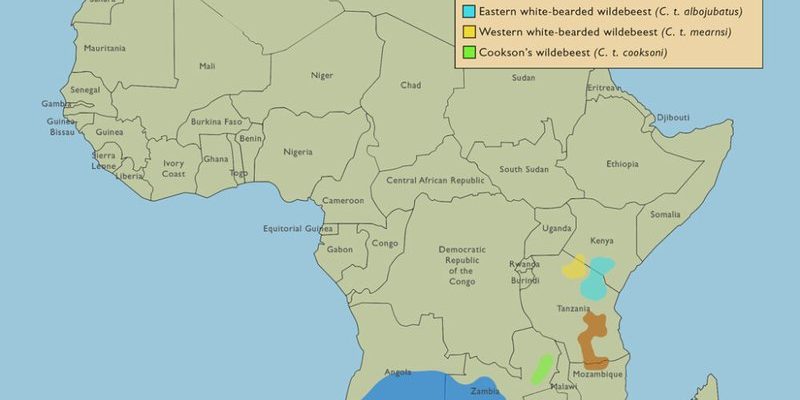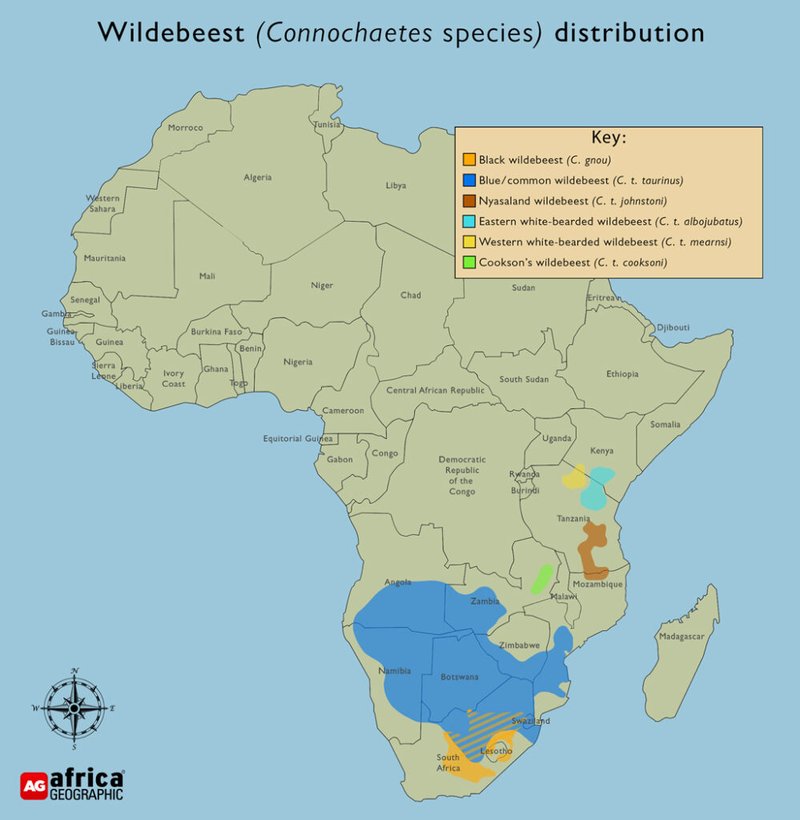
You might be wondering, why do these iconic animals choose such unique habitats? The answer lies in their need for food, safety, and space. Just like us, wildebeests have specific preferences for their living environments. So, let’s dive into their world and explore where they live, how they thrive, and why their habitat is so crucial for their survival.
The African Savannah: Wildebeests’ Primary Habitat
Wildebeests predominantly inhabit **grasslands and savannahs** in eastern and southern Africa. Think of these areas as a buffet filled with their favorite meals—grasses and herbs, perfect for grazing. The savannahs are characterized by open spaces dotted with trees and shrubs, forming a habitat that’s ideal for spotting potential predators.
These lands offer a rich diversity of ecosystems, allowing wildebeests to roam freely. Throughout the year, they move in search of fresh pastures and water sources. During the rainy season, the grass grows lush and tall, making it a perfect feeding ground. But when the dry season hits, the wildebeests pick up their hooves and venture to other areas where greener pastures await.
The wildebeest populations primarily thrive in countries like **Tanzania, Kenya, and Botswana**. In Tanzania’s Serengeti National Park, you can witness the incredible migration of wildebeests, a natural spectacle unlike any other. This annual journey is not just a casual stroll; it’s a life-or-death race for survival where they must dodge predators like lions and crocodiles.
Migration Patterns: The Great Migration
One of the most fascinating aspects of wildebeests’ lives is their **migration patterns**, often referred to as the Great Migration. Picture a massive movement of thousands—sometimes millions—of wildebeests, all in search of better grazing spots. This isn’t just a random journey; it’s a carefully timed expedition that follows the rainy seasons.
Starting in Tanzania, wildebeests migrate towards the lush pastures of the **Maasai Mara** in Kenya. This journey can cover over 1,000 kilometers (about 620 miles) and involves navigating treacherous rivers and open plains. Along the way, they face multiple challenges, from predators waiting in the shadows to harsh weather changing overnight.
The migrants are accompanied by zebras and gazelles, forming a mixed group that adds safety in numbers. When a predator attacks, the sheer size of the herd can deter most threats. It’s like a well-coordinated escape plan, showcasing the strength of community and instinct.
Key Factors Influencing Habitat Selection
Wildebeests are highly adaptable animals, but their habitat choices are influenced by key factors. **Water availability** is one of the most critical elements. Wildebeests are essentially like marathon runners for grazing; they need regular access to water to stay hydrated as they roam.
Another significant factor is **grass quality**. These animals are grazers, meaning they thrive on grasses and low vegetation. In regions where grass is plentiful and healthy, you’re likely to spot larger herds. However, if the grasses become overgrazed, wildebeests might shift to other areas, illustrating their migratory behavior.
Lastly, **predator presence** affects their habitat choices. In regions where lions, hyenas, and crocodiles are rampant, wildebeests may stay closer to safer zones, often developing clever strategies to evade these threats. Their instincts guide them; they’re constantly aware of their surroundings, making decisions that ensure their survival.
Wildebeests and Their Ecosystem
Wildebeests play a vital role in their ecosystems. They are often considered **keystone species**, meaning their presence significantly impacts the environment. Their grazing habits help maintain grassland balance and encourage new growth, providing nourishment for other wildlife.
When wildebeests migrate, they also help distribute nutrients across vast areas. Their droppings enrich the soil, promoting biodiversity and supporting other plant and animal life. In this way, they act as nature’s gardeners, fostering a healthier environment.
However, their role in the ecosystem goes beyond just grazing. They serve as prey for a variety of predators. This balance keeps the ecosystem healthy. If wildebeest numbers dwindle, it could lead to an overpopulation of certain species, throwing the entire ecosystem out of whack.
Threats to Wildebeest Habitat
Unfortunately, wildebeests face several threats that endanger their habitat. One major issue is **habitat loss**, primarily due to agriculture and urban development. As humans expand their territories, the lands that once thrived with wildebeests are now being transformed into fields and cities. This diminishes the area where these animals can roam and find food.
Additionally, climate change has a significant impact. Altered rainfall patterns and increased droughts can lead to food shortages, forcing wildebeests to migrate further—often into more dangerous areas. This constant pressure can be devastating, affecting their numbers and overall health.
Another threat is **poaching**. The illegal hunting of wildebeests for their meat and skins not only reduces their population but also disrupts the intricate balance of the ecosystem. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these magnificent creatures and ensure they can continue to thrive in the wild.
Conservation Efforts and Their Importance
Many organizations actively work to protect wildebeests and their habitats. These conservation efforts focus on **habitat preservation**, which is vital for the survival of wildebeests and countless other species. Protected areas like national parks and wildlife reserves serve as a sanctuary where these animals can live without human interference.
Education is also a key component of conservation. Raising awareness about the importance of wildebeests helps communities understand their role in the ecosystem. This can foster a sense of pride and ownership, motivating locals to participate in protecting their natural heritage.
Moreover, sustainable tourism helps fund conservation initiatives. When people visit to witness the Great Migration, it provides economic incentives for preserving these habitats. It’s a win-win situation; tourists get to experience the beauty of nature, while local communities benefit as well.
Wildebeests are truly remarkable animals that contribute to the beauty and balance of their ecosystems. Their habitats—spanning the African savannahs—are not just homes; they are essential to the survival of numerous other species as well. As we’ve discussed, factors such as water availability, grass quality, and predator presence play vital roles in their lives.
However, threats like habitat loss, climate change, and poaching put these majestic creatures at risk. It’s crucial that we support conservation efforts to protect wildebeests and their habitats for future generations. Remember, every action counts, whether it’s supporting wildlife organizations or simply spreading the word about their importance.
By understanding and appreciating where wildebeests live and the challenges they face, we can all play a part in ensuring their survival. Let’s celebrate these incredible creatures and the ecosystems they call home.