The hornworm stage is critical for these future moths. You might be wondering what exactly happens during this phase and why it matters. Understanding the hornworm’s role helps us appreciate the entire moth lifecycle, and trust me, it’s more than just a stage—it’s a vital step in a fascinating journey. So grab a cup of coffee, and let’s dive into the world of hornworms and their connection to the life of moths.
What Are Hornworms?
Hornworms are the larvae of certain moth species, particularly the tobacco hornworm and the tomato hornworm. They typically have a plump, green body with a distinctive horn-like projection on their rear end. These caterpillars can grow up to four inches long, making them quite noticeable in gardens. If you’ve ever grown tomatoes or tobacco, you might have encountered them—often more than once!
Hornworms feed primarily on leaves. They can cause significant damage to plants, especially tomatoes, as they devour the foliage. While they might be a gardener’s nightmare, these little guys play an essential role in the ecosystem. They provide food for various birds and other predators. Plus, their voracious appetite helps regulate plant growth, ensuring a balance in nature.
Here’s the thing: while many see hornworms as pests, they are simply doing their part in the grand scheme of nature. Their role is not just about being a munching machine. They are crucial in transforming into adult moths, which serve their own purpose in pollination and maintaining the biodiversity of the environment.
The Lifecycle of a Moth
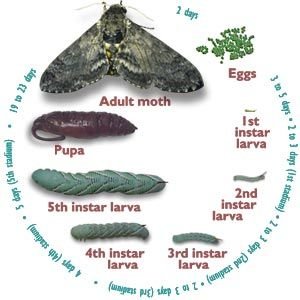
The lifecycle of moths consists of four stages: egg, larva (hornworm), pupa, and adult moth. Understanding each phase gives you a clearer picture of how hornworms fit into the equation. Moths begin their lives as eggs laid on the undersides of leaves. Once these eggs hatch, the tiny larvae emerge, ready to eat—this is where hornworms come in.
After several weeks of eating and growing, hornworms enter the pupal stage. They typically find a safe place, often in the soil or hidden among leaves, and undergo a remarkable transformation. This stage is where all the hard work of munching pays off. The caterpillar breaks down its body and reorganizes itself into a moth.
Finally, the adult moth emerges from the pupa, ready to mate and lay eggs, starting the lifecycle anew. It’s like a full circle in nature. Each stage is critical, but without the hornworm phase, there would be no adult moths to grace our gardens and night skies.
Why Hornworms Are Important
You might be thinking, “Why should I care about hornworms?” Well, there are several reasons they matter, not just to moths but to our ecosystem as a whole.
First, hornworms act as a food source for various birds and insects. This contribution helps sustain the food chain, allowing other species to thrive. Additionally, the presence of hornworms in an area indicates a healthy ecosystem. If they’re around, it usually means that the environment is capable of supporting various life forms.
Moreover, hornworms can help with pollination. As adult moths, they have the potential to pollinate flowers, which is essential for plant reproduction. Imagine a world where certain plants and flowers can no longer reproduce. It would drastically change our environment!
So, while they might not win any popularity contests in your garden, hornworms have a significant role in maintaining ecological balance. It’s nature’s way of saying every creature, even the pesky ones, has a purpose.
The Hardship of Being a Hornworm
Life as a hornworm is not all eating and growing; it comes with its challenges too. Predators are always on the lookout for a meal, and hornworms have developed several defense mechanisms to survive. These include mimicking leaves to blend in and using their horn as a deterrent. Believe it or not, some birds have learned to avoid hornworms due to their bitter taste.
Additionally, hornworms face diseases and parasites. One of the most infamous threats is a type of wasp that lays its eggs inside the hornworm. When the wasp larvae hatch, they eat the hornworm from the inside out. It’s a gruesome yet fascinating part of nature.
Despite these hardships, hornworms show resilience. They continue to thrive in various environments, adapting to changes and overcoming obstacles. This struggle for survival forms an essential part of their lifecycle, reminding us that nature is often about the cycle of life, death, and rebirth.
Gardening Tips: Coexisting with Hornworms
If you’re a gardener, you may be concerned about hornworms munching on your plants. But don’t worry—coexisting with them is possible. Here are a few tips to manage hornworms without resorting to harsh chemicals:
- Handpicking: If you spot hornworms on your plants, simply pick them off and relocate them far from your garden.
- Natural Predators: Encourage birds and beneficial insects to thrive in your garden. They can help keep hornworm populations in check.
- Plant Diversity: Incorporating a variety of plants can confuse hornworms and limit their damage. It’s like giving them too many options and not knowing what to eat!
- Use Of Organic Pesticides: If the infestation is severe, consider organic options that won’t harm beneficial insects.
By taking these steps, you can minimize the impact of hornworms on your plants while still allowing them to play their crucial role in the ecosystem. It’s a win-win situation!
Hornworms may seem like just another pesky caterpillar, but they are a significant part of the moth lifecycle. From their crucial role as larvae to their transformation into adult moths, they contribute to the ecosystem in many ways. Understanding and appreciating hornworms can change your perspective on these little creatures, turning annoyance into fascination.
So, the next time you see a hornworm, remember it’s not just a garden nuisance—it’s a vital player in the cycle of life. Embrace their presence, and you might just find yourself more attuned to the delicate balance of nature all around you. Plus, who knows? You might learn to love those moths a little more too!
