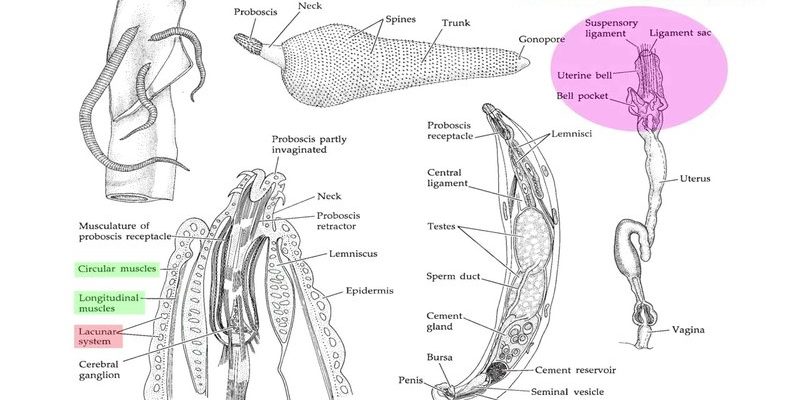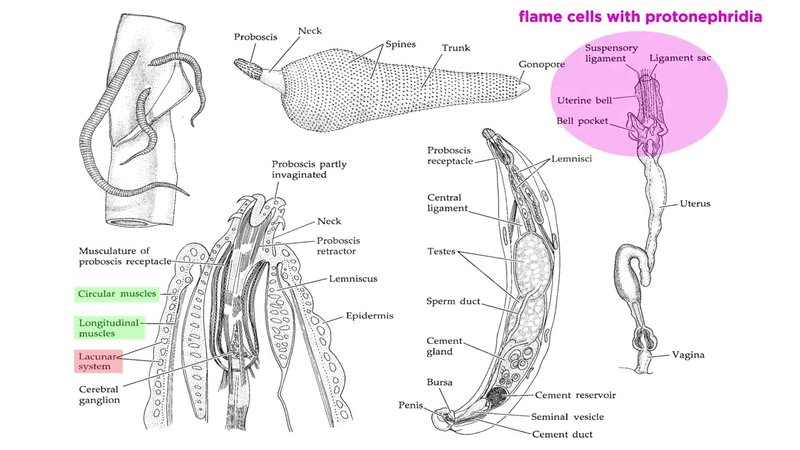
Acanthocephala are unique parasites that inhabit the intestines of various animals, including fish, birds, and mammals. They have this remarkable ability to attach themselves to the host’s gut with spiny proboscises, which is a fancy term for their hook-like appendages. Imagine a tiny, spiky umbrella that anchors itself in place while the rest of its body dangles in the host’s digestive tract! This article dives into their range and distribution worldwide, helping you understand where these quirky critters can be found.
What Are Acanthocephala?
Before we explore their distribution, let’s break down what Acanthocephala really are. These worms are not your typical parasites. They belong to a class of their own, thanks to their distinctive characteristics. Unlike many parasites, Acanthocephala have a complex life cycle that involves at least two hosts. They typically begin their lives in the body of an intermediate host, such as an insect or crustacean.
Once they mature, they will try to find a definitive host, usually a vertebrate like a fish, bird, or mammal. You might wonder why they do this. Well, the definitive host provides the perfect environment for the worms to thrive and reproduce. It’s like an all-you-can-eat buffet for Acanthocephala! Their life cycle can be divided into several phases, including egg, larval, and adult stages, each with its own set of challenges and adaptations.
Now, you might be thinking, “Do they cause harm to their hosts?” Yes, they can! While some hosts may be able to tolerate Acanthocephala, others can suffer from malnutrition or even death if the infestation is severe. This intricate relationship between Acanthocephala and their hosts is a testament to the wonders of nature, but it also highlights their role in the ecosystem.
Where Are Acanthocephala Found?
Now that we have a basic understanding of Acanthocephala, let’s take a look at their geographical distribution. These creatures can be found all over the world, but their habitats vary widely depending on the species. Generally, you can find them in freshwater, marine, and even terrestrial environments.
In freshwater ecosystems, Acanthocephala often inhabit fish and amphibians. For instance, species like *Pomphorhynchus laevis* thrive in European rivers, while others may be well-adapted to North American species. Marine habitats include everything from warm tropical waters to the icy depths of the Arctic. They’ve found their niche in many ocean-dwelling fish, making them quite versatile.
On land, Acanthocephala can be found in mammals, especially those that consume aquatic or semi-aquatic creatures. For example, wild or domestic pigs can harbor these parasites if they consume infected insects. So, to sum it up, you could find these spiny-headed worms nearly everywhere, adapting to survive in the strange environments they inhabit.
Life Cycle and Host Interaction
Understanding the life cycle of Acanthocephala is key to grasping their distribution and impact on ecosystems. As I mentioned before, they require at least two hosts to complete their life cycle. The journey begins when adult Acanthocephala live in the intestines of a definitive host, where they produce eggs. These eggs are excreted in the host’s feces into the environment.
Once in the environment, the eggs hatch into larvae inside an intermediate host, typically an arthropod like a beetle or a crustacean. The larvae will develop further until they’re ready to infect a definitive host. This is where things get really interesting! Acanthocephala are known to manipulate their intermediate hosts’ behavior, making them more likely to be consumed by their definitive hosts. It’s as if they’re pulling strings behind the scenes to ensure their survival.
Once in the definitive host, the cycle continues, and the adult worms can live for several years. This lengthy life cycle allows Acanthocephala to establish significant populations in their hosts, leading to various effects on the host’s health. Some species can even induce changes in their hosts’ feeding behavior, making them more vulnerable to predation. Honestly, it’s a fascinating yet slightly eerie play of nature.
Documented Distribution Patterns
Researchers have conducted numerous studies to map out the distribution of Acanthocephala, and the findings are intriguing. For instance, many species are more commonly found in tropical regions, while others thrive in temperate zones. This distribution is often influenced by factors like water temperature, salinity, and the availability of suitable hosts.
One fascinating aspect is how changes in climate can affect their range. As temperatures rise and habitats shift due to climate change, we may see Acanthocephala expanding into new areas. This could have significant implications for local ecosystems, potentially disrupting food webs and host populations.
In some regions, public health monitoring has also documented the presence of Acanthocephala. Studies have shown how they can affect both wild and farmed animals, causing economic impacts on fisheries and agriculture. Understanding their distribution patterns helps scientists and conservationists predict how these unique parasites might spread and interact with other species.
Impact on Ecosystems and Hosts
The presence of Acanthocephala in various ecosystems brings both challenges and benefits. On one hand, these parasites can significantly impact their hosts, leading to reduced fitness, weight loss, and even death. When fish or birds get infested, their populations can decline, altering the balance of local ecosystems. This is especially concerning for species that are already vulnerable or endangered.
On the flip side, Acanthocephala play a role in regulating host populations. By naturally culling less fit individuals, they can contribute to the overall health of the ecosystem. It’s like a natural selection process—one that’s sometimes harsh, but necessary for maintaining balance.
In addition, studying Acanthocephala can shed light on broader ecological dynamics. They are often used as indicators of environmental health because changes in their populations can reflect shifts in their habitats. This makes them invaluable for researchers looking to understand the impacts of pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change.
Research and Conservation Efforts
With their intriguing yet complex nature, it’s no surprise that Acanthocephala have become a focus of scientific research. Researchers are exploring how these parasites interact with their hosts and how their presence can inform us about ecosystem health. New technologies, such as genetic analysis, are helping scientists identify and classify Acanthocephala species more accurately, leading to better management strategies.
Conservation efforts are also underway to protect both hosts and Acanthocephala. By ensuring the health of ecosystems—like maintaining clean water sources and preserving habitats—we can help balance the presence of these parasites. Healthy ecosystems tend to support healthy populations of both hosts and their parasites, keeping nature in harmony.
Additionally, awareness campaigns aim to educate stakeholders, such as fishery operators and conservationists, about the implications of Acanthocephala. This education can lead to more sustainable practices that benefit both local economies and biodiversity.
Acanthocephala might not be the first creatures that come to mind when you think of wildlife, but they’re an essential part of our planet’s ecosystems. Their documented range and distribution highlight the complexity of life on Earth and the interconnectedness of all living things.
As we learn more about these spiny-headed worms, we uncover valuable insights into how nature operates at every level. From their intricate life cycles to their impacts on host and ecosystem health, Acanthocephala are a reminder that even the smallest creatures can play a significant role in our world.
So, the next time you hear about parasites, remember Acanthocephala. They may be small and often overlooked, but they certainly have a big story to tell. Understanding their role helps us appreciate the delicate balance of life, reminding us that even the tiniest players can make waves in the ecosystem.