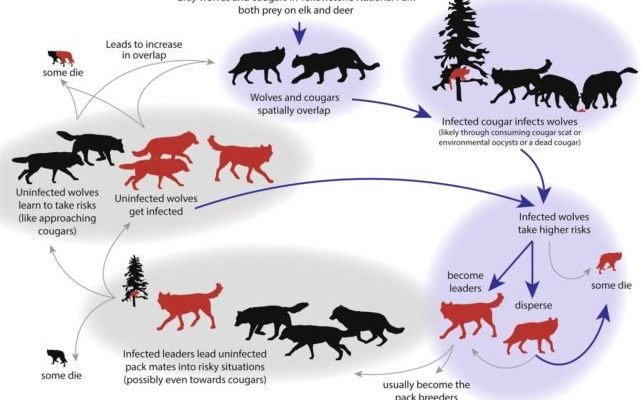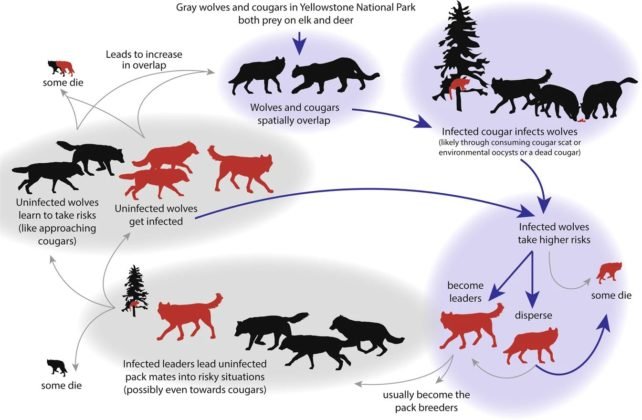
Wolf worms, specifically the larvae of the botfly, can have a dramatic impact on their hosts. When these worms latch on, it’s not just a physical burden; it creates a ripple effect throughout the animal’s behavior. You might be wondering what these changes look like, how they affect the animal’s day-to-day activities, and why understanding this is important—especially if you’re a pet owner or conservation enthusiast. Let’s delve into the behaviors that change during a wolf worm infestation, the reasons behind these changes, and what we can learn from them.
Understanding Wolf Worms and Their Lifecycle
To appreciate the behavioral changes in animals during a wolf worm infestation, it helps to know what these parasites are all about. Wolf worms are the larvae of botflies, which belong to the family Oestridae. These pesky parasites lay their eggs in a host animal, usually when they come into contact with the larvae during grooming or through the skin. Once inside the host, they begin their lifecycle, feeding and growing while causing various health issues.
Imagine the discomfort of having something living inside you, eating your nutrients and causing pain. That’s exactly what animals experience when infested. The larvae can create lumps under the skin, often leading to irritation and inflammation. As these worms grow, the host animal’s body starts to respond, which will ultimately affect their behavior.
Physical Symptoms and Behavioral Changes
With a wolf worm infestation, the physical symptoms can be quite noticeable. You might see your pet scratching more than usual, biting at their skin, or even limping if the infestation is severe. More than just a nuisance, these symptoms impact behavior in several significant ways.
- Increased Agitation: Affected animals may become more irritable and anxious. The constant itching and discomfort make it hard for them to relax.
- Change in Social Interactions: Animals might withdraw from socializing with other pets or wildlife. They may be less playful or even aggressive when feeling sick.
- Altered Eating Habits: A host animal experiencing pain or discomfort might lose their appetite, impacting their energy levels and overall health.
Recognizing these physical and behavioral changes is crucial. If you notice your pet acting out of character, it might be worth investigating a potential wolf worm issue or other health problems.
Social Dynamics: Pack Behavior in Wolves
When we’re talking about wild animals like wolves, social dynamics play an important role in how their behavior shifts during a wolf worm infestation. Wolves are highly social creatures that rely on pack interactions for hunting, protection, and companionship. When one member of the pack gets infested, the entire group’s dynamics can change.
You might see the affected wolf becoming more isolated. It may avoid contact with others or struggle to keep up with the pack during hunts. This can lead to a breakdown in pack roles, as the healthy members must compensate for the weakened individual. The bond that normally exists may fray, causing stress both to the infested wolf and the rest of the pack.
These changes highlight how interconnected animal behavior can be, where one animal’s health issue ripples through the entire group. In turn, this can impact their ability to survive in the wild.
The Impact on Hunting and Survival
Hunting is a vital part of survival for wild animals, and a wolf worm infestation can severely hinder an animal’s ability to hunt effectively. Just think about how difficult it can be to focus on anything else when you’re not feeling well. With the discomfort caused by the larvae, animals may become less efficient hunters.
This doesn’t just affect the individual. If a wolf is unable to hunt properly, it can jeopardize the survival of its entire pack. The consequences can include starvation or injury as they fail to catch prey. Additionally, animals that are less agile may become more vulnerable to predators themselves, creating a cycle of risk that could ultimately affect the population.
Effects on Domestic Pets: What to Watch For
If you’re a pet owner, it’s essential to understand how wolf worms can impact your dog or cat’s behavior. While infestations are more commonly associated with wild canines, domestic pets can also fall victim.
Pets can show a variety of behavioral changes when infested. You may notice your dog becoming less playful, sleeping more, or even displaying signs of aggression when touched around the affected areas. On top of that, their grooming habits might change—often leading them to over-groom the infested area or neglect grooming altogether, which can cause further skin issues.
Being attentive to these subtle behavioral shifts can help you act quickly. Regular checkups with a veterinarian can help catch infestations before they escalate, ensuring your pet stays healthy and happy.
Preventative Measures: Keeping Animals Safe
When dealing with wolf worm infestations, prevention is always better than cure. Here are several steps you can take to protect both wild and domestic animals from these pesky parasites:
- Regular Grooming: For pets, regular brushing can help you identify any lumps or unusual skin changes early.
- Consult a Veterinarian: Regular checkups can keep your pet’s overall health in check. Talk to your vet about preventive treatments for parasites.
- Keep Wild Animals at a Distance: If you have a backyard, limiting contact with wild animals can reduce the chances of your pets becoming infested.
By taking these proactive measures, you can not only protect your pets but also contribute to the overall health of wildlife in your area.
The Bigger Picture: What This Means for Wildlife Conservation
Understanding the behavior changes in animals during wolf worm infestations is crucial for wildlife conservation efforts. Changes in behavior can signal shifts in population dynamics, health, and survival rates in natural ecosystems. Wildlife conservationists look at these changes to make informed decisions about managing wildlife health and habitats.
Keeping a close eye on animal behavior during infestations can help experts understand how disease affects populations over time. This awareness allows for better protective measures and interventions before a small problem turns into a larger epidemic, ensuring healthier environments for both wild and domestic animals.
In conclusion, animal behavior changes during wolf worm infestations reveal a lot about the health and well-being of animals. From increased agitation to altered hunting abilities, these shifts impact not just individuals, but entire populations. Whether you’re a pet owner or a conservation enthusiast, being aware of these changes can help promote healthier lives for animals in your care and in the wild.