When we talk about hookworms, we’re referring to a type of parasitic nematode that thrives in the intestines of its host, often humans. Imagine a tiny, hungry vacuum cleaner that attaches itself to the walls of your intestine, munching away at your nutrients and, frankly, your health. They’re not just living off the land; they actively seek a warm, cozy home where they can thrive and grow. So, how exactly do these creatures snag their meals? Let’s break it down step-by-step.
What Are Hookworms?
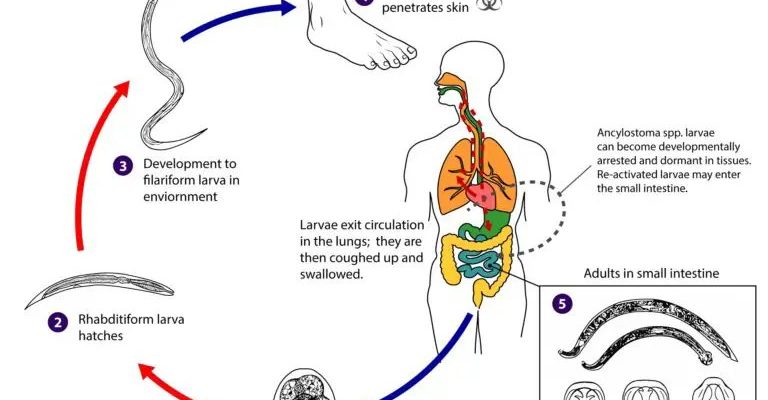
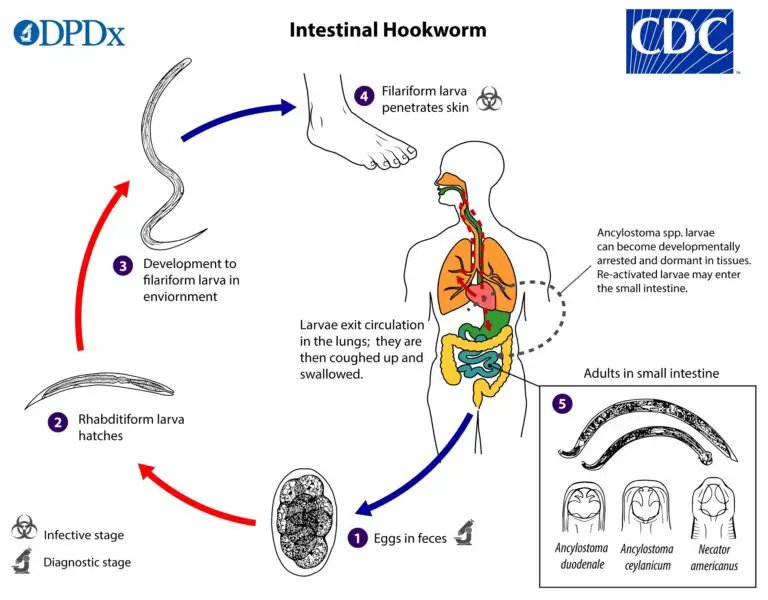
Hookworms are small, parasitic worms that belong to the family Ancylostomatidae. They’re typically less than an inch long, but they pack a punch when it comes to the impact they have on their hosts. The most notorious species affecting humans include *Necator americanus* and *Ancylostoma duodenale*. These species have adapted to live in the intestines of humans, where they latch onto the intestinal walls and feed on blood.
The life cycle of hookworms begins when their eggs are released into the environment through human feces. Once they hatch, the larvae can survive in soil, waiting for a suitable host. Here’s the thing: hookworm larvae can penetrate human skin, often entering through bare feet, which is how many infections begin. This is why people in certain regions, especially those where sanitation is poor, are at higher risk. It’s like a sneaky invitation that the larvae send out to potential hosts!
How Do Hookworms Attach to Their Host?
Once the larvae find a human host, they need to attach themselves to the intestinal wall so they can start feeding. Picture them like little climbers scaling a steep wall. They use their mouthparts, which are equipped with sharp teeth or cutting plates, to latch onto the intestinal lining. This attachment is crucial because it keeps them securely in place while they feast.
The attachment process isn’t just about holding on. As they bite into the intestinal wall, they can also cause damage and bleeding. This is their way of not only securing a meal but also ensuring a steady supply of blood. You might be wondering how this affects the host. Well, as hookworms feed, they can lead to iron deficiency and anemia in humans due to the loss of blood over time. Yep, they really know how to throw a wrench in the works!
Feeding Process of Hookworms
Now, let’s get into the nitty-gritty of how hookworms actually feed. Once attached, they start to ingest blood. Their feeding mechanism is quite effective. They have specialized structures in their mouths that allow them to pierce the intestinal tissue and suck up blood.
Here’s how it works:
- Attachment: They latch onto the intestinal wall with their mouthparts.
- Piercing: Using their sharp teeth or plates, they pierce the tissue to access blood vessels.
- Feeding: They can consume up to 0.2 mL of blood per day, which might seem small but can add up quickly!
Let’s visualize this: it’s like using a straw to sip a drink. Only in this case, the drink is your blood, and the straw is a specialized mouth structure. If you think of it that way, it’s easier to grasp just how invasive these little pests can be.
Effects on the Host
By now, you’re probably wondering why it matters how hookworms feed. Well, their feeding habits can have serious effects on the host’s health. Beyond just blood loss, hookworm infections can lead to various symptoms, including abdominal pain, fatigue, and even cognitive issues in severe cases. The long-term effects can be particularly concerning, especially in children, who may suffer from stunted growth and cognitive impairment.
Anemia is one of the primary concerns. Due to their constant feeding, hookworms can cause a significant loss of red blood cells, leading to iron deficiency. This can manifest as weakness, dizziness, and difficulty concentrating. It’s like having a leaky tire; the more you lose, the harder it is to keep going.
Preventing Hookworm Infections
So, how do we keep these unwelcome guests at bay? Prevention is key! Here are some straightforward steps you can take to avoid hookworm infections:
- Wear shoes: Protect your feet, especially in areas where hookworms are common.
- Practice good hygiene: Wash your hands regularly and ensure proper sanitation when dealing with waste.
- Educate others: Sharing knowledge about hookworm risks and prevention can help protect your community.
Think of these steps as a barrier, helping to keep those sneaky little larvae from making their way into your body. It’s all about being proactive and informed!
Treatment Options for Hookworm Infections
If you suspect that you have a hookworm infection, it’s essential to seek medical advice promptly. Treatments usually involve medications that can kill the worms and help your body recover. Commonly prescribed medications include albendazole and mebendazole. These drugs work by inhibiting the worms’ ability to absorb glucose, essentially starving them out.
Remember, though, treating the infection is just part of the solution. It’s also vital to address any nutritional deficiencies that may have resulted from the infection. This could involve taking iron supplements or adjusting your diet to boost your iron intake.
Understanding the feeding mechanism of hookworms gives us a clearer picture of their impact on human health. These little creatures may seem insignificant, but their ability to latch onto a host and feed can lead to serious health issues if left unchecked. By wearing shoes, practicing good hygiene, and seeking treatment when necessary, we can keep these parasitic pests at bay.
So, next time someone brings up hookworms, you’ll have a lot more to share than just a grimace! They’re fascinating in their own right, and knowing how they feed makes it easier to understand the importance of prevention. Let’s stay informed and healthy!