Imagine your garden. Each plant, insect, and even worm plays a role in maintaining balance. Whipworms are similar; they interact with their hosts and the environment in ways that might not be immediately obvious. Some people might think they only harm their hosts, but it’s not so black and white. Let’s dive deeper into the ecological benefits and drawbacks of whipworm populations to get a clearer picture.
What Are Whipworms?
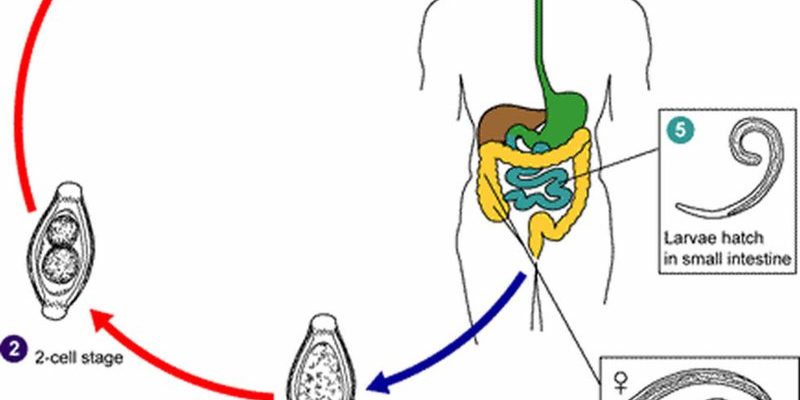
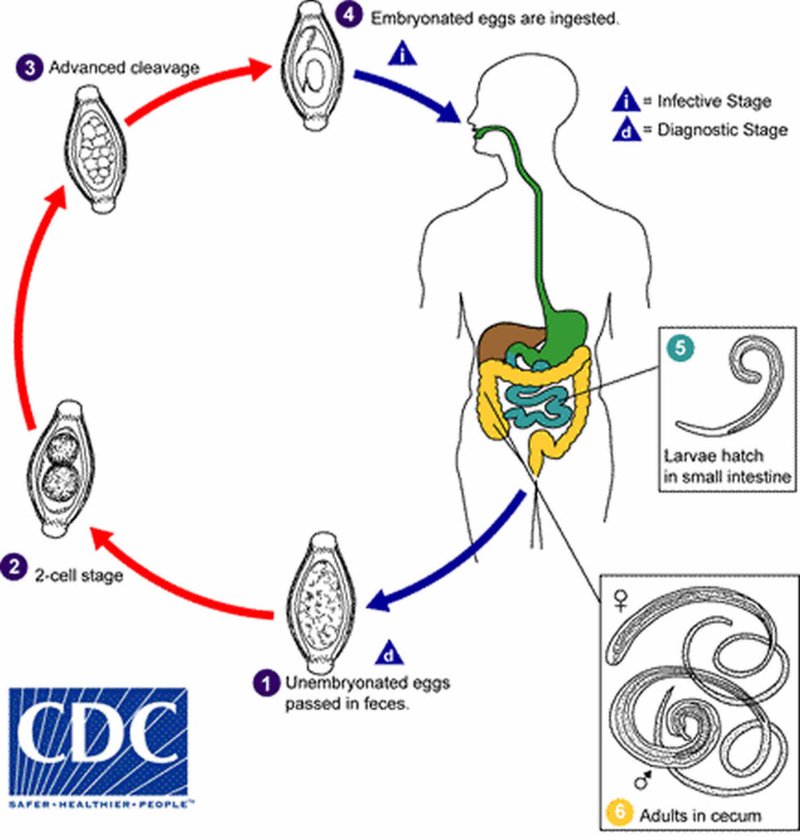
Whipworms are thin, whip-like parasites that primarily inhabit the intestines. They belong to the *Trichuris* genus and can vary in size and shape depending on their host. In humans, they can grow up to 5 centimeters long! It’s easy to forget that these tiny creatures play a significant role in their ecosystems. Whipworms are transmitted through contaminated soil or fecal matter, making sanitation a top priority in areas where they are prevalent.
You might be wondering, how do these parasites thrive? Once inside a host, whipworms anchor themselves to the intestinal wall, where they can live for years. They feed on nutrients from their host but can cause symptoms like abdominal pain and diarrhea if their numbers get too high. So, while they may be harmful, they also help control host populations and their immune responses.
Ecological Benefits of Whipworm Populations
One of the main benefits of whipworm populations is their role in maintaining the balance in ecosystems. They can help control host populations by limiting the numbers of certain animals in a given area. This can prevent overgrazing or overpopulation, which can lead to habitat degradation. When whipworms are present, they help ensure that hosts do not become too numerous, ultimately allowing for healthier ecosystems.
Another fascinating aspect of whipworms is their potential to influence immune responses. Research has shown that whipworms and other parasites can help train the immune system. This means that, in some cases, having whipworms can actually help reduce autoimmune diseases. It’s a little like giving your immune system a workout, helping it learn to distinguish between harmless substances and real threats.
In agricultural settings, whipworms can impact livestock health as well. By controlling parasite populations, they can create a more balanced ecosystem for farm animals. This can lead to healthier herds and flocks, which is essential for sustainable farming practices. So, while we often think of parasites as harmful, whipworms can actually help create a more robust agricultural system.
Role in Disease Regulation
Whipworms also play a role in regulating disease within their host populations. For example, by keeping certain species’ numbers in check, they can indirectly reduce the spread of disease among animals. When one species becomes too dominant, it can become a hotspot for pathogens. Whipworms help balance these populations, which can lead to healthier overall ecosystems.
The Drawbacks of Whipworm Populations
Despite their benefits, whipworms come with notable drawbacks. First and foremost, in high numbers, they can cause significant health issues for their hosts. In humans, whipworm infections can lead to malnutrition, anemia, and other gastrointestinal problems. This is particularly concerning in areas where access to clean water and sanitation is limited.
Another downside is that whipworm infections often go unnoticed until they cause noticeable symptoms. This can lead to complications, as people may not seek treatment promptly. In veterinary contexts, whipworm infections can also pose a risk to pets, especially when they are young or immunocompromised.
Whipworms can also affect ecosystems negatively if their populations grow unchecked. For instance, if whipworms severely reduce a host population, it can disrupt food chains and impact other species that rely on those hosts for nutrients. Consequently, while they can help with population control, they can also create imbalances if not kept in check.
Impact on Biodiversity
The presence of whipworms can influence biodiversity as well. If whipworms decimate a host population, it can lead to a decline in species diversity. When one species is overrepresented, it can alter the dynamics of an ecosystem, which may lead to a collapse of certain interactions and eliminate competition for resources. This impact can resonate throughout the food web, affecting everything from plants to top predators.
Controlling Whipworm Populations
So, how do we manage whipworm populations to enjoy their benefits while minimizing their drawbacks? The key often lies in maintaining proper hygiene and education about prevention methods. For humans, promoting handwashing and safe sanitation practices can significantly reduce the risk of whipworm infections.
For pet owners, regular veterinary check-ups can help monitor and treat whipworm infections in our furry friends. There are medications available that can effectively treat whipworm infestations, keeping pets healthy and happy. Additionally, understanding the lifecycle of whipworms can empower individuals and communities to take proactive measures.
In agriculture, practices like rotating pastures and maintaining clean living conditions for livestock can help control whipworm populations. By reducing potential breeding grounds for these parasites, farmers can keep their animals healthier without necessarily wiping out whipworms completely.
Community Education and Awareness
Building community awareness about whipworms and their potential impact is crucial. Educational programs that inform people about the life cycle of whipworms and safe hygiene practices can make a big difference. When people understand how whipworms transmit and how to mitigate their risks, it can lead to healthier communities and ecosystems.
Final Thoughts
Whipworms might seem like a pesky problem at first glance, but they have a complex role in our ecosystems. While they can cause various challenges for their hosts, they also help maintain balance and health within environments. Recognizing both the ecological benefits and drawbacks of whipworm populations allows us to appreciate their place in nature.
Understanding their role can help us manage them effectively, ensuring that their benefits outweigh their drawbacks. With proper hygiene and awareness, we can live in harmony with these tiny worms, turning potential problems into a chance for growth and understanding in our ecosystems. Isn’t it amazing how such small creatures can impact our lives and the world around us?