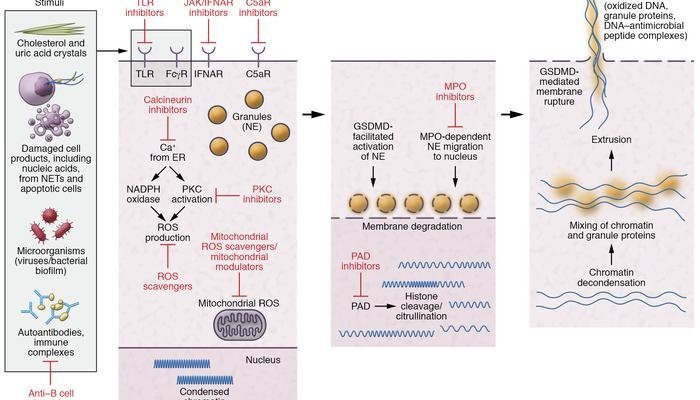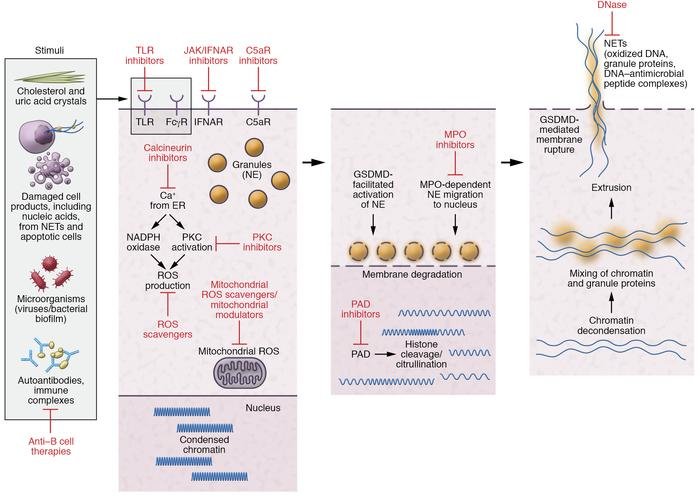
When we dive into the world of wolf worms, we’re stepping into a realm of biology that’s often overlooked. While most people think about the immune system in the context of viruses or bacteria, the world of parasites like wolf worms presents a different challenge. You might be wondering how these critters survive and thrive inside other animals, and that’s where the fascinating dance between parasite and host comes into play.
What Are Wolf Worms?
Let’s start at the beginning. Wolf worms, also known as larval fly or wolf maggots, are the larvae of certain fly species, particularly from the family Oestridae. They’re often found in the furry bodies of mammals, especially canines like wolves and domestic dogs. Imagine tiny, wriggling invaders making themselves at home in their cozy host; that’s essentially what wolf worms do!
These larvae burrow into the skin of their hosts, often causing irritation and harm. They’re not just passively hanging out, either—they can cause significant health issues. For instance, their presence can lead to infections or, in severe cases, even death. The host’s immune response is crucial in fighting off these intruders, and that’s where things get particularly interesting.
How Mammalian Immune Systems Work
So, how does the mammalian immune system react to these unwelcome guests? First, it’s essential to understand that our immune systems are complex and incredibly efficient. Think of it as a high-tech security system for your body, constantly on the lookout for intruders. The immune system detects foreign invaders, such as viruses, bacteria, and parasites, and mounts a defense.
When a wolf worm enters a mammal, the immune system kicks into gear. White blood cells, like T-cells and macrophages, sense the invader and start working to eliminate it. These cells are like little soldiers on patrol, ready to fight anything that doesn’t belong. They identify the wolf worm as a threat and try to destroy it through various means, such as engulfing it or releasing chemicals to attack.
Stages of Immune Response Against Wolf Worms
The immune response happens in stages, almost like a well-rehearsed play. Here’s a look at how it unfolds:
– Recognition: The first stage is when the immune system recognizes the wolf worm. Specialized cells detect the presence of the larvae and signal other immune cells that there’s a problem.
– Activation: Once the intruder is recognized, the immune system activates. This involves several types of immune cells working together to launch an attack. They produce antibodies specifically targeting wolf worms.
– Elimination: Finally, the immune system works to eliminate the worm. This can involve killing the parasite directly or isolating it in a way that prevents it from causing harm.
It’s a finely-tuned process, but it doesn’t always go smoothly. The wolf worm has some tricks up its sleeve that can help it evade the immune response.
How Wolf Worms Evade the Immune System
You might be thinking, “If the immune system is so powerful, how can a worm manage to survive?” That’s a great question! Wolf worms have developed several strategies to dodge the immune response.
– Camouflage: One of the biggest advantages for these larvae is their ability to blend in. They can mimic certain substances that the host’s body produces, which helps them go unnoticed for longer.
– Suppressing Immune Responses: Some studies suggest that wolf worms can secrete substances that dampen the host’s immune response. It’s almost like throwing a smoke bomb to distract the immune system while they do their thing.
– Rapid Reproduction: Once they’re in, they can reproduce quickly, creating an overwhelming situation for the host’s immune system. By the time the body can respond, there may be too many larvae to handle effectively.
These tactics make it challenging for the immune system to completely eradicate the threat, leading to prolonged infections and ongoing health issues for the affected mammals.
Impact of Wolf Worms on Their Hosts
The presence of wolf worms can significantly impact a mammal’s health. For example, dogs infected with wolf worms may exhibit symptoms such as:
– Skin inflammation: The worms can cause irritation at the entry point, leading to red, swollen skin.
– Infections: Secondary infections can occur as a result of the immune system’s response to the larvae.
– Behavioral changes: Animals may become lethargic, stop eating, or show signs of discomfort due to the presence of these parasites.
In some cases, the infection can become severe enough to require medical intervention. Veterinary treatment may involve removing the larvae or administering medications to help the host’s immune system fight back.
Research and Future Directions
There’s still a lot to learn about wolf worms and how they interact with mammalian immune systems. Researchers are investigating various aspects of this relationship, including:
– Immunology: Understanding the immune mechanisms at play can help us find better ways to protect animals from these parasites.
– Prevention: Developing treatments or vaccines to enhance the immune response against wolf worms is an active area of research.
– Ecological Impact: Studying the roles of wolf worms in their ecosystems can yield insights into host-parasite dynamics and how to manage wildlife health.
This type of research is crucial not only for animal health but also for understanding broader biological principles. By exploring these relationships, we can learn more about evolution, immunity, and even how these processes can be applied in human medicine.
Wolf worms may seem like tiny villains in the grand tapestry of life, but they play a role that contributes to our understanding of immune responses in mammals. The battle between these parasites and the immune systems of their hosts is a fascinating dance of survival.
From the initial invasion to the complex immune reactions, each stage tells us something valuable about biology and ecology. As we move forward, ongoing research into these interactions will not only help protect our furry friends but also enhance our overall understanding of immune responses. So, the next time you hear about wolf worms, remember—it’s not just a story about pests, it’s a deeper narrative about life itself.