect moment to hatch.
2. Larval Stages: Once conditions are right, the eggs hatch, and out come the larvae. Most roundworms have several larval stages, typically three. In these stages, they may molt, which means shedding their outer layer as they grow.
3. Adult Stage: After several molts and some hard work, the larvae mature into adults. This is where things get exciting! Adult roundworms can start reproducing, continuing the cycle.
Each stage is vital for the survival of the species, and each has its challenges.
Egg Stage: The Beginning of It All
The egg stage is the foundation of the roundworm’s life cycle. Roundworms produce eggs that are surprisingly resilient. They can survive extreme temperatures and dry conditions. It’s like they’re little survival pods, just waiting for the perfect environment to hatch.
When conditions are favorable—like warmth and moisture—the eggs begin to develop. Depending on the species, this can take anywhere from a few days to several months. Think of it as the incubation phase for these tiny creatures. The longer they wait, the stronger they become, ready to tackle the world outside once they hatch.
Larval Development: A Journey of Growth
After hatching, the larvae enter the first of several stages. This part of the roundworm’s life is all about growth and development. During each larval stage, they undergo molting—a process similar to shedding old skin.
This is an essential part of their growth because it allows them to expand and adapt to their environment. While in this phase, larvae often rely on external sources for food, such as bacteria, fungi, or decaying organic matter. You can think of them as teenagers, trying to find their place in the world while relying on their surroundings for support.
Adult Roundworms: The Circle Continues
Once the larvae have matured, they become adults and are ready for reproduction. Adult roundworms come in various forms, depending on the species. Some are free-living in soil, while others are parasites living in hosts.
For those that are parasitic, their life cycle can get even more complicated. They may need a host to survive and reproduce. For instance, some roundworms will infect animals, waiting for the right moment to lay their eggs inside their hosts. This can lead to all sorts of health issues for the host, which is why understanding roundworm behavior is crucial for managing pest control in agriculture and animal husbandry.
Behavioral Traits of Roundworms
Roundworms may seem simple at first glance, but their behavior is quite complex. They have various adaptations that help them survive in their environments. For instance, they can sense chemicals in their surroundings, allowing them to find food or avoid predators.
Some roundworms exhibit unique behaviors depending on whether they are free-living or parasitic. Free-living roundworms tend to be more mobile, crawling around to feed on bacteria and organic material. In contrast, parasitic roundworms often remain stationary, relying on their hosts for sustenance.
This variety in behavior is what makes studying roundworms so intriguing. It shows us how even the smallest organisms can have complex lives and play significant roles in the ecosystem.
Roundworms in Ecosystems: A Key Role
Just like every character in a story has a purpose, roundworms play a vital role in their ecosystems. They contribute to soil health, nutrient cycling, and even plant disease control. By breaking down organic matter, they help recycle nutrients, making them available for plants to use.
You might be surprised to learn that some gardeners even welcome certain roundworm species because of their positive impact on soil fertility. This is a classic case of looking at the bigger picture and recognizing the importance of every creature in the ecosystem.
The life cycle of a roundworm, with its various stages and behaviors, is a remarkable example of nature’s complexity. From egg to larvae to adulthood, each step in this journey is essential for their survival and the ecosystems they inhabit. Understanding these tiny creatures can help us appreciate their role in our environment and how they impact our lives more than we might think.
So, next time you come across a worm in the garden, remember this little journey. It’s more than just a squiggly creature; it’s a vital player in the story of life on Earth. Whether you’re fascinated by science or just curious about nature, the world of roundworms is worth exploring.