Understanding the role of pinworms in ecosystems can help us recognize the interconnectedness of life forms. From helping to break down organic matter to influencing the food web, they contribute to the fragile balance of their environments. So, let’s dive deeper into how these small creatures affect both soil and aquatic systems.
What are Pinworms?
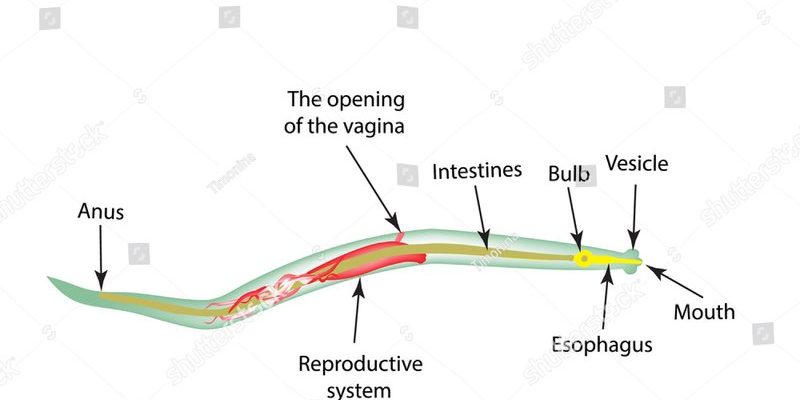
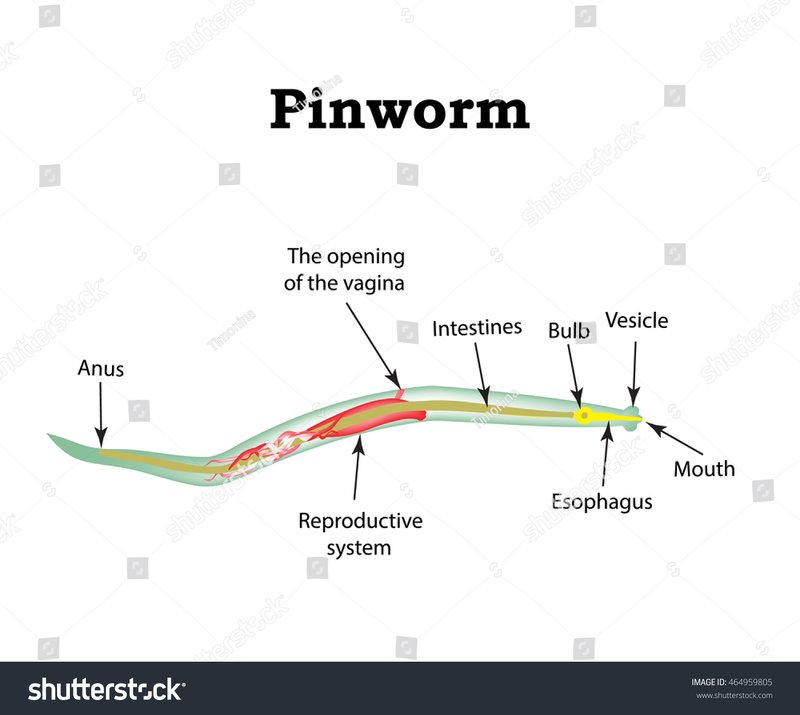
Pinworms, scientifically known as *Enterobius vermicularis*, are small, thin parasites primarily found in the intestines of humans. However, the term “pinworm” can also refer to several other small nematodes that inhabit soil and aquatic environments. They measure about 1-2 centimeters in length, and their long, slender bodies resemble threads. What makes them intriguing is not just their size but their life cycle and interactions with their environment.
Unlike many other worms, pinworms are known primarily for their role in human health, particularly in children. They can cause itchiness around the anus and are usually transmitted through the fecal-oral route. It’s a common issue in households, especially where hygiene practices may not be strictly followed. However, when we look beyond their impact on health, pinworms also serve essential functions in their ecosystems.
Pinworms in Soil Ecosystems
You might be surprised to learn that pinworms contribute significantly to the health of soil ecosystems. In soil, they are involved in nutrient cycling, helping to break down organic matter like decomposing plant material. This process is crucial because it transforms complex organic substances into simpler forms that plants can absorb, ultimately enriching the soil.
When pinworms feed, they consume organic debris and bacteria, processing these materials in their digestive systems. As they excrete waste, they release nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus back into the soil. This natural fertilizer promotes plant growth, fostering a diverse community of flora. Here’s the thing: without organisms like pinworms playing this vital role, we might see a decline in soil fertility, making it harder for plants to thrive.
Moreover, pinworms help in aerating the soil. As they burrow through the earth, they create tiny channels that allow air and moisture to circulate more freely. This aeration is essential for root health, as it supports the growth of beneficial microorganisms. Plants, in turn, benefit from these interactions, establishing a symbiotic relationship that sustains the ecosystem.
Pinworms in Aquatic Ecosystems
Moving to aquatic ecosystems, pinworms play fascinating roles as well. Some types of pinworms thrive in freshwater environments, contributing to the food web. They serve as a food source for various aquatic organisms, including fish and other small invertebrates. This makes them a critical part of the ecosystem’s energy transfer.
In these aquatic settings, pinworms help decompose organic material, such as fallen leaves and dead organisms. Through their feeding habits, they break down this matter, returning vital nutrients to the water. This process enhances water quality, creating a healthier habitat for other aquatic life. Honestly, without these little workers, we could see an accumulation of organic waste that could disrupt the balance of the ecosystem.
Pinworms also interact with microorganisms in aquatic systems. For instance, they can influence the populations of bacteria and other microbes, which play crucial roles in nutrient processing and cycling. This interaction helps maintain the overall health of the aquatic ecosystem, emphasizing the interconnectedness of life forms in even the smallest environments.
The Importance of Biodiversity
Pinworms are just one example of how small organisms contribute to biodiversity, which is vital for resilient ecosystems. Biodiversity refers to the variety of life in a particular habitat or ecosystem, and it’s important because it ensures stability and productivity. When pinworms coexist with other species, they help create a balanced environment where various life forms can thrive.
In terms of soil and aquatic ecosystems, a diverse range of organisms—from bacteria to larger animals—ensures that resources are utilized efficiently and waste is broken down adequately. The presence of pinworms, along with other small species, adds to this complexity, promoting health and resilience in ecosystems.
You might wonder, what happens when biodiversity is reduced or disrupted? Well, it can lead to degraded ecosystems, which might struggle to recover from disturbances. For instance, if we lose pinworms due to pollution or habitat destruction, we could see a ripple effect that impacts plant growth, water quality, and even larger species like fish that rely on a stable food web.
How Do Human Activities Impact Pinworms?
While pinworms play essential roles in ecosystems, human activities can significantly affect their populations. For instance, the use of pesticides in agriculture can harm not only harmful pests but also beneficial organisms like pinworms. These chemicals can disrupt their life cycles, leading to declines in their populations and, consequently, the services they provide.
Additionally, pollution can have lasting effects on both soil and aquatic ecosystems. Contaminants can alter the habitats where pinworms thrive, making it challenging for them to survive. This can lead to a decrease in their numbers and disrupt the overall ecosystem balance.
On the flip side, some human practices can support healthy pinworm populations and ecosystems. For example, sustainable farming techniques that minimize chemical inputs can enhance soil health, thereby supporting diverse soil organisms, including pinworms. It’s about finding that balance—recognizing how our actions can either help or harm these tiny contributors to ecosystem health.
Pinworms may be small, but their contributions to soil and aquatic ecosystems are substantial. By breaking down organic matter and cycling nutrients, they help maintain healthy environments for plants and animals alike. As we’ve seen, they play roles in aerating soil and supporting food webs in aquatic settings, underscoring their importance in maintaining ecological balance.
As we continue to explore the fascinating interactions in nature, let’s appreciate the little things—the unseen heroes like pinworms that impact our world in ways we might not have considered before. Protecting these organisms means embracing practices that support biodiversity and overall ecosystem health. After all, every creature, no matter how small, plays a part in the intricate dance of life.