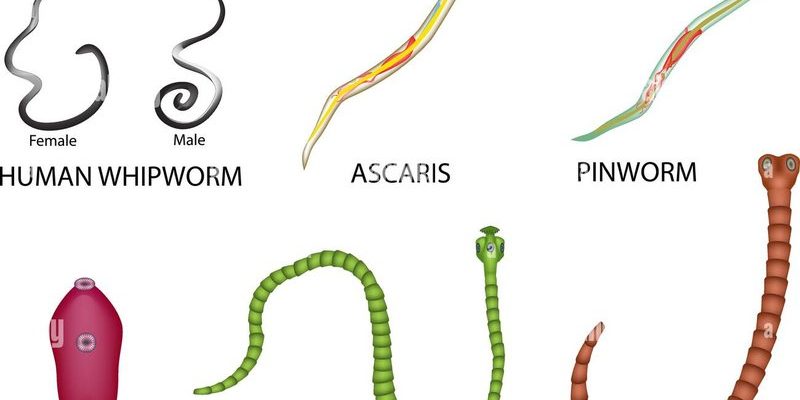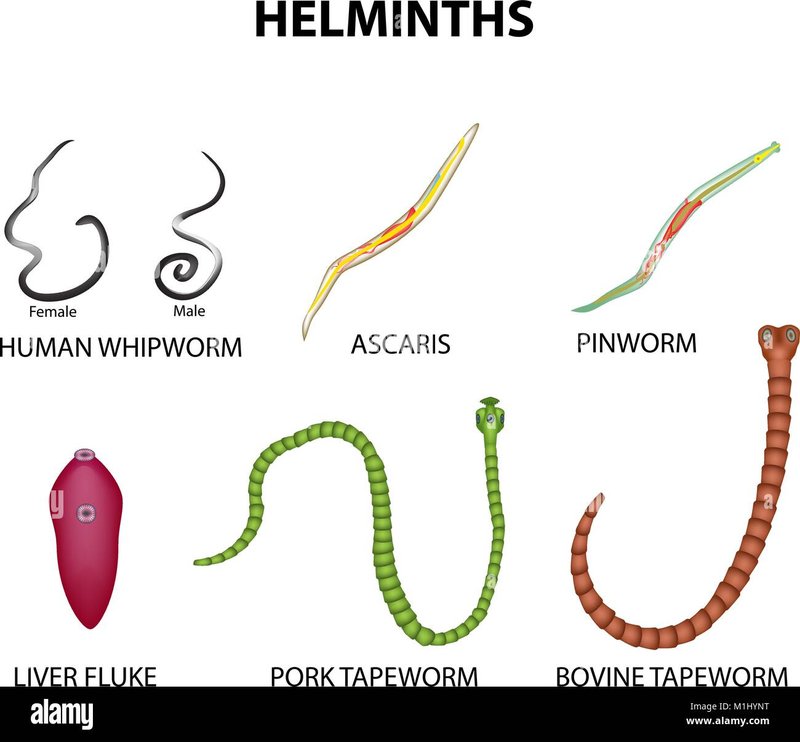
Whipworms, particularly the species *Trichuris trichiura*, are often found in the same places as other similar worms. Think of them like roommates sharing a cozy apartment—each with its quirks and habits but all coexisting in the same environment. In this article, we’ll explore whipworms and compare them to a few of their wormy counterparts. By the end, you’ll have a good grasp of what makes whipworms tick and how they differ from others in the crowd.
What Are Whipworms?
Whipworms are fascinating little critters that primarily reside in the intestines of their hosts. They can be found in a variety of animals but are best known for their role in human infections, often linked to poor sanitation. Picture them as the uninvited guests who set up camp in your gut, causing discomfort and a range of gastrointestinal issues.
These worms thrive in warm, humid areas, particularly where hygiene practices are lacking. After all, whipworms have a life cycle that begins with their eggs being passed out in the feces of the infected host. Once the eggs land in suitable soil, they hatch and look for new hosts—essentially waiting for their big break.
Whipworms are named for their whip-like appearance, which is quite distinctive compared to other worms. They have a thin, long anterior part and a thicker posterior part, making them look like a twisted piece of spaghetti. This shape helps them anchor themselves in the intestinal lining, where they can feed and reproduce.
How Do Whipworms Compare to Roundworms?
If you’ve heard of roundworms, you’re looking at one of whipworm’s closest relatives. Roundworms, or *Ascaris lumbricoides*, are often larger and can grow up to 35 cm long, whereas whipworms usually max out at around 5 cm. Think of them as the heavyweight champion versus the featherweight contender in the worm world.
Both types of worms share similar habitats, often residing in the intestines of their hosts. However, their effects on the host can vary significantly. Roundworms can cause a variety of health issues, including malnutrition and intestinal blockages. In contrast, whipworms tend to cause less severe symptoms, although chronic infections can lead to significant health problems.
Interestingly, while whipworms are more specialized in their habitat, roundworms are able to survive in a broader range of environments. Roundworms can also infect different types of animals, whereas whipworms have a more narrow host preference. It’s like comparing a specialized chef who only cooks one cuisine to a jack-of-all-trades who can whip up dishes from around the world.
Tapeworms: A Different Kind of Intestinal Invader
Now let’s introduce tapeworms into the mix. These guys are quite different from whipworms both in shape and lifestyle. Tapeworms, like *Taenia saginata*, can grow quite large, sometimes reaching lengths of several meters! Imagine a snake that’s made your intestines its new home—that’s a tapeworm for you.
Unlike whipworms that attach themselves to the edge of the intestinal wall, tapeworms hang out in the gut and absorb nutrients directly through their skin. This method of feeding means they don’t even need a mouth—pretty wild, right? Tapeworm infections can often be asymptomatic, meaning you might not even know you have one, while whipworm infections are typically more symptomatic.
Both these types of worms are spread through contaminated food or water, but their life cycles and impacts on health differ significantly. While both can cause issues, tapeworms are usually a bit more discreet with their effects.
Roundworm vs. Whipworm: Symptoms and Diagnosis
When it comes to symptoms, whipworms and roundworms can often confuse us. Both can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, but their presentations can differ. Whipworm infections might cause symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, or even more severe issues like rectal prolapse in children.
Roundworm infections can present with additional symptoms, such as a cough or fever, mainly because they can migrate outside the intestines to other parts of the body. This journey can lead to more widespread issues, especially if they end up in the lungs or bloodstream.
Diagnosing these infections typically involves stool tests. Doctors can look for the eggs of the respective worms, helping determine which worm is causing your troubles. It’s important to see a healthcare professional if you suspect you have a worm infection, as treatments vary based on the specific type of worm in question.
Prevention: Keeping Worms at Bay
So, how do you keep these pesky worms away? Prevention is your best bet, and it starts with hygiene. For whipworms, this means ensuring access to clean water, proper sanitation, and maintaining hygiene practices, especially in areas where these worms are more common.
You might be wondering about how to protect against roundworms and tapeworms, too. The same rules apply. Washing hands before meals, consuming well-cooked food, and avoiding contaminated water are key steps in keeping these critters at bay.
In some cases, regular deworming medications can be beneficial, especially in places where worm infections are prevalent. It’s like a proactive approach to safeguard your gut health. Staying informed and cautious in your eating habits goes a long way in preventing these unwelcome guests.
In the grand scheme of worms, comparing whipworms to similar species like roundworms and tapeworms opens up a fascinating world of biology. Each species has unique adaptations, life cycles, and impacts on their hosts. It’s a delicate dance of survival, reproduction, and, unfortunately, sometimes, disease.
By understanding these differences, we can better appreciate the complexity of these tiny creatures and the importance of good hygiene and preventive measures. So next time you hear about whipworms or their squirmy counterparts, you’ll have a clearer vision of who’s who in the worm world. With a little knowledge and effort, keeping your gut healthy is within reach—no unwelcome guests allowed!