You might be wondering, how does a worm this big even eat? What does it munch on in its subterranean home? Well, you’re in for a treat! The feeding mechanism of the Giant Palouse Earthworm is a fascinating process that showcases its unique adaptations to life underground, where traditional feeding methods just won’t cut it. Let’s break it down step by step.
Overview of the Giant Palouse Earthworm
The Giant Palouse Earthworm (Driloleirus americanus) is native to the Palouse region of the Pacific Northwest, primarily found in eastern Washington and northern Idaho. It’s not just its size that makes it special; this worm is also known for its distinctive burrowing behavior and lifespan, which can span several decades.
These earthworms thrive in rich, moist soils, primarily in grasslands and agricultural areas. They face significant threats from habitat loss and soil degradation, making their conservation vital. Their unique adaptations have evolved over time, enabling them to extract nutrients from the soil efficiently.
These worms have a fascinating lifestyle, living deep underground, often several feet below the surface. Their burrowing not only creates channels for air and water to reach plant roots but also helps in nutrient cycling, which is essential for soil health.
How the Feeding Mechanism Works
Now, let’s break down how the Giant Palouse Earthworm feeds. This worm has a specialized feeding mechanism that allows it to thrive in its unique habitat. Instead of the traditional worm diet, these guys have adapted to a diet that’s a bit more sophisticated.
Giant Palouse Earthworms primarily feed on decaying organic matter, such as dead leaves, roots, and other decomposed plant material. They break down this organic material through a process called detritivory, where they consume and digest organic debris. This is crucial since it helps recycle nutrients back into the soil.
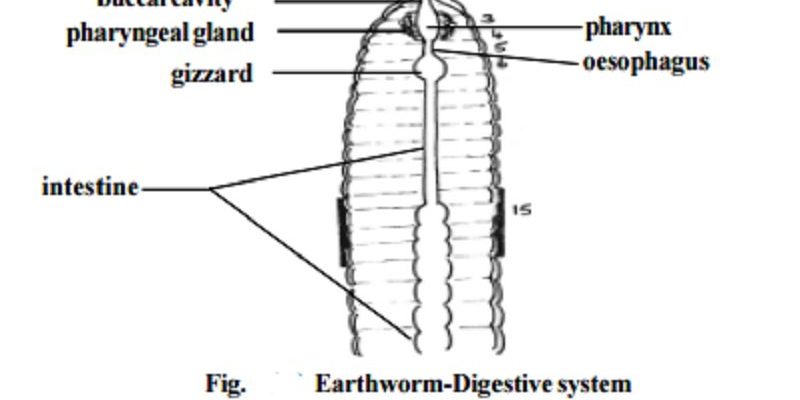
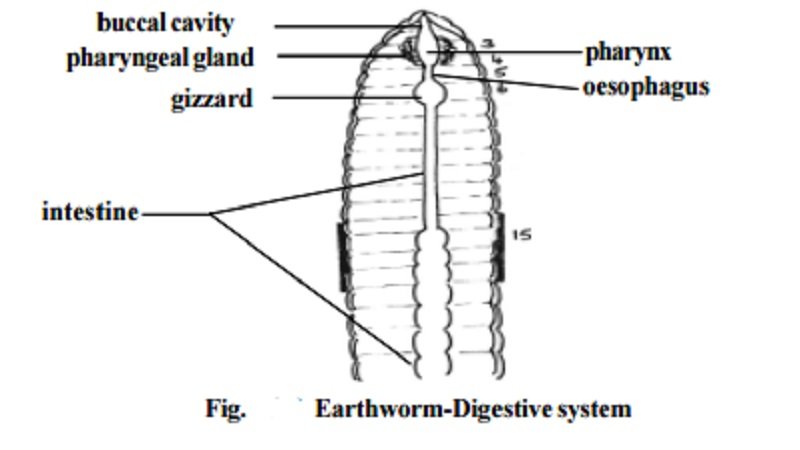
The process starts when the earthworm uses its muscular pharynx to suck in bits of soil and organic matter. The earthworm then processes this material in its gizzard, where it’s ground up. Finally, the nutrient-rich material is passed to the intestine for absorption. This process allows the earthworm to extract essential nutrients while helping aerate and enrich the soil.
The Role of Soil in Feeding
Soil plays a pivotal role in the feeding mechanism of the Giant Palouse Earthworm. The nutrient content and composition of the soil can directly influence its feeding habits. The worm utilizes soil-dwelling microorganisms to aid in digestion, which further enhances their ability to extract nutrients from organic matter.
The earthworm’s burrowing activity is crucial here. As it moves through the soil, it creates channels that facilitate water and air movement, making it easier for nutrients to reach plant roots. This symbiotic relationship with the soil and plants is an essential element of the ecosystem.
Interestingly, the quality of soil can vary greatly. If the soil is compacted or depleted of nutrients, the feeding efficiency of the worm can be negatively affected. This is one reason why maintaining healthy, biodiverse soil is vital not just for these worms but for the entire ecosystem.
Feeding Behavior in Different Seasons
The feeding behavior of the Giant Palouse Earthworm can change with the seasons. In spring and fall, when moisture levels are higher, these worms become more active. They will feed more frequently, taking advantage of the abundance of organic matter that’s available during these times.
In contrast, during the hot and dry summer months, their feeding can slow down. To cope with dry conditions, they may retreat deeper into the soil to find cooler, moister areas. This adaptation is crucial for survival, as it allows them to conserve moisture and avoid the harsher surface conditions.
You might find it interesting that during colder months, especially winter, the Giant Palouse Earthworm goes into a sort of dormancy. It reduces its activity significantly, which helps it conserve energy when food is scarce.
Importance of the Giant Palouse Earthworm in Ecosystems
These massive worms play a significant role in their ecosystems. By breaking down organic material and aerating the soil, they contribute to a more fertile environment that supports plant growth. Healthy soils lead to healthier plants, which then support a variety of wildlife.
Their feeding habits also help in nutrient cycling, making essential nutrients available to plants. This is particularly important in agricultural settings, where the presence of these worms can improve soil quality and promote crop yield. Farmers often overlook these little heroes; however, their contributions are invaluable.
Plus, they serve as a food source for various predatory species, such as birds and mammals, thereby creating an intricate food web. The decline of the Giant Palouse Earthworm could have ripple effects throughout the ecosystem.
Conservation and Threats
Unfortunately, the Giant Palouse Earthworm faces several threats, primarily from habitat destruction due to agricultural practices and urban development. Soil erosion and chemical runoff also pose significant risks to their populations.
Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure the survival of this unique earthworm. Protecting their habitat and promoting sustainable agricultural practices can help maintain healthy populations. Local organizations and researchers are actively working to raise awareness about the importance of preserving the Giant Palouse Earthworm and its habitat.
You might be surprised to learn that even simple actions, like maintaining native plant cover and reducing chemical use, can have a big impact on the survival of these worms. Everyone has a role to play in conserving these incredible creatures.
The feeding mechanism of the Giant Palouse Earthworm is a remarkable example of nature’s ingenuity. From its specialized diet of decaying organic matter to its critical role in aerating and enriching the soil, this earthworm showcases the delicate balance within ecosystems. Understanding its feeding habits helps us appreciate how interconnected life can be and emphasizes the importance of conserving such unique species.
By taking steps to protect their habitats, we can ensure that the Giant Palouse Earthworm continues to thrive and play its vital role in the environment. So, next time you think about earthworms, remember the Giant Palouse Earthworm and all the hard work it’s doing underground!