Imagine going for a peaceful day of fishing at your favorite stream. You cast your line, but instead of the usual excitement of a trout nibbling at your bait, the water feels warmer than before, and the fish seem few and far between. This scenario is becoming more common as rising temperatures and changing weather patterns reshape the habitats that trout depend on. In this article, we’ll dive into the various ways climate change is affecting trout populations, from rising water temperatures to habitat loss.
The Importance of Trout in Ecosystems
Trout aren’t just popular with anglers; they play a vital role in their ecosystems. These fish are predators that help maintain the balance of aquatic life. By feeding on insects and smaller fish, they help control populations and keep the ecosystem in check. Moreover, trout are a food source for larger predators like eagles, bears, and humans.
There’s something special about trout habitats, too. They often thrive in cold, clear waters, which are essential for their breeding and survival. Healthy trout populations can indicate a thriving ecosystem. When trout are healthy, it suggests that water quality is good, which benefits other wildlife and plants in the ecosystem.
Unfortunately, trout are sensitive to changes in their environment. They need specific conditions to survive, and climate change throws those conditions into disarray. That’s why it’s so important to understand how these changes impact trout and, by extension, the entire ecosystem.
Rising Water Temperatures
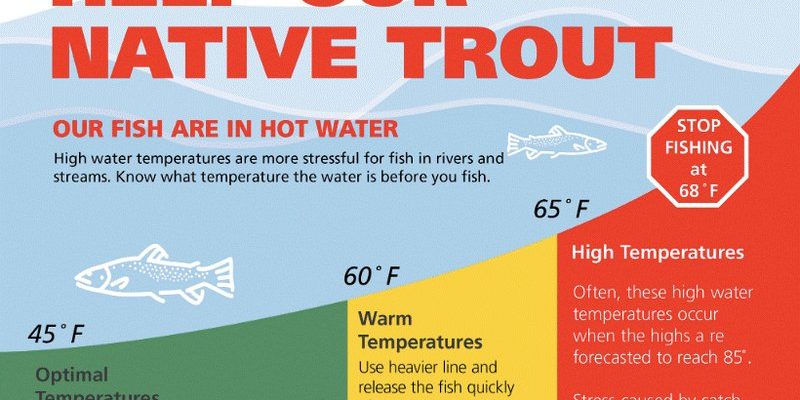
One of the most significant effects of climate change on trout is rising water temperatures. Trout prefer cooler waters—typically between 50°F to 65°F. As global temperatures rise, so do the temperatures in rivers and lakes.
Warmer water holds less oxygen, which is crucial for trout survival. Without enough oxygen, trout can experience stress, leading to reduced growth and even mortality. In some areas, rivers that once provided ideal habitat for trout are turning into too-hot environments.
You might be wondering, “What does that mean for the fishing experience?” Well, it can lead to fewer trout in popular fishing spots. Some anglers might need to change their favorite fishing locations as trout move to cooler waters—streams higher up in the mountains or deeper lakes.
Increased Runoff and Pollution
Climate change can also lead to increased rainfall and runoff, washing pollutants into rivers and streams. More intense storms can overwhelm wastewater systems, leading to contamination of previously clean waters. This runoff can introduce sediments, nutrients, and chemicals into trout habitats, making it difficult for them to thrive.
Pollution can lead to algal blooms, which further deplete oxygen in the water. These blooms can block sunlight, affecting aquatic plants that provide oxygen and food for many species, including trout.
Imagine a once-clear stream that has turned murky due to pollution. It’s not only uninviting for anglers but also dangerous for the fish relying on that habitat. Protecting water quality is key to maintaining healthy trout populations.
Loss of Habitat
As the climate continues to change, the habitats that trout rely on are disappearing. Deforestation, urban development, and other human activities can fragment or destroy natural habitats. When trees along riverbanks are cut down, it can lead to increased water temperatures and erosion. The absence of shade means the water warms, driving trout away.
It’s not just about losing the physical space; it’s about losing the entire ecosystem that supports trout. Streams that once flowed freely can become obstructed due to changes in land use, making it harder for trout to migrate to their spawning grounds.
Trout need clean, connected waterways to thrive, and habitat loss complicates their lives. Conservation efforts are essential to preserve these habitats for future generations of fish and humans alike.
Changing Migration Patterns
Trout have been known to migrate in search of cooler waters, especially during warmer months. With climate change, their traditional migration patterns are being disrupted. Warmer water temperatures can force trout to migrate earlier in the year or to different locations altogether.
This can lead to mismatches in timing between trout and their food sources, affecting their growth and survival rates. If trout spawn too early or too late, it can have cascading effects on their populations.
For example, if they migrate to cooler waters only to find that those areas are also warming, they might struggle to find the right habitats. This shifting dynamic highlights the need for adaptive management strategies in fisheries to help ensure trout populations remain viable.
How Conservation Efforts Can Help
So, what can be done to protect trout from the effects of climate change? Conservation efforts are critical. This can include creating protected areas where trout habitats are preserved and restored.
Additionally, implementing better land-use practices can help promote clean water and healthy habitats. For instance, maintaining forest buffers along streams can keep waters cool and reduce runoff.
Fisheries management must adapt to these changing conditions. By tracking trout populations and monitoring their habitats, we can make informed decisions to support their survival. Engaging local communities in conservation efforts also raises awareness and encourages sustainable practices.
You might think, “Can my actions really make a difference?” Absolutely! Simple choices, like participating in local clean-up events or advocating for sustainable practices, can contribute to the health of trout and their habitats.
Final Thoughts: Protecting Our Trout and Ecosystems
As we’ve discussed, climate change poses real threats to trout and their ecosystems. From rising water temperatures to habitat loss and pollution, the impacts are profound. However, there’s hope through conservation efforts and sustainable practices.
Trout are more than just fish; they are indicators of ecological health and part of a larger ecosystem that supports countless species, including humans. By understanding how climate change affects them, we can take action to protect these valuable resources.
Honesty, it’s up to us to ensure that future generations can enjoy fishing in clean, cool waters and that trout can thrive in their natural habitats. Let’s work together to keep our streams and lakes vibrant and healthy for everyone—trout and humans alike.