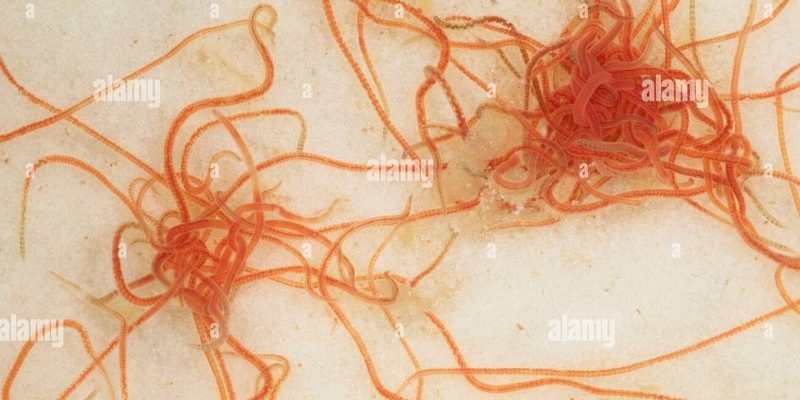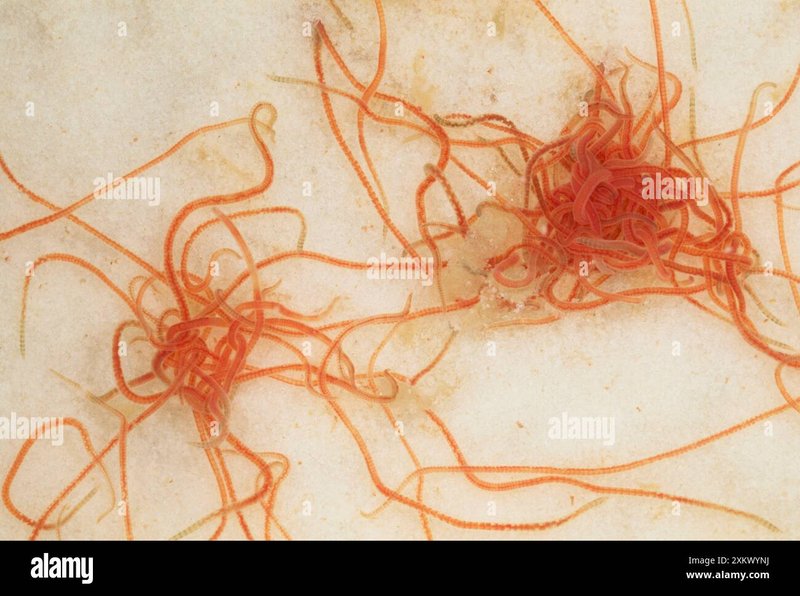
So, where do these little guys prefer to live? It’s all about the right conditions. Tubifex worms thrive in soft, nutrient-rich sediments where they can burrow and feed on organic material. Think of them as tiny gardeners of our water systems, aerating the soil and breaking down waste. In this article, we’ll explore their habitat preferences in detail, looking at their environmental needs, ideal living conditions, and how various factors influence where they choose to settle.
Understanding Tubifex Worms
Before we dive deeper, let’s talk a bit about what Tubifex worms actually are. These worms belong to the family of oligochaetes, which means they have a segmented body structure. They can grow to about 10 centimeters long and are usually red or pink. You might find them in places that others would avoid, like slow-moving waters or even sewage!
These worms are pretty remarkable. They can tolerate low oxygen levels, which makes them perfect for polluted environments. By consuming decaying plant material and microorganisms, they help clean up the ecosystem. So, when we talk about their habitat, we’re really exploring how they interact with their surroundings to thrive.
Preferred Environments
Tubifex worms are often found in the bottom sediments of freshwater bodies like lakes, rivers, and ponds. Here’s a breakdown of what they need:
- Soft Sediments: They prefer silty or muddy substrates that allow them to burrow easily.
- Nutrient-Rich Material: These worms thrive in areas rich in organic matter, as this is their primary food source.
- Low Flow Areas: They favor regions with slow-moving or still water to maintain their delicate bodies.
Think of these environments as a buffet for Tubifex worms, serving up all the nutrients they could ever want. That’s why you’ll often find them in areas where human activity can introduce organic waste, like near farms or wastewater treatment facilities.
The Role of Oxygen Levels
You might be wondering why the Tubifex worm can thrive in low-oxygen areas when many organisms can’t. Here’s the thing: Tubifex worms have adapted to survive in environments where oxygen isn’t abundant. They can absorb dissolved oxygen through their skin, allowing them to live in places where other creatures might suffocate.
This brings us to an interesting point about their habitat choices. In a typical freshwater ecosystem, oxygen levels are highest near the surface and decrease as you go deeper. Tubifex worms often make their homes in the sediment where oxygen levels are limited, but they still manage to flourish. This resilience makes them key indicators of environmental health, as their presence usually means there’s organic material for them to feed on.
Temperature and Turbidity Preferences
Another critical factor influencing the habitat of Tubifex worms is temperature. These worms generally prefer cooler waters, which are often rich in oxygen and nutrients. Being ectothermic, their activity levels and reproduction rates can significantly slow down in warmer temperatures, making them less successful in hotter environments.
In addition to temperature, turbidity—or how clear the water is—also plays a role. Tubifex worms do well in murky waters filled with organic material but don’t thrive where the water is too muddy. They need a balance that allows them to access food while still being able to move through their environment. If the water is too clear, they might miss out on the nutrients they rely on.
Human Impact and Habitat Disruption
The habitats of Tubifex worms can be greatly affected by human activities. Urban development, agricultural runoff, and pollution can change the water quality where these worms live. When sediment becomes contaminated or when nutrients from fertilizers enter the water, it can lead to algal blooms and lower oxygen levels, disrupting the delicate balance that these worms rely on.
Here’s the thing: when we disrupt their habitat, we don’t just hurt the Tubifex worms; we impact the entire ecosystem. Since they play an essential role in breaking down waste and improving sediment quality, a decline in their population can lead to larger problems for fish and other aquatic life. It serves as a reminder that every creature, no matter how small, has a role to play in our environment.
Conservation and Future of Tubifex Worms
Given their sensitivity to environmental changes, conservation efforts are crucial for the future of Tubifex worms and their habitats. Protecting waterways from pollution and maintaining healthy ecosystems can help ensure that these worms continue to thrive. Restoration projects focusing on improving water quality and sediment health can also benefit their populations.
Moreover, educational initiatives that teach about the importance of these worms can inspire people to take action. Understanding the role of Tubifex worms can make us more aware of the impact of our daily choices on the environment, from reducing plastic waste to supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
So, what have we learned about the habitat preferences of Tubifex worms? These creatures thrive in nutrient-rich, soft sediments of freshwater environments, showing remarkable resilience to low oxygen levels. They prefer cooler temperatures and can adapt to murkiness, making them unique members of the aquatic ecosystem.
Understanding their habitat helps us appreciate their role in maintaining the health of our waterways. By ensuring their survival, we contribute to a balanced environment that benefits all forms of life, including ourselves. If we take care of our rivers and lakes, we’re also taking care of the Tubifex worms that help keep them clean and vibrant.