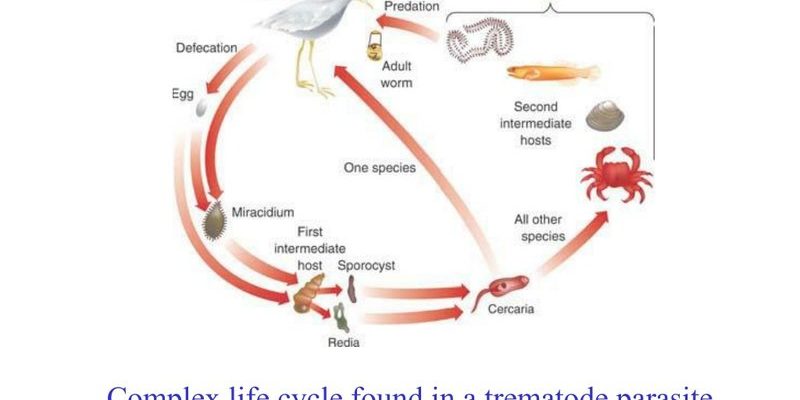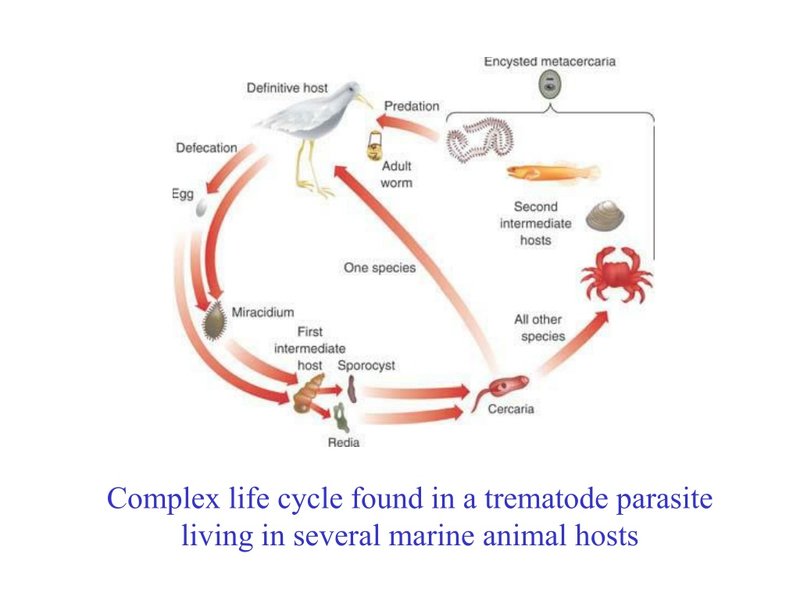
Trematodes, also known as flukes, have life cycles that often depend on multiple hosts, including snails and fish. This makes them fascinating but also a bit perplexing. Imagine a relay race where each member plays a vital role in completing the circuit. That’s how trematodes operate in their ecosystems. While they can be harmful to certain species, they also contribute to the balance of food webs and nutrient cycles. Ready to better understand these miniature organisms? Let’s unpack the ecological implications of trematodes together!
Understanding Trematode Populations
Before we dive deep into the benefits and drawbacks, it’s essential to understand what trematodes are. These are flatworms belonging to the class Trematoda, and they often have complex life cycles that include different stages and hosts. Typically, they begin life as eggs, hatch into larvae, and then move onto snails or other invertebrates before making their way into vertebrates, like fish or mammals.
Trematodes can be found in a variety of habitats, mostly in freshwater environments like lakes and rivers, but they can also inhabit saltwater and even terrestrial ecosystems. Their ability to adapt to various hosts and environments allows them to thrive in different ecological niches. Honestly, they’re like the ultimate survivors in the animal kingdom.
One striking feature of trematodes is their highly specialized mouthparts, allowing them to attach to their hosts with precision. This anatomical adaptation is crucial for their survival, as it helps them absorb nutrients and evade the host’s immune system. But while they’re busy making a living, what are the broader ecological impacts? This is where things get interesting.
Ecological Benefits of Trematodes
You might be wondering how a parasite can actually contribute positively to an ecosystem. Here’s the thing: trematodes play essential roles in maintaining biodiversity and energy flow. They fulfill several ecological functions that are vital to the health of ecosystems.
- Regulating Host Populations: Trematodes can help control the populations of their host species, particularly in aquatic environments. By parasitizing certain species, they help prevent overpopulation, which can lead to resource depletion.
- Nutrient Cycling: Trematodes contribute to nutrient cycling in aquatic systems. When they infect their hosts, valuable nutrients are released back into the ecosystem when the host dies or excretes waste, helping to nourish other organisms.
- Food Web Dynamics: They are an integral part of food webs. Many organisms, from snails to larger fish, rely on trematodes as part of their diet. By hosting trematodes, these organisms serve as a food source for others, helping maintain the balance of the ecosystem.
These benefits illustrate how trematodes are more than just parasites. They can be seen as vital players in keeping ecosystems balanced, getting rid of excess host populations, and supporting food webs. It’s a classic case of nature’s complexity, showing that even organisms with a bad reputation can be essential for ecological health.
Drawbacks of Trematode Populations
On the flip side, trematodes also come with their share of drawbacks. Just like that well-meaning roommate who forgets to pay bills, trematodes can cause trouble if their populations become too high or if they invade sensitive species.
- Impact on Host Health: Trematodes can cause significant harm to their hosts. For instance, heavy infestations can lead to malnutrition or even death in fish and amphibians. This can disrupt local populations, particularly if the host in question is a keystone species.
- Decline in Biodiversity: In some cases, trematodes can contribute to the decline of certain species, particularly in vulnerable ecosystems. If a native species is heavily infested, it might struggle to compete with non-native species, leading to shifts in community structure.
- Transmission of Diseases: Trematodes can act as vectors for diseases in wildlife and even humans. Some studies have linked specific trematodes to increased disease susceptibility in their hosts, raising concerns for public health and environmental management efforts.
These drawbacks highlight the potential consequences of unchecked trematode populations. It’s a delicate balance; while they can have ecological benefits, too many trematodes can disrupt the health of their ecosystems and the organisms that inhabit them.
Case Studies of Trematodes in Various Ecosystems
To really see the effects of trematodes in action, let’s look at a few case studies from different ecosystems. These examples illustrate both the benefits and drawbacks we’ve discussed.
In the Great Lakes, for instance, trematodes have been studied for their role in controlling invasive species. Researchers found that certain trematodes infect invasive fish species, helping reduce their populations. This, in turn, creates space for native fish to thrive. Here, trematodes demonstrate their potential as natural biocontrol agents.
On the other hand, in tropical regions, researchers studied the impacts of trematode infections on amphibians. They found that high levels of infection led to deformities, such as extra limbs, and even mortality in some populations. This highlights how trematodes can have adverse effects, especially in species that are already under environmental stress.
These real-world examples show how trematodes are not simply good or bad—they’re part of the complex web of interactions that shapes ecosystems.
The Role of Climate Change on Trematode Populations
Now, let’s talk about the big picture: climate change. It’s having profound effects on ecosystems globally, and trematode populations are no exception. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and habitat loss can alter how trematodes interact with their hosts and environments.
For starters, warmer water temperatures can speed up the life cycle of trematodes, potentially leading to explosive population growth. In already stressed ecosystems, this could exacerbate the negative impacts on host species, particularly in places like coral reefs or freshwater environments where organisms are already vulnerable.
Moreover, climate change affects the distribution of host species. As some species move to new areas in response to changing conditions, trematodes may follow suit, potentially invading new ecosystems. This could lead to novel interactions and impacts, sometimes with unpredictable outcomes.
Understanding how climate change affects trematodes is essential for managing ecosystems. It calls for strategies that consider these interactions to maintain biodiversity and protect sensitive species.
Management Strategies for Trematode Populations
So, what can be done about the ecological impacts of trematodes? Effective management strategies require a balanced approach that considers both their benefits and drawbacks.
- Monitoring Populations: Regular monitoring of trematode populations can help identify imbalances before they lead to larger ecological issues. This could involve sampling water and host organisms in critical habitats.
- Habitat Restoration: Restoring habitats can strengthen native species and increase their resilience against trematode infestations. Healthy ecosystems are better equipped to handle the ups and downs of parasite populations.
- Research and Education: Investing in research helps us understand the complexities of trematode-host interactions. Educating local communities about the ecological roles of these organisms fosters an appreciation for biodiversity and encourages protective actions.
These management strategies underscore the importance of thoughtful approaches to ecological health. Just like how we might take care of a shared living space, maintaining a balance within ecosystems ensures that all organisms, including trematodes, can coexist.
The Future of Trematode Research and Ecological Understanding
As we continue to learn about trematodes, their ecological roles will become clearer. Emerging technologies, like environmental DNA (eDNA) sampling, give researchers new tools for studying these organisms and their interactions.
Here’s the thing: understanding trematodes isn’t just an academic exercise; it has real implications for biodiversity conservation and ecosystem management. As ecosystems face the pressures of human activity and climate change, the knowledge we gain about trematodes can help us make informed decisions that benefit both wildlife and humans.
In the end, trematodes remind us that nature is incredibly intricate. They exist at the intersection of life and death, contributing to the balance of ecosystems in ways that aren’t always easy to see.
As we continue to explore the ecological impacts of these fascinating creatures, we’ll be better equipped to appreciate their roles and ensure the health of our ecosystems for generations to come. By integrating this knowledge into environmental strategies, we can help create a sustainable future for all species, including the humble trematode.