Now, let’s break it down step-by-step so you can understand exactly what’s going on with mudworms as they chow down on their meals. From their anatomy to their feeding habits, we’ll cover everything you need to know. Ready? Here we go!
What Are Mudworms?
Before we dig into their feeding mechanism, let’s get familiar with mudworms. These worms belong to the family of polychaetes, specifically in the genus *Lumbricus*. They thrive in muddy or silty environments, often found in estuaries, marshes, and sediment-rich areas. Just picture a squirming mass of soft-bodied worms digging and wriggling around in the mud, creating their own little underworld.
Mudworms vary in size but typically measure a few inches long. They have a soft, segmented body and a distinct head with bristles. These bristles, or chaetae, help them navigate through their mucky homes. Overall, mudworms are pretty unassuming creatures, but they play a vital role in their ecosystems.
So, why should we care about mudworms? Well, they help break down organic material and recycle nutrients, which benefits the environment. Plus, many fish and birds rely on them as a food source. Understanding their feeding mechanism helps us appreciate their role in maintaining healthy aquatic ecosystems.
The Anatomy of a Mudworm
Understanding how mudworms feed starts with knowing their anatomy. These creatures may look simple, but they have specialized structures that help them gather food efficiently.
– Head and Segments: At the front, the head features sensory organs, enabling the worm to detect food in its murky environment. The body is segmented, with each segment containing muscle and other essential organs.
– Bristles: As mentioned earlier, mudworms have tiny bristles (chaetae) along their body. These bristles not only provide grip as they burrow into the mud but also aid in locomotion. Think of them as the tiny feet of the mudworm.
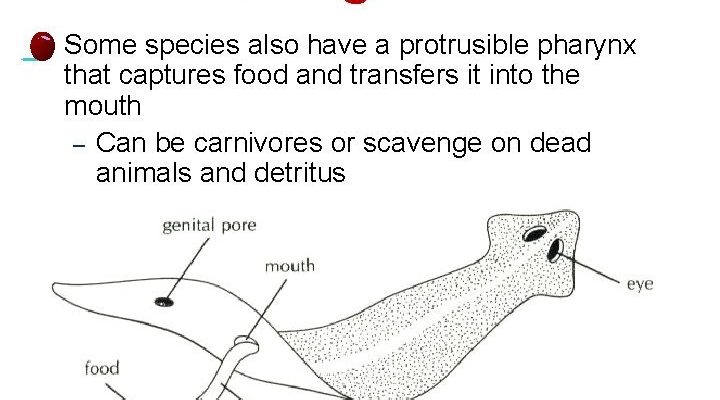
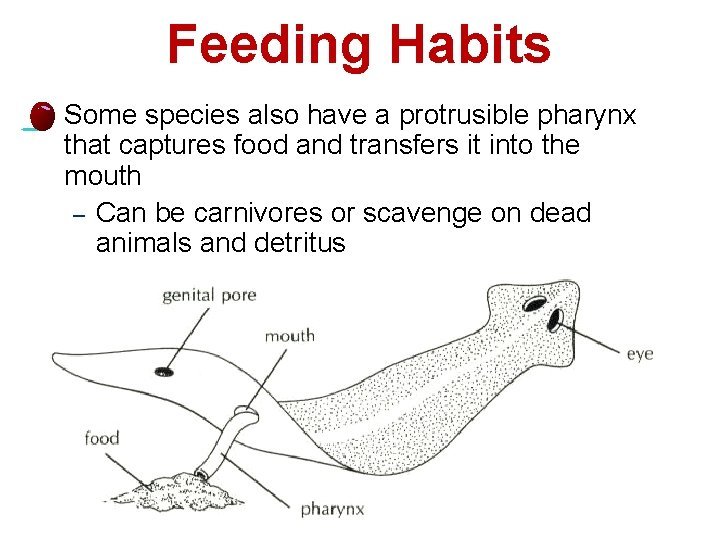
– Mouth and Pharynx: The mouth is equipped with a muscular pharynx that helps create suction. This suction is crucial for drawing food into the worm’s body.
Each part of a mudworm is designed for survival, allowing it to thrive in its environment and find those tasty morsels hidden in the sediment.
How Do Mudworms Feed?
So, how exactly do mudworms suck down their meals? It’s a pretty impressive process that combines anatomy and behavior. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
1. Locating Food: To start, mudworms rely on their sensory organs to detect organic material in the mud, such as decaying plants, tiny algae, or detritus.
2. Creating Suction: Once they find a food source, they use their muscular pharynx to create suction. This action pulls food particles into their mouth, much like a vacuum cleaner.
3. Ingestion: The food goes into their digestive tract. Here, enzymes break down the organic material, which provides essential nutrients for the mudworm.
4. Expelling Waste: After digesting the food, undigested material is expelled back into the environment. This process not only clears the mudworm’s digestive system but also contributes to nutrient recycling in the ecosystem.
Isn’t it fascinating how these small creatures can effectively gather food? Their feeding mechanism plays a crucial role in their ecosystem, helping to maintain balance and support food webs.
The Role of Mudworms in the Ecosystem
You might be wondering why we should pay attention to how mudworms feed. Well, their feeding method has significant implications for their environment. Here’s how:
– Nutrient Recycling: By breaking down organic matter, mudworms help recycle nutrients back into the soil and water. This process supports plant growth and healthy aquatic habitats.
– Food Source: Mudworms serve as an essential food source for various fish, birds, and other wildlife. They help sustain local ecosystems by providing nutrients to higher trophic levels.
– Soil Aeration: As mudworms burrow and feed, they aerate the soil. This action allows oxygen to penetrate deeper into the sediment, which is beneficial for other organisms living in the mud.
In essence, mudworms are unsung heroes of the ecosystem, playing a vital role in maintaining balance and health in their habitats.
Feeding Adaptations of Mudworms
Mudworms have developed some interesting adaptations that help them effectively find and consume food. Let’s take a closer look:
– Flexible Bodies: Their soft, flexible bodies allow them to navigate through dense sediment easily. This flexibility is crucial for accessing various food sources buried in the mud.
– Suction Power: The strong muscle control in their pharynx helps them generate suction, enabling them to pull in food quickly and efficiently. This adaptation is essential in a competitive environment where every meal counts.
– Detritivorous Diet: Mudworms primarily feed on detritus, which is the organic material derived from decomposing plants and animals. This diet allows them to thrive in environments where other food sources might be scarce.
These adaptations not only improve their feeding efficiency but also ensure they can survive in challenging environments.
Common Misconceptions About Mudworms
When it comes to mudworms, there are several misunderstandings that can arise. Let’s clear up a few of these misconceptions:
– Not Just A Food Source: While mudworms are indeed a food source for many animals, they also play a significant role in the ecosystem. Their contributions to nutrient recycling and soil aeration are essential for maintaining healthy aquatic habitats.
– Low Impact: Some may think mudworms don’t impact their environment significantly. However, their feeding habits can drastically affect sediment quality and nutrient levels, making them vital players in their ecosystems.
– Simple Creatures: It’s easy to classify mudworms as simple, unimportant beings. However, their complex feeding methods and ecological roles illustrate that they are far from simple.
Understanding these misconceptions can deepen our appreciation for mudworms and their place in the natural world.
So, what have we learned about the feeding mechanism of mudworms? They’ve got a unique way of feeding that involves some fascinating anatomy and clever adaptations. By using suction to draw in organic material, they not only nourish themselves but also help maintain the health of their ecosystems.
The next time you see a mudworm wriggling around in the muck, remember the little powerhouse it is. Their contribution to nutrient cycling and as a food source for other wildlife makes them vital to our planet’s health. In nature, every creature has a role, and mudworms are perfect examples of how even the smallest beings can have a big impact.