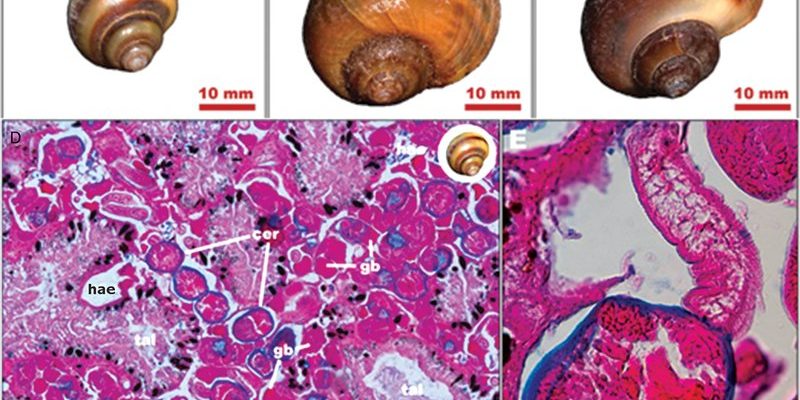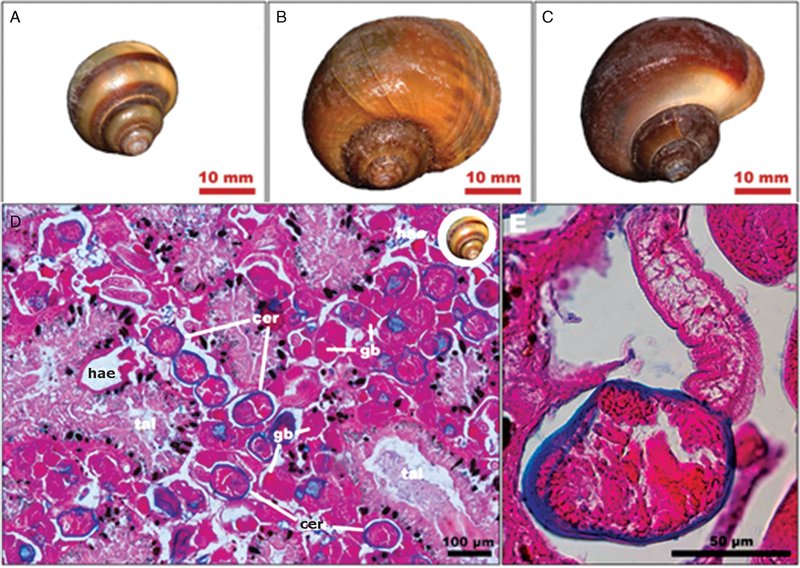
Trematodes have been around for millions of years, and though they’re often viewed in a negative light due to their parasitic nature, they also contribute significantly to their ecosystems. Like many organisms, they have complex life cycles that can impact everything from nutrient cycling to population dynamics. Let’s dive into the world of trematodes and see how they interact with their environments, both in soil and aquatic ecosystems.
What Are Trematodes?
Trematodes, often referred to as flukes, are a class of parasitic flatworms belonging to the phylum Platyhelminthes. They typically have complex life cycles that involve multiple hosts, which can include snails, fish, and mammals. Most notable is their structure: they usually possess a flattened body and suckers that help them attach to their hosts.
In essence, these organisms can often be compared to the “bad boys” of the worm world. They thrive by extracting nutrients from their hosts, but they also have a unique charm—like an engine that, while it may be harmful to one car, could help the larger ecosystem run smoothly. Their life stages often include both aquatic and terrestrial phases, making them versatile players within their environments.
Life Cycle of Trematodes
The life cycle of a trematode is fascinating, resembling a complex dance between hosts. It usually starts when eggs are released into water or soil, hatching into larvae called miracidia. These larvae seek out a suitable snail host, where they undergo several transformations, eventually becoming cercariae.
Once cercariae leave the snail, they might infect other animals, like fish or mammals, or attach to vegetation. This multiple-host strategy is a survival mechanism, ensuring that trematodes can thrive in diverse ecosystems. In this way, they can be seen as connectors within the food web, passing nutrients along as they move from one host to another.
The Role of Trematodes in Aquatic Ecosystems
In aquatic ecosystems, trematodes play an essential role in maintaining the balance of various populations. Because they parasitize fish and amphibians, their presence can influence the health and behavior of these species.
For example, when a fish is infected, it may become vulnerable and less likely to survive. This can lead to a decrease in the fish population, which, in turn, impacts their predators. You might say trematodes are like unwelcome house guests who alter the dynamics of the household; they might not be ideal, but a certain level of their presence can indicate a thriving ecosystem.
Indicators of Ecosystem Health
Interestingly, trematodes can serve as bioindicators. This means that the types and numbers of trematodes present can provide insights into the health of an aquatic system. For instance, a rise in certain species of trematodes might indicate pollution or stress in the environment.
So, scientists often study these parasites to gauge the overall quality of water bodies and understand how ecosystems react to changes. This makes trematodes both complicated and invaluable! They remind us that every creature, even the ones we might not appreciate, plays a part in the bigger picture.
Trematodes in Soil Ecosystems
While trematodes are mostly discussed in relation to aquatic settings, they also have roles in soil ecosystems. Here, they can interact with plants and soil-dwelling organisms, contributing to nutrient cycling. This is essential for maintaining soil health and fertility.
The presence of trematodes in soil can signify biodiversity. A rich variety of organisms is often a sign of a healthy ecosystem. In this context, trematodes can be seen as part of a larger symbiotic relationship, where they help break down organic materials, making nutrients more accessible to plants.
Impact on Soil Microorganisms
Trematodes can influence populations of other soil microorganisms. By feeding on certain hosts, they can control the population dynamics of these organisms. This is important because microorganisms play a massive role in nutrient cycling, organic matter decomposition, and overall soil structure.
You can think of trematodes as part of the gardening crew in your local ecosystem. They help regulate the “vegetation” of microworlds, ensuring that no single organism dominates the soil.
The Complex Relationships Within Ecosystems
Trematodes form part of a larger web of life that includes hosts, predators, and the environment itself. Their interactions with hosts can lead to various outcomes, depending on the host’s health and the ecosystem’s condition.
When we talk about these relationships, it’s helpful to remember that ecosystems thrive on balance. Although trematodes are parasites, they also help keep populations in check. For example, they can prevent overpopulation of certain fish species, allowing for greater diversity in aquatic systems.
Food Web Dynamics
In the context of food webs, trematodes play a crucial role. They serve as prey for many small organisms, which are then consumed by larger predators. This means that even if trematodes are parasites, they contribute to the energy flow within ecosystems.
The presence of trematodes can indicate a diverse and stable food web. They remind us that even undesirable organisms have their place in nature. It’s a complex relationship—much like a game where everyone has a role to play, even if some participants wouldn’t be your first choice.
Implications for Biodiversity Conservation
Understanding the role of trematodes can also help in biodiversity conservation efforts. By studying these organisms, researchers can gain insights into ecosystem health and the impacts of environmental changes.
As habitats face threats from pollution, climate change, and human activity, keeping an eye on trematode populations can signal needed conservation actions. Their presence and health can reflect broader ecosystem issues, making them crucial to environmental monitoring.
Challenges in Conservation
However, working with trematodes in conservation isn’t always straightforward. Their complex life cycles and interactions with numerous hosts mean that many variables are in play. Conservationists must consider not just the trematodes but also the health of their hosts and overall habitat quality.
Treating these systems holistically is essential. Just as a gardener must consider soil, water, and plants, conservationists need to view ecosystems through a wide lens to ensure all elements, including trematodes, are thriving.
Trematodes may not be the stars of the ecosystem show, but their role is undeniably significant. From maintaining population dynamics in aquatic environments to contributing to soil health, these little parasites are vital to Earth’s complex web of life.
So, next time you think of soil or aquatic ecosystems, remember that even the smallest and often overlooked organisms carry the weight of the world on their tiny shoulders. They remind us that every player in the ecosystem, even the trematodes, is integral to the health and balance of nature. By understanding and protecting these organisms, we foster healthier environments for future generations.