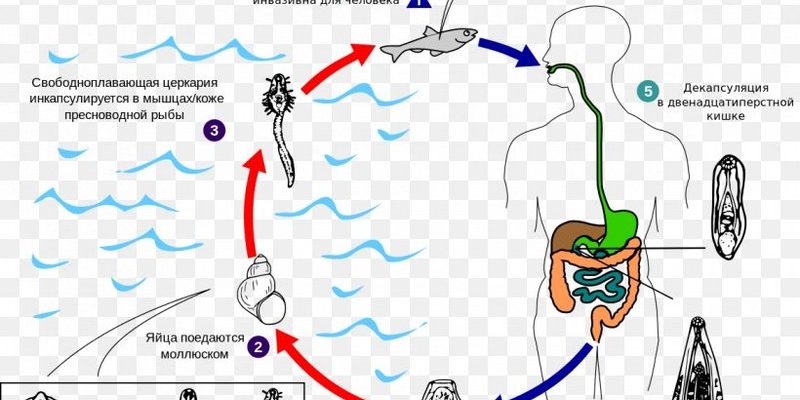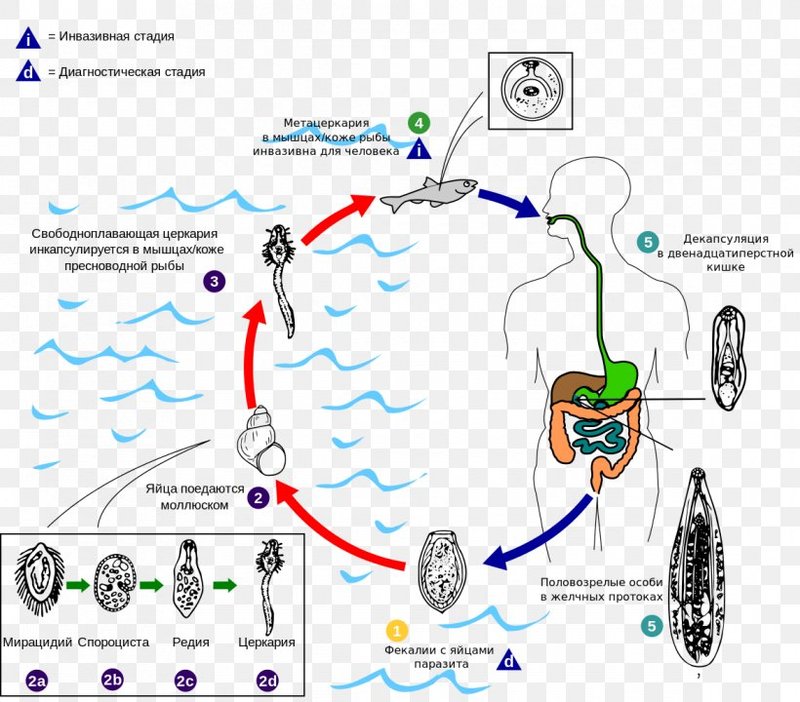
Liver flukes belong to the class Trematoda and can cause a range of health issues. They thrive in the livers of their hosts, which include livestock and wild animals, not to mention humans in some regions. Knowing where these flukes are found can help us understand their impact on health and agriculture. So, grab a cup of coffee, and let’s explore this topic together!
What Are Liver Flukes?
To start, it helps to understand what liver flukes actually are. These are flat, leaf-shaped worms that belong to the trematode family. They’re not just a single species; instead, a few different types exist, such as *Fasciola hepatica* and *Fasciola gigantica*. You might think of them as the uninvited guests at a party—wherever there’s a suitable host, these flukes are likely to show up.
Their life cycle is pretty complex, involving several stages and hosts. They usually begin their life in freshwater, where they infect snails. From there, they make their way to grazing animals or even humans, where they can cause all sorts of trouble.
Life Cycle of Liver Flukes
The journey of a liver fluke is nothing short of adventurous. Here’s how it typically goes:
- The adult fluke lays eggs in the liver of the host.
- The eggs are excreted in the host’s feces, often into water.
- In water, the eggs hatch into larvae, which then infect snails.
- Inside the snail, they develop into another stage and eventually leave the snail seeking out their next host.
- The flukes can then infect grazing animals, completing their life cycle.
Understanding this life cycle is key, especially for farmers and health officials, as it helps pinpoint how these flukes spread and infect hosts.
Global Distribution of Liver Flukes
Now that we have a grasp on what liver flukes are, let’s take a closer look at their global distribution. You might be surprised to learn that these parasites aren’t just lurking around in your backyard. They have a documented range across continents, affecting many ecosystems and livestock.
Liver flukes tend to thrive in tropical and subtropical regions, where conditions are perfect for their life cycle. They have been reported in various parts of Africa, Asia, and even Europe. In fact, one of the most prevalent species, *Fasciola hepatica*, is a significant concern in areas with high livestock farming.
Regions Most Affected
Some specific areas of concern include:
- Africa: Countries like Nigeria and Egypt see high rates of infection in both livestock and humans.
- Asia: Areas like China and Thailand have been noted for their prevalence of liver flukes, particularly in rice paddies where snails thrive.
- Europe: Parts of the UK and Ireland often report cases, especially where sheep and cattle farming is common.
These regions are not just affected by the flukes themselves; the economic costs can stack up due to decreased livestock productivity and increased healthcare costs.
Health Implications of Liver Fluke Infections
You might be wondering, why does this matter? Well, liver fluke infections can lead to serious health issues. For animals, they can cause liver damage, leading to a condition known as fascioliasis. In humans, symptoms can vary from mild abdominal pain to severe liver issues.
Honestly, it’s like the liver fluke throws a party inside the host’s body, but nobody enjoys it. The liver, which is supposed to work efficiently, gets disrupted. In severe cases, untreated infections can lead to liver failure, which is no joking matter.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
For both animals and humans, identifying an infection can be tricky. Common symptoms might include:
- Abdominal discomfort
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Jaundice due to liver damage
Diagnosis usually involves checking for fluke eggs in feces or conducting blood tests. If you’re a farmer or someone living in an area where liver flukes are common, paying attention to these signs is crucial.
Preventative Measures and Treatments
Now that you know about the risks associated with liver flukes, let’s talk about how to prevent and treat infections. Prevention is always better than cure, right?
For livestock, proper grazing management is key. Keeping animals away from stagnant water where snails breed can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
Treatment Options
If infections do occur, treatments vary depending on the species of fluke involved. Some common anti-parasitic medications include:
- Triclabendazole: Particularly effective against *Fasciola hepatica*.
- Praziquantel: Used for treating different kinds of flukes.
Always consult a veterinarian for livestock or a healthcare provider for human cases, as they can provide tailored treatment plans.
Research and Future Directions
Researchers continue to study liver flukes to better understand their biology and develop effective prevention strategies. Understanding their specific adaptations helps in crafting targeted methods to control their spread.
You might be wondering what politicians or health organizations are doing about it. In many countries, initiatives are being set up to educate farmers and the public about risks, ways to prevent infections, and appropriate treatments.
Community Involvement
It’s also vital for communities to work together. Sharing knowledge and resources can help mitigate the effects of liver fluke infections, as healthcare professionals and farmers can collaborate on best practices.
Liver flukes may not be the most glamorous topic, but understanding their range and distribution is essential for public health and agriculture. These tiny, flat worms can have a significant impact on both livestock and human health worldwide. By knowing where they thrive and the risks they pose, we can better protect ourselves and our communities from their effects.
Whether you’re a farmer, a healthcare provider, or just a curious reader, staying informed about liver flukes can help us all take action. So next time you hear about a parasite, remember the liver fluke’s adventurous life and the importance of keeping an eye on these uninvited guests!