Now, tapeworms belong to a large group of flatworms known as Cestoda, and they can be found in a variety of animals, including humans. They’re not just hanging out in your backyard; they thrive in diverse environments around the world. Understanding where these creatures are found is crucial, not only for scientists but also for anyone interested in health and wildlife. After all, knowing where they thrive helps us understand how to avoid them and keep ourselves safe. So, pour yourself a cup of coffee and let’s explore the extensive territories that tapeworms claim as their own.
What Are Tapeworms? Understanding Their Biology
First things first, let’s cover the basics. Tapeworms are flat, segmented worms that can grow remarkably long—some up to 30 feet or more! They attach themselves to the intestines of their hosts using tiny hooks and suckers. This is kind of like having a roommate who occupies your fridge and eats all your food without contributing anything in return.
Tapeworms have a unique life cycle. They start as eggs, which are often found in contaminated food or water. When ingested by a host, the eggs hatch into larvae, which then attach to the intestinal wall. Over time, they grow and reproduce, releasing more eggs that exit the host’s body in their feces. This cycle continues, making tapeworms incredibly resilient.
These worms can infect a variety of hosts, ranging from humans and pets to wild animals. They often target animals that graze or scavenge, as these creatures will unknowingly consume tapeworm eggs or larvae. This adaptability is part of why tapeworms can be found in so many different regions.
Global Distribution of Tapeworms: Where Are They Found?
Tapeworms have a wide distribution, found in almost every part of the world. Their presence primarily depends on the environment and the availability of suitable hosts. Here’s a breakdown of where they like to call home:
- Tropical and Subtropical Regions: Many species thrive in warm climates. Countries in Africa, Asia, and South America often report higher instances of tapeworm infections due to conditions that facilitate their lifecycle.
- Temperate Regions: In places like Europe and North America, tapeworms are also common, particularly in rural areas where livestock are raised. Here, animals like cattle and pigs act as hosts.
- Urban Areas: Surprisingly, urban settings can have tapeworms too, especially where sanitation is poor. Contaminated food and water sources can lead to infections among humans.
You might be wondering how tapeworms manage to spread so efficiently. One of the key factors is their ability to survive in diverse environments. Whether it’s a farm in the countryside or a bustling city market, if conditions are right, they can flourish.
Types of Tapeworms: A Closer Look
There are over a thousand species of tapeworms, each with its own unique characteristics. The types most commonly discussed include:
- Taenia saginata: Commonly known as the beef tapeworm, it usually infects cattle and can be transmitted to humans through undercooked beef.
- Taenia solium: This is the pork tapeworm, which is transmitted through undercooked pork. It’s particularly concerning because it can also cause cysticercosis, a serious condition that affects the brain.
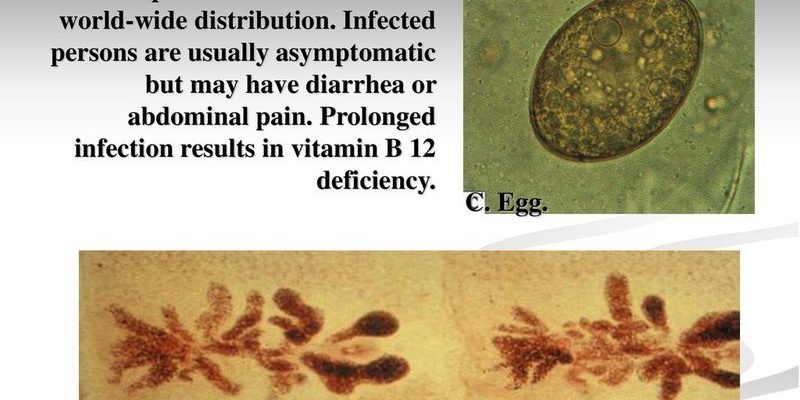
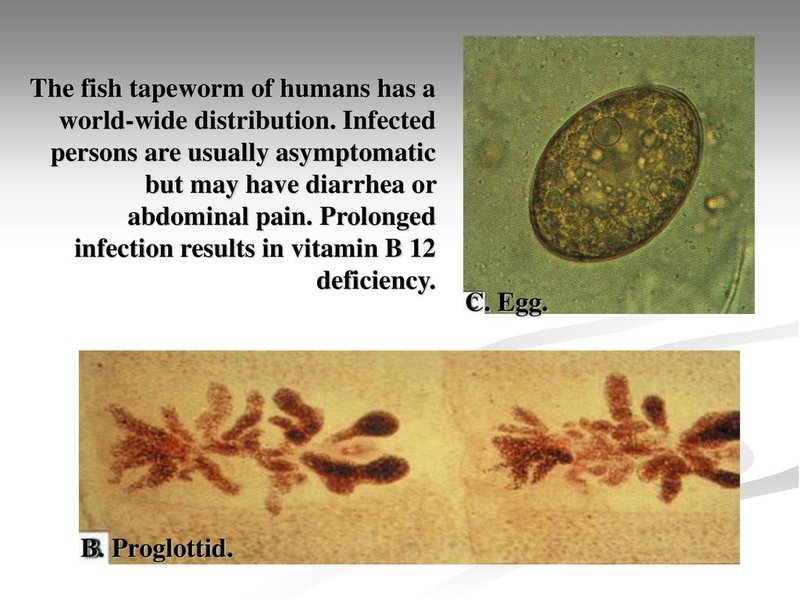
- Diphylobothrium latum: Known as the fish tapeworm, it primarily comes from eating raw or undercooked fish.
Each species has its own preferred hosts and habitats, making their distribution even more diverse. For instance, farm animals are prime candidates for certain tapeworms, while others may find their home in wild creatures. Understanding these variations helps scientists track outbreaks and develop preventive measures.
The Impact of Tapeworms on Host Populations
Tapeworms can significantly affect the health of their hosts, often leading to malnutrition and other complications. Here’s how they impact different populations:
1. In Humans: The presence of a tapeworm can lead to digestive issues. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, nausea, and weight loss. In severe cases, they can lead to vitamin deficiencies and more serious health problems.
2. In Animals: Livestock infected with tapeworms may show reduced growth rates and poor overall condition. This can affect farmers economically, as underperforming livestock can lead to losses.
3. In Wildlife: Wild animals can also be impacted, especially those that are already facing stress from environmental changes. An increase in tapeworm populations can further weaken their health and reduce their reproductive success.
Recognizing the influence of tapeworms on various populations is crucial for public health efforts and wildlife conservation strategies. It’s a reminder that these tiny parasites can have big consequences.
Prevention and Control of Tapeworm Infections
Preventing tapeworm infections is vital for both humans and animals. Here are some effective strategies to keep in mind:
- Cook Food Thoroughly: Always cook meat, especially pork and beef, to safe temperatures. This can kill tapeworm larvae and eggs.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands regularly, especially after handling raw meat or using the bathroom.
- Control Livestock Infections: Farmers should monitor their animals for signs of tapeworms and use veterinary services to manage infections.
These practices don’t just benefit individual health—they also help prevent the spread of infections within communities and populations.
Research and Future Directions
As we learn more about tapeworms, scientists are focusing on understanding their biology and lifecycle in greater detail. New research aims at developing more effective treatments and preventive measures.
One interesting area of study is the use of technology to track tapeworm distribution better. Researchers can use GPS tracking and genetic analysis to understand how these parasites spread and evolve over time.
Another important direction is raising awareness about tapeworms and their impact on public health. Campaigns to educate people, especially in high-risk areas, can greatly reduce the rates of infection.
Tapeworms are more than just creepy parasites; they play a complex role in ecosystems and human health. Their wide range and distribution underline the intricate connections between hosts, environments, and health outcomes. By understanding where tapeworms live and how they affect different populations, we can take meaningful steps to prevent infections and protect ourselves and our pets.
Next time you think about what’s on your plate or your furry friend’s dinner bowl, remember that being mindful about food safety is key to keeping those unwanted guests at bay!