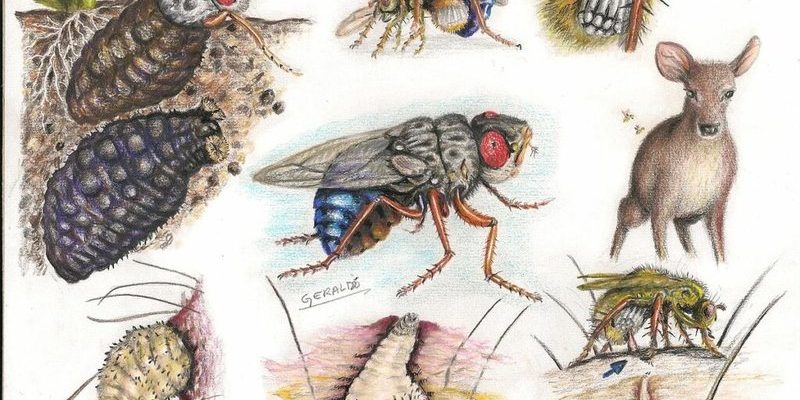
Botflies, with their peculiar life cycle, have a knack for embedding themselves in other animals to thrive. Think of it like an unwanted guest who arrives uninvited and decides to stay a lot longer than you’d like. These fascinating little creatures have evolved a unique method of survival that highlights nature’s intricate web of life. So, do they harm their hosts? Or is it simply a part of nature’s own balancing act? Let’s dive in and explore the coexistence of botflies and the animals they host.
What Are Botflies?
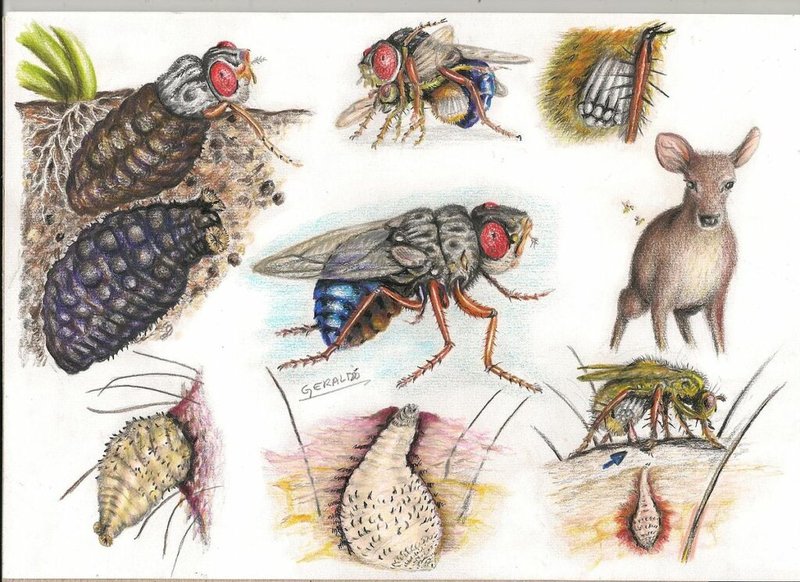
Botflies belong to the family of flies known as Oestridae, and they can be found in various parts of the world. There are several species of botflies, but they all share a common characteristic: their larvae develop inside the bodies of their hosts. This unusual lifestyle helps them grow and develop safely, away from the outside world.
These flies come in different shapes and sizes, and their hosts can vary widely—from rodents to livestock, and even humans in some rare instances. Botflies are known for their distinctive appearance, often resembling small bumblebees. Their adult forms don’t feed, meaning their primary focus is to reproduce. Here’s where it gets intriguing: the female botfly lays her eggs on a host or nearby, and when the eggs hatch, the larvae burrow into the host’s skin.
The Life Cycle of a Botfly
Let’s break down how this works. The life cycle of a botfly consists of four main stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult fly. Here’s a simple explanation of each stage:
- Egg Stage: A female botfly lays eggs on the skin of a host or on an insect that will eventually come into contact with the intended host.
- Larva Stage: The eggs hatch into larvae, which then burrow into the host’s skin. This is where the larval stage can last several weeks as they feed and grow.
- Pupa Stage: After developing, the larvae will exit the host, drop to the ground, and pupate in the soil until mature.
- Adult Stage: Once the adult botfly emerges, it’s time to find a new host and start the cycle all over again.
You might be wondering why these botflies have developed such a method. It’s mainly about survival. By using a host, they get the nutrients they need to grow without the constant threat of predators. However, this creates a complex relationship with their hosts that’s not as straightforward as it seems.
How Do Botflies Affect Their Hosts?
The relationship between botflies and their hosts can be bonkers. On one hand, you have the botfly securely feeding on its host; on the other, the host can experience some uncomfortable consequences. The larvae can cause irritation, pain, and even infections as they grow beneath the skin.
Here’s the crux: not all hosts react the same way. Some animals, like certain rodents, can tolerate the presence of botfly larvae better than others. In fact, a few studies suggest that the immune responses of hosts can sometimes manage the infestation without severe harm. However, in livestock or pets, the presence of botfly larvae can lead to serious issues, including weight loss and infection, which may require veterinary attention.
The Hosts of Botflies
Botflies have quite an impressive range of hosts. From domesticated animals like cows and sheep to wild creatures such as deer and rabbits, the list goes on. Each species of botfly has its preferred hosts. For example:
- Dermatobia hominis: This species primarily targets humans and other mammals in Central and South America.
- Oestrus ovis: Commonly found in sheep, this botfly can have significant health impacts on its hosts.
- Hypoderma lineatum: Known as the common cattle grub, it infests cattle and is economically significant due to livestock production losses.
While we might often think of botflies as harmful, it’s important to see this relationship from a broader perspective. Coexistence in the animal kingdom doesn’t always mean a peaceful partnership; sometimes, it’s a struggle for survival where both parties have to adapt in different ways.
Understanding the Balance of Nature
When we look at the coexistence of botflies and their hosts, we begin to see the bigger picture of nature’s balance. Each species plays a role in its ecosystem, even those that might not seem beneficial at first glance. Botflies may initially appear to be just parasites, but they also contribute to controlling host populations and even serve as food for other creatures once they emerge as adults.
Let’s think about it this way: every creature, no matter how unpleasant, has a role to play. Even though botflies can negatively affect their hosts, they are part of the natural cycle of life and death. For example, when botflies exit their hosts to pupate, they may become food for other animals, thus reinforcing the cycle.
In this way, botflies help bolster the biodiversity of their ecosystems. This interplay might seem harsh, but it’s essential for maintaining healthy populations of various species.
Implications for Wildlife Conservation
In wildlife conservation, understanding relationships like that of the botflies and their hosts is crucial. Conservationists focus on protecting environments where both hosts and parasites coexist naturally. Disrupting this cycle could lead to unintended consequences, such as overpopulation of a host species or the extinction of a botfly species key to its ecosystem.
Here’s the thing: when we protect habitats, we protect all the interactions that come with them. This includes the sometimes uncomfortable relationships like that between botflies and their hosts. It serves as a reminder of how interconnected we are, even when it feels icky.
Why Should We Care About Botflies?
You might be wondering, “Why should I care about botflies anyway?” Well, aside from their bizarre and fascinating life story, botflies offer us insights into ecological balance and health. They remind us that nature is complex, and every creature has its place.
Understanding botflies can also help us appreciate the health of animal populations. An increase in botfly populations could signal a change in host species health or environment. By studying these relationships, we can gain a better understanding of overall ecosystem health. It’s all about looking at the bigger picture and realizing that every little bit counts.
Human Interference and Its Effects
Human activities can disrupt the delicate balance between botflies and their hosts. Habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change are just a few factors that can lead to changes in animal populations, impacting botfly life cycles.
For example, overfarming can reduce host animal populations, leading to a decrease in available nutrients for botflies, thus affecting their survival. Conversely, if botflies are eradicated, their absence could lead to an unchecked rise in host populations, causing new environmental issues.
Understanding these impacts emphasizes the importance of sustainable practices. Protecting ecosystems means we also protect the fascinating but complex relationships that exist within them.
The coexistence of botflies and their animal hosts is a great reminder of how intricate nature can be. While it might seem strange and uncomfortable, this relationship teaches us invaluable lessons about survival, balance, and interconnectedness.
So, the next time you hear about botflies or even see one buzzing around, take a moment to appreciate the wild story unfolding in nature. It’s not just about survival for one species; it’s about the beautiful chaos of life—messy, complicated, and endlessly fascinating. Nature has its ways of balancing itself, and sometimes those ways are a little more bizarre than we might have imagined.

