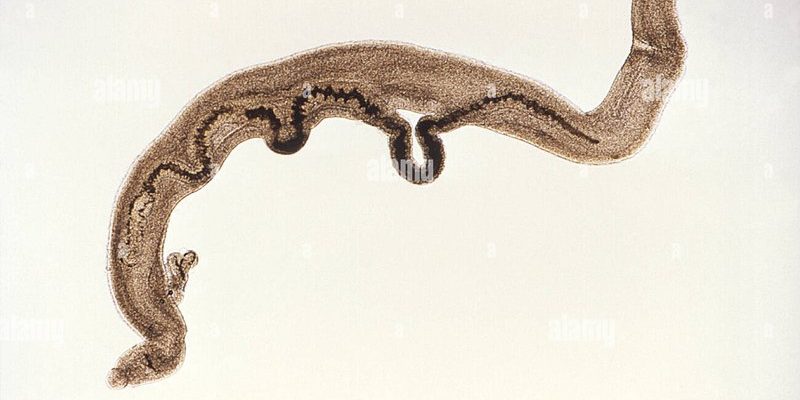
So, what exactly are trematodes, and why should you care? Well, these little guys play a significant role in the ecosystems they inhabit. Knowing about them can help you appreciate the intricate web of life that connects various species. If you’re a naturalist or just a curious person, understanding trematodes might deepen your appreciation for biodiversity. So, grab a cup of coffee, and let’s dive into the fascinating world of trematodes!
What Are Trematodes? A Quick Overview
Trematodes belong to the class Trematoda within the phylum Platyhelminthes, which means they’re flatworms. They have a unique body structure that’s not just flat but also leaf-shaped, which is where the term “fluke” comes from. These parasites have an intriguing life cycle that often involves multiple hosts, typically starting with a snail and moving on to larger animals, including fish, reptiles, and mammals.
The fascinating part? Trematodes can be incredibly specialized. Some only infect a specific type of animal, while others have a broader range. This specialization often helps them thrive in specific habitats. For instance, liver flukes, which are a type of trematode, are specially adapted to live in the livers of animals, where they can absorb nutrients directly. It’s like they’ve found a perfect little apartment within their hosts!
There are over 18,000 species of trematodes, each with its unique adaptations. They might not be the most glamorous creatures, but their impact on the ecosystems they inhabit is pretty significant. They can influence the health of their hosts and even affect entire populations of animals.
The Life Cycle of Trematodes
The life cycle of a trematode is nothing short of a soap opera. It typically involves multiple hosts and stages, each critical for their survival. The journey usually starts when a mature trematode releases its eggs into the environment, often in water. These eggs hatch into larvae called miracidia, which then swim around looking for their first host—a snail, in most cases.
Once inside the snail, the miracidia undergo several transformations, eventually developing into a different stage known as cercariae. These are like the teenage version of trematodes, ready to venture out into the world. They leave the snail to find their next host, which can be a fish, a mammal, or even a human.
Here’s where it gets interesting: once the cercariae find their new host, they burrow into the body and begin to grow into adults. They’ll reproduce and go through the cycle again, releasing eggs back into the water. It’s a journey filled with twists and turns, showcasing nature’s creativity. You might be wondering why this matters. Well, understanding their life cycle can help in controlling diseases caused by these parasites, especially in agriculture and human health.
Different Types of Trematodes
Trematodes can be categorized into a few major types, each with its unique host preferences and life cycles. Here are some of the most notable categories:
- Liver Flukes: These trematodes, like Fasciola hepatica, primarily infect the livers of various mammals. They can cause serious health issues, especially in livestock.
- Blood Flukes: Schistosoma species fall into this category. They’re infamous for causing schistosomiasis, a disease affecting millions of people around the world.
- Lung Flukes: Paragonimus species usually infect the lungs of mammals, including humans. Eating undercooked crab or crayfish can transmit these parasites.
Each type of trematode has distinct features but shares the same overarching theme: survival through parasitism. Understanding these categories can help us address the medical and ecological issues related to these organisms effectively.
How Do Trematodes Affect Their Hosts?
The relationship between trematodes and their hosts is a classic example of parasitism. In many cases, their presence can significantly impact the health of the host. For instance, liver flukes can cause liver damage and affect the overall well-being of livestock. This can lead to economic losses for farmers due to decreased productivity and increased veterinary costs.
On the human side, trematodes like schistosomiasis can lead to serious health problems. Symptoms might include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and even long-term complications if left untreated. It’s not just about individual health; outbreaks can affect entire communities, especially in areas where sanitation is poor.
So, what can be done? Preventative measures, such as proper sanitation and cooking food thoroughly, can help reduce the risk of infection. Understanding how these organisms operate is crucial for addressing and managing their impact.
Why Should We Care About Trematodes?
You might still be asking yourself, “Why should I care about trematodes?” Well, here’s the thing: these creatures are key players in their ecosystems. They can indicate the health of their environment and the well-being of other species.
When trematode populations are thriving, it may suggest a healthy ecosystem. However, when diseases linked to trematodes increase, it can signal environmental changes or health issues within populations. They serve as a reminder of how interconnected life is—what happens to one species can ripple through the entire food web.
Additionally, studying trematodes helps scientists learn about evolution and adaptation. These parasites have had to adapt over millions of years to survive, offering insight into biological resilience and evolution.
Research and Future Directions
Research on trematodes is ongoing and incredibly important. Scientists are continually investigating their life cycles, host interactions, and potential for causing diseases. Understanding these aspects can lead to better prevention and treatment options for diseases linked to trematodes.
There’s also growing interest in using trematodes in ecological studies. They can serve as indicators for environmental changes, helping researchers track ecosystem health over time. This can inform conservation efforts and resource management, emphasizing the need to protect not just the big, charismatic animals but also the smaller, less glamorous ones.
While they may seem insignificant, trematodes can significantly impact our ecosystems and health. By learning about them, we foster a deeper respect for nature’s intricate web and the importance of each species, no matter how small.
Trematodes may not be the stars of the animal kingdom, but their role in our ecosystems is undeniably essential. From influencing the health of hosts to offering insights into evolution, these tiny parasites are fascinating in their ways.
As you step outside next time, remember that even the smallest creatures can have a big impact. Whether it’s a liver fluke affecting livestock or a blood fluke challenging human health, understanding their lives can deepen our appreciation for the complexity of life on Earth. So let’s keep exploring and advocating for all creatures, big and small. After all, nature has a way of surprising us with how interconnected we really are.

