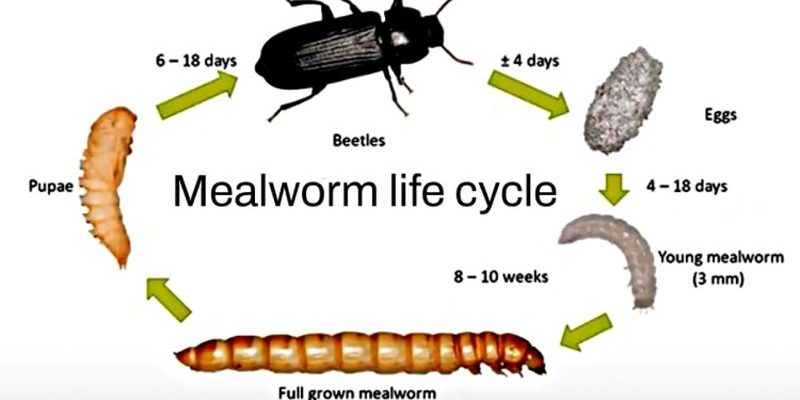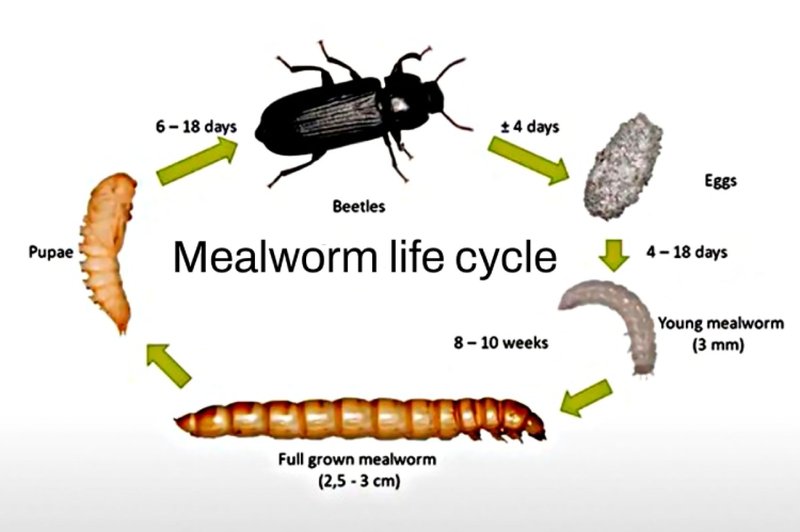
Mealworms are the larvae of darkling beetles (Tenebrio molitor), and they play big roles in composting and even as a sustainable food source. Let’s dive into the stages of their life and how they behave throughout this incredible journey. Buckle up for a fun ride through the world of mealworms!
1. The Egg Stage: A Tiny Beginning
The mealworm’s life starts from a tiny, almost invisible egg. Female darkling beetles lay these eggs in clusters, often in dark, moist environments like decaying leaves or grains. Each female can lay up to 500 eggs over her lifetime. Isn’t that something? Those little eggs look like tiny grains of sand, but inside, they’re packed with potential.
Once laid, the eggs take about a week to hatch, depending on the temperature and humidity. If conditions are just right, you can expect to see tiny mealworms emerging, ready to embark on their life journey. It’s like the moment a popcorn kernel pops—unexpected and exciting!
2. The Larval Stage: Growing Up Mealworm
After hatching, mealworms enter the larval stage, which is where they spend the majority of their life—around 10 weeks. During this time, they feast on organic materials, with a preference for grains, fruits, and veggies. It’s almost like they’re in an all-you-can-eat buffet!
Mealworms grow through a process called molting, shedding their skin multiple times as they grow. Each molt reveals a slightly larger worm, and they can grow up to about 2.5 inches long! This stage is crucial, as their diet and environment will significantly affect their health and development.
You might be wondering how you can spot a healthy mealworm. Look for a firm body, an active demeanor, and a bright yellow-brown color. If they’re sluggish or discolored, they might be struggling with their environment or diet.
3. The Pupal Stage: A Time of Transformation
Once they reach their full size, mealworms enter the pupal stage. This is a fascinating yet vulnerable time, as they’ll stop eating and become inactive, forming a hard casing around themselves. You might think of this as their version of a superhero’s transformation scene.
This pupal stage lasts about 1-3 weeks, depending on the conditions. Inside the pupal casing, mealworms undergo significant changes, almost like a caterpillar turning into a butterfly. They’re restructuring into their adult forms, and it’s all happening out of sight, which is kind of magical if you think about it.
While pupating, it’s essential to keep them in a safe, humid environment. Too much dryness or disturbance can lead to stress, and we want our little mealworms to thrive!
4. The Adult Stage: Becoming a Darkling Beetle
After the pupal stage, mealworms emerge as adult darkling beetles. Adult beetles are often black or dark brown and measure about 1⁄2 inch long. When you see them, you might be surprised by how different they look from the larvae. It’s like seeing a caterpillar become a butterfly!
Once they’re out of the pupal casing, these beetles will spend the rest of their lives exploring and mating. They can live for several months, consuming a variety of organic materials much like their larval stage. Adult darkling beetles are not just about survival; they also play a role in breaking down organic matter, contributing to the ecosystem.
It’s interesting to note that beetles are nocturnal creatures. They are most active at night, which adds another layer of mystery to their behavior. Watching them is like entering a world where tiny creatures lead their quiet lives under the moonlight.
5. Life Cycle Duration: Timing Matters
From egg to adult, the entire life cycle of a mealworm can take anywhere from 10 weeks to several months, depending on factors like temperature and food availability. Warmer temperatures generally speed up their development. Think of it like how you might speed up cooking when you’re feeling hungry.
If you’re interested in breeding mealworms, understanding their timing is key. Keeping them at a consistent temperature (around 70-80°F) will help you get a predictable life cycle, making it easier to manage their growth and reproduction.
Keeping track of these stages can be an engaging project, whether for educational purposes or as a sustainable food source. You’ll find that patience pays off, just like tending to a garden or waiting for cookies to bake.
6. Mealworms in Nature and Culture
Mealworms aren’t just interesting for their life cycle; they’ve also found a place in human culture and nature. In many countries, they’re considered a nutritious snack, packed with protein and healthy fats. It’s fascinating to think that what we sometimes view as pests can be a valuable food source elsewhere.
In addition to being a food source, mealworms play an ecological role by breaking down organic matter. This helps keep ecosystems healthy and can even assist with waste management. They fit right into the circle of life, breaking down what’s old to give way to new growth.
You might find mealworms in pet food and as feed for reptiles, birds, and fish. Their popularity is on the rise, making them a superstar in the world of sustainable living.
7. Caring for Mealworms: Best Practices
If you’re considering raising mealworms, you’ll want to know how to care for them properly. Here are some tips to keep your mealworms happy and healthy:
- Environment: Keep them in a dark, cool place with good ventilation.
- Food: Provide a balanced diet of grains, fruits, and vegetables. Oatmeal is a favorite!
- Moisture: Add a small piece of vegetable for moisture, but avoid over-wetting their environment.
- Space: Don’t overcrowd them. They need space to grow and move around.
By following these tips, you can help ensure a healthy life cycle and avoid common pitfalls. You’d be surprised how quickly they can multiply if they’re well cared for!
8. Conclusion: A Life Worth Learning About
Understanding the life cycle of the mealworm not only enriches our knowledge of these tiny creatures but also ties us to a larger environmental narrative. From egg to larva, then to pupa, and finally as beetles, mealworms teach us about resilience, transformation, and sustainability.
Next time you encounter mealworms—whether in nature, in your backyard, or at the grocery store—take a moment to think about their incredible journey. They play more vital roles in our ecosystems than we often realize, and caring for them can be a rewarding experience. Whether you’re considering breeding them for pet food or simply appreciating their contributions to the environment, mealworms deserve a spot in your curiosity roster. Happy exploring!