![Comparing The Clouded Leopard Vs. [Similar Species]](https://gudri.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Comparing_The_Clouded_Leopard_Vs___Similar_Species__image_0.jpg)
Imagine you’re in the lush forests of Southeast Asia, where the clouded leopard elegantly navigates the treetops, its thick, cloud-like spots blending seamlessly with the dappled sunlight. Contrast that with the snow leopard, a formidable presence in the icy heights of the Himalayas, camouflaged against the rocky terrain with its thick, smoky-gray fur. So why compare these two species? Understanding their differences and similarities not only enriches our appreciation of nature but also highlights the incredible adaptability of wildlife.
Let’s dive deeper into the traits, habitats, and behaviors of these fascinating leopards and see what sets them apart.
Physical Characteristics
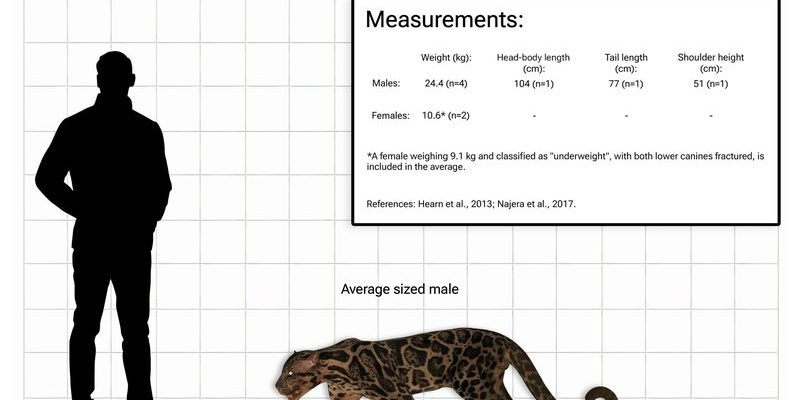
When you compare the clouded leopard and the snow leopard, their physical traits jump out at you. The clouded leopard is smaller, typically weighing between 25 to 50 pounds, with a body length of about 32 to 54 inches, not including its long, thick tail. This cat sports distinctive cloud-like patterns on its coat, which helps it blend into the tropical forest canopies where it hunts.
In contrast, the snow leopard is much larger, weighing between 60 to 120 pounds, and can reach lengths of 39 to 51 inches, with a shorter tail that can still be as long as 30 inches. Its thick, pale fur is sprinkled with black rosettes and spots, providing excellent camouflage against rocky, snowy terrain. This adaptive coloration is crucial for survival in the harsh climates of Central Asia where it resides.
Both species have large paws which work as natural snowshoes, allowing them to traverse their respective habitats effectively. The clouded leopard’s paws are more suited for climbing, while the snow leopard’s robust legs are built for agility on rugged mountains.
Habitat and Range
The clouded leopard thrives in the dense, tropical forests of Southeast Asia, including countries like Malaysia, Thailand, and Vietnam. These environments are incredibly rich in biodiversity, with towering trees that offer plenty of opportunities for climbing and stalking prey. The clouded leopard is a master of the trees and often hunts birds and small mammals that reside in the upper canopies.
On the other hand, the snow leopard calls the cold mountains of Central and South Asia its home. With its range stretching from the Himalayas to the Tibetan Plateau, this remarkable animal prefers rocky outcrops and steep cliffs, often at altitudes over 10,000 feet. The snow leopard’s habitat is sparse and harsh, requiring it to hunt medium-sized ungulates like ibex and blue sheep.
What’s fascinating is how both species have adapted to their environments. The clouded leopard’s agility in trees contrasts sharply with the snow leopard’s incredible strength and stealth on rocky ledges, showcasing how different environments shape the dynamics of survival.
Behavior and Hunting Techniques
Looking at behavior, there’s a world of difference between the clouded leopard and the snow leopard. The clouded leopard is primarily arboreal, meaning it spends a lot of its time in trees. It uses its incredible climbing skills to sneak up on prey, relying on its keen eyesight and stealth. This cat is more solitary, often marking its territory with scent markings to communicate with others of its kind.
In contrast, although snow leopards are also solitary creatures, they can sometimes be found in small groups, particularly during mating season or when a mother is raising her cubs. Their hunting technique is more about patience, as they stalk and ambush their prey on the steep slopes of their mountainous habitats. With their powerful legs, snow leopards can make incredible leaps to catch their unsuspecting prey.
Both leopards exhibit fascinating behaviors that suit their lifestyles, emphasizing the diverse strategies animals use for survival.
Conservation Status
Conservation is a pressing issue for both the clouded leopard and the snow leopard. The clouded leopard is classified as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, primarily due to habitat loss and poaching. Deforestation for agriculture and logging has significantly reduced its habitat, making it more challenging for these cats to find prey and flourish.
The snow leopard, while also labeled as vulnerable, faces threats mainly from poaching and retaliatory killings by herders who lose livestock to these cats. Conservation efforts are underway for both species, focusing on habitat protection and anti-poaching initiatives. Organizations are working hard to educate local communities about the importance of these majestic felines and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Protecting these species not only ensures their survival but also maintains the balance of their respective environments. It’s a critical issue that connects wildlife conservation with broader ecological health.
Diet and Feeding Habits
When it comes to diet, the clouded leopard tends to target small to medium-sized mammals and birds, which it can easily catch while climbing through tree branches. Their diet may include animals like monkeys, birds, and rodents, making them skilled opportunistic hunters.
On the flip side, the snow leopard has a more substantial diet due to its larger size. Its prey includes ibex, blue sheep, and even domestic livestock in certain areas. Snow leopards are known for their incredible stealth, allowing them to get as close as possible to their prey before launching a surprise attack.
Both cats are excellent hunters, but their prey selection and hunting methods reflect the unique environments they inhabit. Understanding these feeding habits enriches our appreciation of how each species fits within its ecosystem.
Cultural Significance
Both the clouded leopard and the snow leopard hold cultural significance in their native regions. The snow leopard, often called the “ghost of the mountains,” appears in various folklore and is seen as a symbol of strength and endurance in many Central Asian cultures. Its majestic presence has inspired stories and art that celebrate its elusive nature.
The clouded leopard, while less well-known, is also an important cultural symbol in Southeast Asia, where it represents beauty and agility in many local myths. The unique pattern of its fur has caught the imagination of artists and designers alike, often symbolizing the beauty of the rainforests that it inhabits.
Understanding the cultural importance of these leopards helps highlight our connection to wildlife and the need to protect it. They are not just animals; they embody the spirit of their environments and cultural identities.
In comparing the clouded leopard and the snow leopard, we uncover a world of adaptation, beauty, and survival. Each species represents a unique response to its environment, showcasing the incredible diversity among big cats. From their physical characteristics to their dietary habits and cultural significance, these leopards are more than just majestic predators—they are emblematic of their ecosystems and reminders of the fragile balance of nature.
As we learn more about these fascinating felines, it becomes clear that conservation efforts are vital. By protecting their habitats and fostering a deeper understanding of their roles within the ecosystem, we can help ensure that future generations will share our planet with these awe-inspiring creatures. So next time you think about leopards, remember the clouded and snow leopards, and appreciate the intricate web of life they represent.