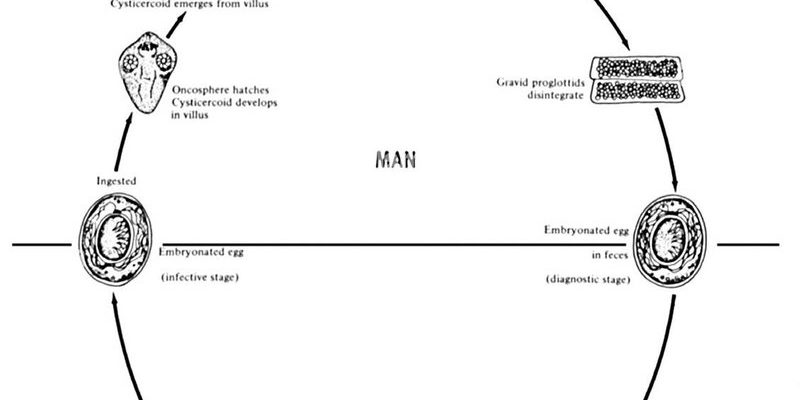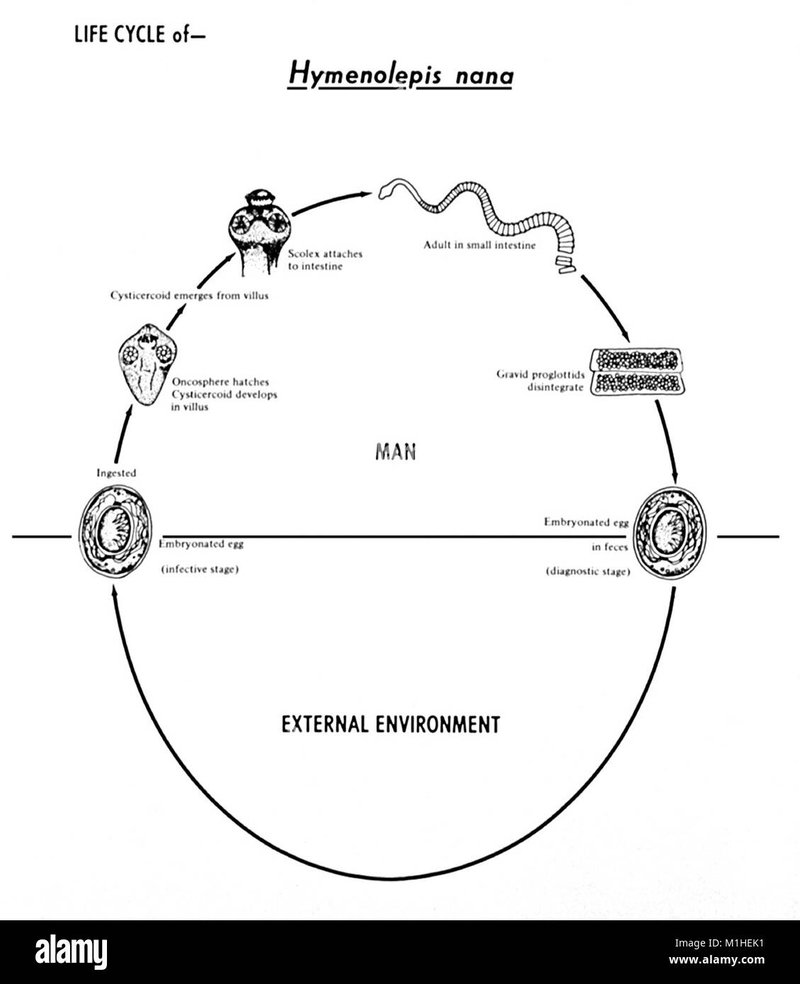
So, what exactly is a tapeworm? They’re flat, ribbon-like worms that can grow quite long, often measuring several feet. They have a unique biological structure that allows them to cling to the intestines of their hosts. The more we learn about the life cycle of these worms, the more we can appreciate the way life operates in unexpected ways.
Stage 1: Egg Stage
The journey of a tapeworm begins with its eggs. Picture these tiny, almost invisible specks, waiting to be swallowed by a host. Tapeworms reproduce by shedding thousands of eggs in the feces of an infected animal, which can include cats, dogs, or livestock. These eggs are incredibly resilient, capable of surviving in harsh environments until they find a suitable host.
Once in the right environment, whether in grass or water, the eggs get their chance to hatch. If an intermediate host, like a pig or a cow, ingests them, that’s when the tapeworm’s life really kicks off. This stage is critical because it ensures the continuation of the tapeworm species. Without this phase, the life cycle would come to a halt.
Stage 2: Larval Stage
After the eggs hatch inside the host, they don’t waste any time. They transform into larvae called *oncospheres*. Imagine these little larvae as tiny invaders, navigating through the host’s intestines. Once they find their way into the bloodstream, they can travel to various tissues, including muscles and organs.
Inside the host, the larvae develop into a cyst, a protective sac that helps them survive. This stage can last several weeks to months, depending on the type of tapeworm and its host. For example, the pig tapeworm can take several months to mature, while the beef tapeworm might take slightly longer. This is where they gain the strength and resources they need to survive for their next stage.
Stage 3: Adult Stage
Once the larvae have matured and are ready for their next chapter, they make their way back to the intestines. Here’s where the magic happens: they attach themselves to the intestinal wall using their scolex, or head. It’s like finding a cozy spot to settle in for a long stay. Adult tapeworms can live for many years inside their hosts, continuously feeding off the nutrients that pass through, which can lead to issues for the host if left untreated.
During this time, the tapeworm grows rapidly. Some species can reach lengths of up to 30 feet! Think of all the food they’re consuming. This stage is essential for their reproduction, as a mature tapeworm can produce thousands of eggs daily, starting the cycle all over again. If you’re wondering why it matters, consider this: the more tapeworms reproduce, the higher the risk of infection spreading to new hosts, including humans.
How Tapeworms Behave
Tapeworms have some intriguing behaviors that help them survive. For starters, they’re masters of disguise. They don’t have a digestive system like we do. Instead, they absorb nutrients directly through their skin. It’s a clever adaptation that saves energy and allows them to grow quickly. They also have the ability to regenerate. If a tapeworm loses part of its body, it can regrow it. Kind of like a superhero, don’t you think?
Interestingly, some tapeworms can change their behavior based on their environment. For example, if they sense they’re in a host that’s about to be eaten, they may release chemicals to manipulate the host’s behavior, increasing its chances of being eaten by the next big predator. This stage of manipulation is a fascinating aspect of their survival strategy.
Transmission to Humans
You might wonder how these little creatures make their way into the human body. Generally, humans get tapeworms through undercooked meat or contaminated water. If you’ve ever had a rare burger or sushi, you might have unknowingly invited a guest for dinner! It’s crucial to cook meat thoroughly to prevent infection.
Once inside, humans can experience a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to more severe issues like nutritional deficiencies. It’s particularly concerning in children, as their growth can be affected. So, it’s essential to take preventive measures, like practicing good hygiene and ensuring food is cooked properly.
Treatment and Prevention
If someone suspects they have a tapeworm, they shouldn’t fret. Treatment typically involves a prescription medication that helps clear the infection. These medications work by either killing the tapeworm or allowing it to detach from the intestines. Afterward, it gets expelled from the body naturally.
Preventing tapeworm infections mainly revolves around good hygiene practices. Here are some helpful tips:
- Always wash your hands before eating or preparing food.
- Cook meat thoroughly, especially pork and beef.
- Avoid drinking untreated water from lakes or streams.
- Keep your pets healthy, and deworm them regularly.
Taking these precautions can help decrease the risk of tapeworm infections significantly.
The life cycle of the tapeworm is a fascinating journey, from tiny eggs to a long, thriving parasite. Understanding this cycle not only enlightens us about these creatures but also highlights the importance of hygiene in our daily lives. By being aware of how tapeworms operate and practicing simple preventive measures, we can protect ourselves and our loved ones from these unwanted guests.
Next time you think about tapeworms, remember their complex life cycle and how they adapt to survive. It’s a wild world out there, even in the tiniest of creatures!