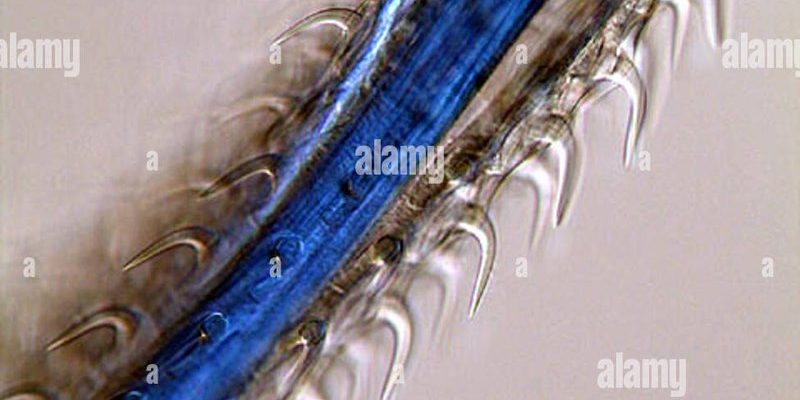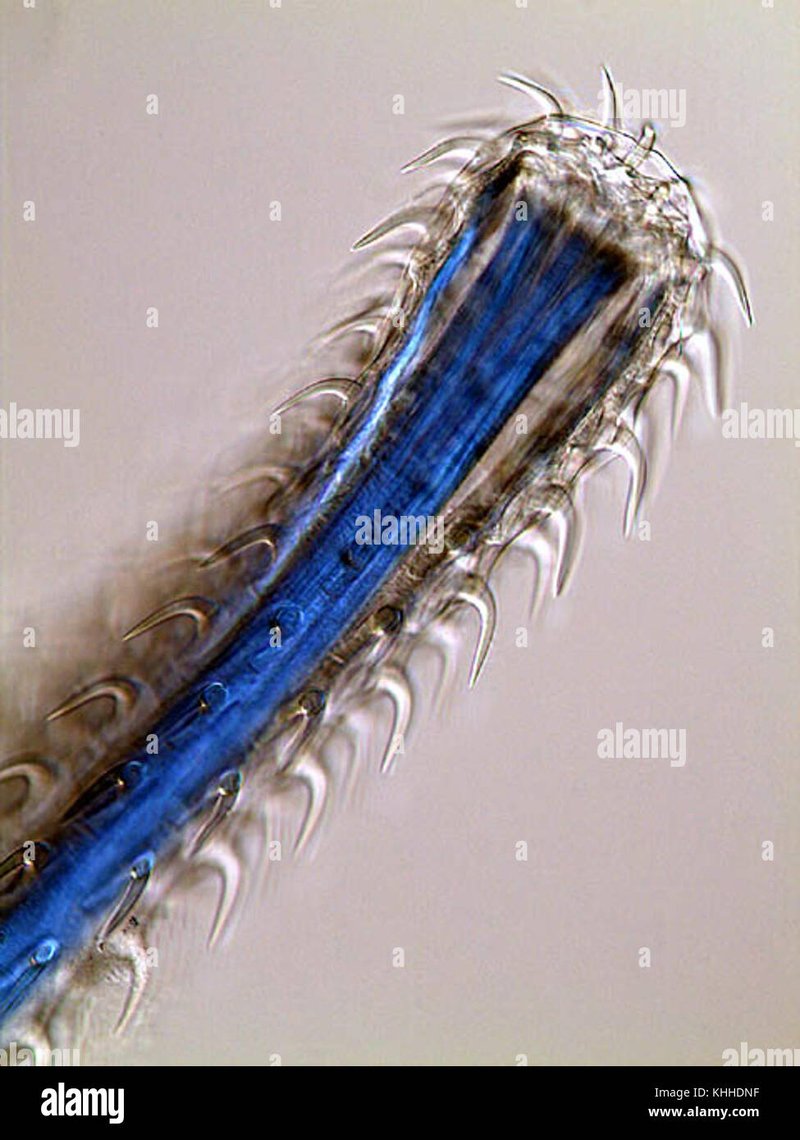
Acanthocephala, commonly known as thorny-headed worms, rely on host animals to survive. These worms have spiny heads that help them attach to their hosts, which can include fish, birds, and mammals. While it might sound a bit icky, these little guys actually contribute to the overall health of ecosystems. Let’s dive into their world, and I’ll explain how they affect the systems around them, both in soil and aquatic habitats.
What Are Acanthocephala?
Acanthocephala are a unique type of parasite, primarily found in the intestines of various vertebrate hosts. These worms have a bulbous body and, as the name suggests, a head embedded with spines. This design helps them latch onto their host, allowing them to live off their nutrients. But why evolve this way? Well, it’s all about survival.
In terms of reproduction, Acanthocephala can produce hundreds or even thousands of eggs every day. These eggs are usually excreted by their hosts into the environment, where they can hatch and infect intermediate hosts, such as insects. This lifecycle is important because it connects Acanthocephala to larger food webs. Each stage of their lifecycle contributes to nutrient cycling, something that’s crucial for keeping ecosystems healthy and functioning.
You might be wondering how a creature like this could possibly benefit the ecosystem. It turns out they play several important roles, which we’ll explore next.
The Role of Acanthocephala in Aquatic Ecosystems
Aquatic ecosystems are incredibly diverse and complex, and Acanthocephala fit in as key players. They often inhabit fish, which makes sense given that many of their hosts live in water. When these fish are consumed by higher predators—like birds or larger mammals—the worms can continue their lifecycle, ensuring their persistence in the food web.
One major impact of Acanthocephala in aquatic ecosystems is their role in regulating fish populations. By infecting fish, they can influence which individuals survive and reproduce. Healthy fish populations are crucial for maintaining balanced ecosystems, as they help control algae levels and support various other species. Therefore, while they may seem harmful to individual fish, they’re part of a much larger picture that supports ecosystem health.
Moreover, Acanthocephala can impact nutrient cycling in water bodies. When fish infected with these worms die and decompose, they release nutrients back into the water. This process is essential as it replenishes the ecosystem, supporting everything from bacteria to larger aquatic organisms.
How Acanthocephala Affect Soil Ecosystems
So, what about soil ecosystems? Well, Acanthocephala may also influence terrestrial habitats indirectly. Their lifecycle can include terrestrial intermediate hosts, such as beetles or other insects. When these insects feed on decomposing organic matter or soil nutrients, they contribute to soil health, which is vital for plant growth.
When Acanthocephala infect and alter the behavior of their intermediate insect hosts, it can lead to changes in how these insects interact with the soil. For instance, infected insects might forage differently, which can alter nutrient distribution in the soil. This could benefit plants and other organisms that rely on healthy soil to thrive.
Additionally, as these parasites are part of the food web, their presence in soil ecosystems helps maintain balance among various organisms, ensuring that no single species dominates. This balance is critical, especially in environments where a range of plant and animal species rely on one another for survival.
The Impact of Acanthocephala on Biodiversity
Biodiversity is vital for healthy ecosystems, and Acanthocephala help maintain it in several ways. By controlling host populations, they prevent the overpopulation of certain species that could lead to ecological imbalances. This means that these worms, in their own peculiar way, contribute to the vast diversity of life forms we see in nature.
Furthermore, the presence of Acanthocephala can encourage genetic variability in host populations. This variability is crucial for species to adapt to changing environments, whether that’s altering their feeding habits, resisting disease, or surviving climate changes. In short, these little worms are contributing to a robust gene pool in their host species, which is essential for long-term survival.
You might also consider their role in predator-prey dynamics. As Acanthocephala influence which individuals survive in host populations, they indirectly support the species that prey on these hosts. A balanced predator-prey dynamic contributes to overall ecosystem resilience.
Potential Implications for Human Activities
With increasing human activity impacting ecosystems across the globe, understanding Acanthocephala’s role is more relevant than ever. Pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change can disrupt the delicate balance that these parasites help maintain. For instance, if fish populations decline due to pollution, the overabundance of Acanthocephala could lead to a further decline in host diversity and overall health of aquatic ecosystems.
Additionally, fisheries that rely on healthy fish populations can be adversely affected by disruptions in the ecosystem balance. If Acanthocephala populations grow unchecked, this could lead to fish that are less viable for consumption and affect the livelihoods of many communities.
In urban areas, soil management is also tied to these parasitic interactions. Understanding how Acanthocephala influence soil-dwelling insects and other organisms can guide better practices in agriculture and landscaping, helping to foster healthier environments.
So, the next time you think about soil or aquatic ecosystems, consider the role of Acanthocephala. These thorny-headed worms may not be the first thing that comes to mind, but they are crucial players in maintaining ecological balance. Their complex lifecycle and unique interactions with various hosts help regulate populations, enhance biodiversity, and contribute to nutrient cycling.
In a world where we often focus on the most visible aspects of nature, it’s important to remember that sometimes, the smallest players have the biggest impact. By understanding Acanthocephala and their roles in both soil and aquatic ecosystems, we can appreciate the intricate web of life that supports everything around us. Whether you’re a nature enthusiast, a student of ecology, or just curious, recognizing the small yet significant contributions of such organisms can deepen your connection to the environment.