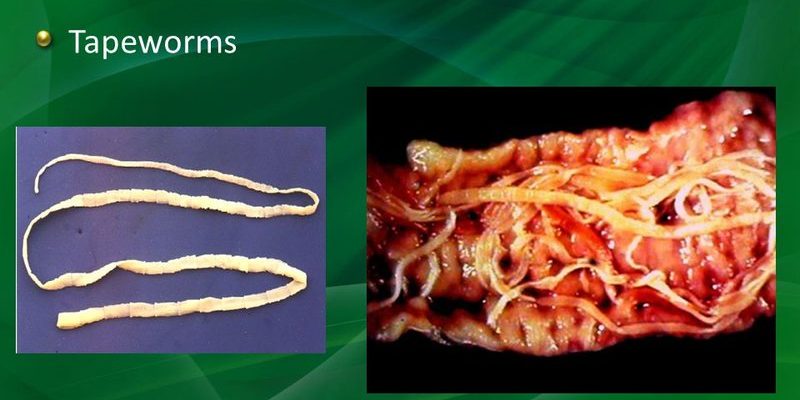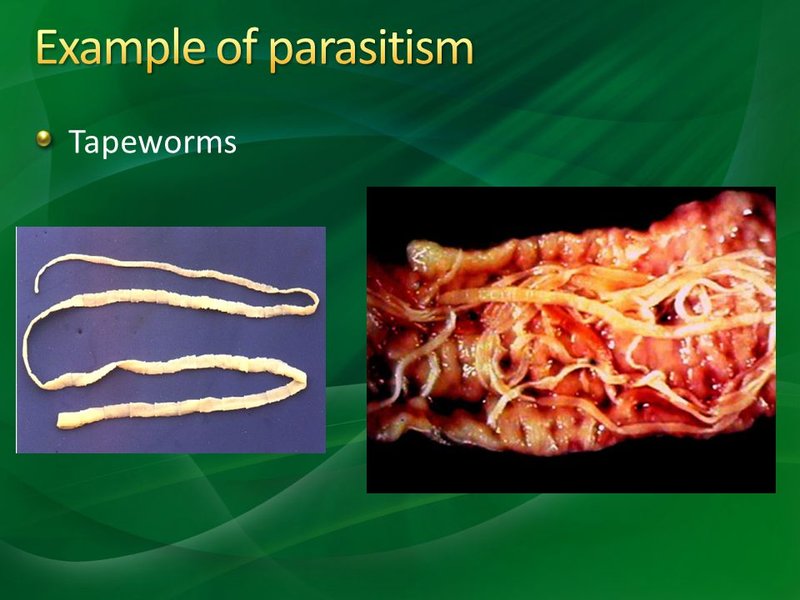
You might be wondering how a parasite could hold any ecological importance. Well, just as every player in a sports team has a role, even the guppy tapeworm plays a part in its environment. From nutrient cycling to the health of fish populations, they connect to larger ecological narratives. So, let’s dive into the murky waters of this fascinating species and explore why they matter to ecosystems and fish alike.
Understanding the Guppy Tapeworm
The guppy tapeworm, scientifically known as *Hymenolepis nana*, primarily resides in guppies, a common freshwater fish. They attach themselves to the fish host’s intestines and absorb nutrients directly. Picture a tiny hitchhiker getting a free ride on the bus while munching on snacks. This relationship may seem one-sided, but it’s important to understand how it fits into the bigger picture of aquatic ecosystems.
These tapeworms can reproduce rapidly, creating a balance within fish populations. A healthy level of tapeworms can actually indicate a balanced ecosystem. When guppies become hosts, the tapeworms take advantage of the nutrients from the fish’s diet. This process helps regulate the fish’s energy stores, ensuring that no single fish becomes too dominant or overpopulated in a pond or tank.
Tapeworm Life Cycle
The life cycle of the guppy tapeworm is fascinating. Their eggs are released into the water, where they’re eaten by fish. Inside the guppy, they grow and mature, continuing to produce more eggs. It’s a cycle that keeps repeating, like the seasons changing each year.
Here’s a quick breakdown of their life cycle:
- Egg Stage: Eggs are released into the water.
- Larval Stage: Fish ingest the eggs, and they hatch inside their intestines.
- Adult Stage: Tapeworms grow and attach themselves to the fish’s intestinal wall.
Understanding this cycle highlights the interconnectedness of aquatic life. The presence of guppy tapeworms can serve as a barometer for the health of their broader ecosystem.
Role in Nutrient Cycling
One of the key ecological functions of the guppy tapeworm is nutrient cycling. They perform a critical role in breaking down and recycling nutrients within their aquatic environments. When tapeworms digest the nutrients from their fish hosts, they contribute to the nutrient pool available in the water.
This can sound a bit technical, but it’s similar to how compost enriches garden soil. Just as compost breaks down organic materials into rich nutrients that plants can use, guppy tapeworms ultimately help recycle materials that might otherwise be lost. This nutrient cycling supports not only guppies but also other aquatic life, from plants to larger fish.
Impact on Host Fish Health
You might be curious if guppy tapeworms are harmful to their hosts. While heavy infestations can lead to health problems for guppies, typically, the relationship is more balanced.
Here’s the thing: a small number of tapeworms can help keep guppies from overindulging in food, maintaining a healthy weight and energy level. Just like how a little competition can motivate us in our daily lives, a few tapeworms can encourage host fish to maintain their health by preventing overpopulating.
However, if guppy populations get too high, this can lead to larger tapeworm infestations, which can affect their overall health and reproduction rates. So, monitoring tapeworm levels is crucial for ensuring guppy health.
Indicators of Ecosystem Health
The guppy tapeworm also serves as a useful indicator of ecosystem health. Like canaries in a coal mine, these tapeworms can signal changes in the water quality and the health of fish populations.
If tapeworm levels are rising rapidly, it might indicate an overpopulation of guppies or an imbalance in the aquatic environment. Conversely, a notable decline in tapeworms may suggest issues like poor water quality or diseases affecting fish. Monitoring these little parasites can give biologists a sneak peek into the overall health of aquatic ecosystems.
Interactions with Other Species
These tapeworms don’t just hover around guppies; they’re part of a larger web of interactions within their habitats. They can influence the dynamics of predator and prey relationships, acting as both a food source for some species and a population regulator for guppies.
For instance, smaller fish or aquatic invertebrates might feed on eggs or larvae, showcasing a natural cycle of life. This interconnectedness makes them a small but significant player in the grand ecosystem narrative. Just like how every character in a movie contributes to the plot, the guppy tapeworm plays a role in the aquatic ecosystem.
Conservation Implications
As we dig deeper into the ecological importance of the guppy tapeworm, we start to see broader implications for conservation efforts. Ensuring healthy populations of guppies—and by extension, their tapeworms—can aid in maintaining balanced ecosystems.
Conservationists often focus on larger species or habitats, but recognizing the roles of smaller, less glamorous creatures can provide a fuller picture of ecosystem health. By preserving environments where guppies thrive, we indirectly support the guppy tapeworm and the intricate web of life around them.
Community Involvement and Awareness
Public awareness is crucial in conservation efforts. Many people might not even know about the guppy tapeworm or its role in the ecosystem. By educating communities about these little creatures, we can promote a broader understanding of aquatic health and biodiversity.
Local schools and organizations can hold workshops on the importance of all species, including parasites like the guppy tapeworm. When people understand that even the smallest creatures play a part in environmental balance, they are more likely to support conservation initiatives.
So, the guppy tapeworm might seem like a small player in the aquatic world, but its role stretches far beyond just being a parasite. From nutrient cycling to serving as indicators of ecosystem health, these tiny organisms contribute significantly to their aquatic environments.
Understanding their ecological importance fosters a greater appreciation for all parts of the ecosystem, no matter how small. Next time you gaze into an aquarium, think beyond the vibrant fish swimming about and remember the hidden connections that sustain life beneath the surface. The guppy tapeworm, along with its guppy hosts, is part of a delicate balance that plays a critical role in maintaining healthy ecosystems.