Planaria, often found in freshwater environments like ponds and streams, are fascinating creatures, especially when you delve into their ecological importance. Let’s walk through why these little flatworms hold such immense significance in the balance of nature.
What Are Planaria?
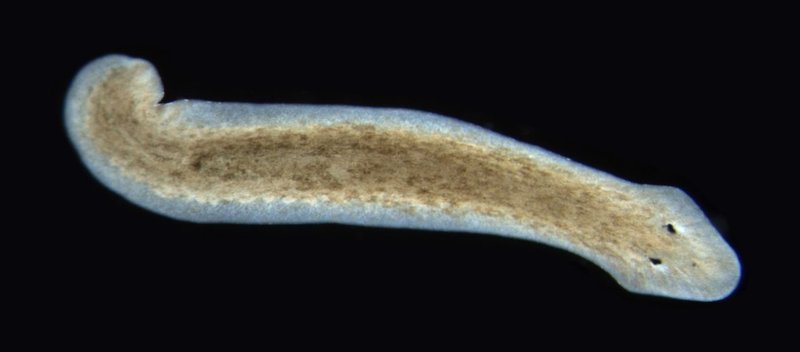
Before exploring their ecological significance, let’s get familiar with what Planaria actually are. Planaria are a type of flatworm belonging to the class Turbellaria, and they are known for their soft bodies and remarkable regenerative abilities. Picture a worm flattened out like a pancake—essentially, that’s what they look like! They come in various colors, often brown, black, or even greenish, and are typically less than a few centimeters long.
These creatures have fascinating biological attributes, including a simple nervous system and the ability to regenerate lost body parts. If you cut a Planaria in half, both halves can regenerate into fully functional worms! This impressive trait has made them a prime subject for scientific research, especially in studies about regeneration and stem cells.
You might wonder why they matter in the grand scheme of things. Well, let’s dig deeper into their ecological role.
Planaria as Ecosystem Indicators
Planaria are more than just cool creatures; they serve as important indicators of environmental health. When we talk about ecosystem indicators, think of them like the early warning system for our waterways. A diverse population of Planaria indicates a healthy, balanced ecosystem. If something’s off—like pollution or a drastic change in water quality—you’ll often see a decline in their numbers.
By studying Planaria and their habitats, scientists can assess the condition of the surrounding environment. For example, if they notice fewer Planaria in a river, it might signal the presence of harmful substances in the water or an imbalance in the aquatic ecosystem. This helps researchers and conservationists monitor water quality and take action before bigger problems arise.
The Role of Planaria in Nutrient Cycling
Another key ecological role of Planaria is their part in nutrient cycling. In simple terms, nutrient cycling is how nutrients move through the ecosystem. Planaria feed on decaying organic matter, such as algae, bacteria, and even small invertebrates, breaking them down into simpler forms.
Imagine a garden. The decomposition process, where Planaria step in, enriches the soil, making it fertile and promoting plant growth. Similarly, in aquatic environments, the nutrients released by Planaria through feeding and excretion help sustain various life forms, from plants to other animals.
Their ability to recycle nutrients is crucial for maintaining the ecosystem’s productivity. Without Planaria, nutrients would accumulate and lead to an imbalance, potentially disrupting the entire food web.
Planaria and Their Predators
Planaria also play an essential role in the food chain. They are prey for many creatures, including fish, amphibians, and other invertebrates. This relationship highlights the interconnectedness of ecosystems.
Think of Planaria as a snack in nature’s buffet. Larger organisms rely on them for sustenance, and their presence helps sustain populations of those predators. If Planaria were to disappear, it could lead to a ripple effect, where the decline of predator species would follow, disrupting the entire food chain.
In healthy ecosystems, the balance of predator and prey is fundamental. Planaria help maintain this balance, supporting biodiversity and ensuring that various species can thrive.
Research and Biomedical Importance of Planaria
The fascinating biology of Planaria extends beyond their ecological roles; they are also critical to scientific research. Their ability to regenerate has garnered massive interest, particularly in the fields of regenerative medicine and developmental biology.
Scientists study *Planaria* to understand how regeneration works at a cellular level. This research could unlock new therapies for humans, potentially leading to advancements in wound healing and organ repair. The insights gained from Planaria could revolutionize how we approach medical treatments for various injuries and diseases.
In this sense, the ecological importance of Planaria ties directly into human health and well-being, showcasing how these tiny creatures impact our lives in ways we might not readily see.
Conservation Efforts and Planaria
Given their ecological importance, conserving Planaria and their habitats is crucial. Although they are not usually at the forefront of conservation discussions, their well-being reflects the health of aquatic ecosystems. Protecting wetlands, ponds, and streams not only safeguards Planaria but also the myriad of life forms that depend on these habitats.
Engaging with local conservation efforts, reducing pollution, and educating others about the significance of even the smallest creatures can make a difference. Remember, every action counts! You can contribute by supporting clean water initiatives and engaging in activities that promote biodiversity.
In summary, Planaria might not be the most glamorous creatures in nature, but their ecological importance is immense. From serving as indicators of environmental health to playing vital roles in nutrient cycling and being a food source for other animals, these little flatworms are essential for maintaining the balance of ecosystems.
Next time you think about nature’s heroes, don’t forget to consider the humble Planaria. These fascinating creatures remind us that even the smallest organisms can play a critical role in the grand scheme of life on Earth. So, whether you’re walking by a stream or enjoying nature, take a moment to appreciate the hidden gems like Planaria working hard behind the scenes!
