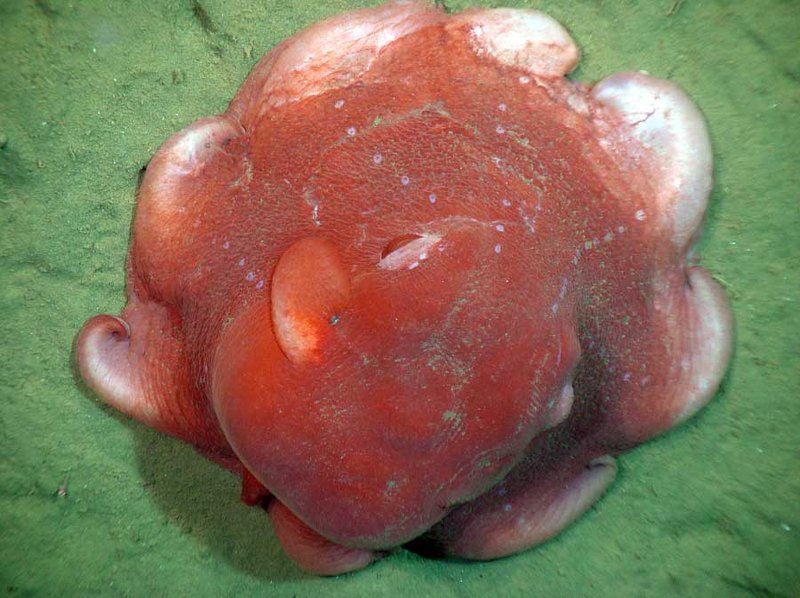
The Dumbo Octopus is not your ordinary octopus. With its large, ear-like fins that flutter as it swims, this deep-sea creature resembles a whimsical character from a children’s movie rather than a real animal. You might find it fascinating that the Dumbo Octopus, scientifically known as Grimpoteuthis, is one of the more adorable denizens of our oceans. Instead of the typical eight arms stretching out like a magician’s assistant, the Dumbo Octopus uses its unique fins to glide gracefully through the water, giving it a gentle and almost cartoonish appearance.
These creatures inhabit deep-sea environments and are known for their unusual behavior and adaptations. Imagine exploring the ocean’s depths, where the light barely penetrates, and encountering this captivating cephalopod. Want to know more? Let’s dive in and uncover the mysteries surrounding the Dumbo Octopus, learning what makes it such a unique inhabitant of the ocean.
Physical Characteristics
The Dumbo Octopus is a fascinating sight to behold! Most species of this group grow to about 8 to 12 inches in length, which is quite small compared to other octopuses. Their body is soft and gelatinous, giving them a unique, blob-like appearance. Unlike many other marine creatures, they lack a hard shell, which allows for greater flexibility and maneuverability in the water.
What stands out the most are those adorable fins resembling Dumbo’s ears, which indeed gives the creature its name. These fins allow it to swim by flapping them gently, making it seem as if it’s flying through the water. Additionally, their skin can display various colors and patterns, often shifting to match their surroundings, which is a brilliant adaptation for camouflaging from predators.
Apart from their fins, Dumbo Octopuses have large, expressive eyes. Imagine looking into the deep blue sea and seeing these eyes peering back at you, filled with curiosity! Their eyes are well adapted for low-light environments, allowing them to spot both prey and potential threats in the dark, murky depths.
Habitat and Distribution
Diving deeper into the ocean, you’ll find that the Dumbo Octopus predominantly resides at depths of 8,200 to 13,000 feet, making it one of the deeper-living octopus species. They are typically found in deep-sea habitats, like the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, thriving in areas where sunlight barely reaches. This environment is rich in nutrients, making it an ideal hunting ground for these remarkable creatures.
It’s quite interesting how they have adapted to life in such extreme conditions. The extreme pressure and cold temperatures of the deep sea mean that the Dumbo Octopus has developed specific traits to thrive. For instance, their ability to move slowly and steadily allows them to conserve energy while gliding through the water, which is crucial in such a resource-scarce environment.
Further, these octopuses tend to prefer soft substrates like mud or sand, where they can easily camouflage themselves while waiting for unsuspecting prey to pass by. With such unique adaptations, it’s no wonder they play a vital role in their ecosystem.
Diet and Feeding Habits
The diet of the Dumbo Octopus primarily consists of small crustaceans and other invertebrates. Using their keen eyesight, they can spot prey from a distance. Here’s the thing: they don’t hunt like other active predators; instead, they often gently hover near the ocean floor, waiting patiently for food to come close enough to catch.
When it’s time to eat, the Dumbo Octopus uses its arms to snatch up prey. They have a specialized beak, much like a parrot’s, which allows them to crack open hard shells and access soft-bodied prey inside. This adaptation is necessary, given that many of the creatures they consume have protective outer layers. Imagine having a toolbox that lets you reach delicious food hiding behind a tough exterior—pretty neat, right?
Interestingly, Dumbo Octopuses have a unique feeding strategy. Instead of the rapid, aggressive feeding seen in many other predators, their approach is calm and deliberate. They use their arms to gather food, sometimes even employing a technique called “suction feeding,” where they suck in small prey to devour them. This behavior not only showcases their intelligence but also emphasizes their adaptability in a challenging environment.
Reproduction and Lifespan
The reproductive habits of the Dumbo Octopus are as fascinating as the creatures themselves. After mating, females lay anywhere from 20 to 100 eggs, which they attach to the seafloor or plants. One unique aspect of their reproduction is that the female often cares for her eggs, sometimes staying with them for several months until they hatch. During this time, she stops eating, dedicating all her energy to guarding her budding offspring. Talk about dedication!
Once the eggs hatch, the tiny Dumbo Octopuses are independent and must fend for themselves right away. They’re miniature versions of adults but face challenges navigating the vast ocean. Unfortunately, the lifespan of a Dumbo Octopus is relatively short, typically lasting around three to five years.
Despite their brief existence, these creatures contribute significantly to their ecosystem. They can reproduce quickly when conditions are right, which helps maintain their populations in the deep, dark depths. It’s a tough life out there, but they’re perfectly adapted to handle it!
Conservation Status
Currently, the Dumbo Octopus is not listed as endangered, but that doesn’t mean they are entirely free from threats. As our oceans face rising temperatures and increased pollution, their deep-sea habitats are at risk. Overfishing and deep-sea mining also pose dangers to these delicate ecosystems, potentially impacting the Dumbo Octopus populations.
Maintaining healthy ocean ecosystems is vital for the survival of all marine life, including the Dumbo Octopus. Organizations around the world are working to raise awareness about deep-sea conservation efforts and the importance of protecting these often-overlooked creatures. You might think it’s just “the ocean,” but every small part, including the Dumbo Octopus, plays a crucial role in maintaining balance.
Conservation measures involve stricter regulations on fishing and pollution control, alongside efforts to understand more about their biology and ecology. After all, the more we know about creatures like the Dumbo Octopus, the better we can protect them and their unique underwater world.
Fun Facts about the Dumbo Octopus
- The Dumbo Octopus can change color to blend in with its surroundings.
- They are not aggressive and will often flee from larger predators.
- Despite being deep-sea creatures, they have very delicate bodies.
- The Dumbo Octopus is named after the Disney character Dumbo, due to its ear-like fins.
Interesting Comparison: Dumbo Octopus vs. Other Octopuses
| Feature | Dumbo Octopus | Common Octopus |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat Depth | 8,200 to 13,000 feet | Up to 650 feet |
| Size | 8 to 12 inches | Up to 16 feet |
| Feeding Strategy | Suction feeding, slow approach | Aggressive hunting and ambush |
FAQ
What is the Dumbo Octopus known for?
The Dumbo Octopus is known for its unique ear-like fins that resemble the Disney character Dumbo, allowing it to swim gracefully through the water. This soft-bodied cephalopod is a deep-sea dweller with intriguing adaptations for life in extreme conditions.
Where can you find Dumbo Octopuses?
Dumbo Octopuses inhabit the deep-sea areas of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, typically living at depths of 8,200 to 13,000 feet. They thrive in cold, dark waters where sunlight cannot penetrate.
How do Dumbo Octopuses catch their prey?
These octopuses use their keen eyesight to spot small crustaceans and invertebrates. Instead of rapid movements, they gently approach their prey and use a technique called suction feeding, allowing them to capture food with ease.
Are Dumbo Octopuses social animals?
Dumbo Octopuses are generally solitary creatures. They do not form social bonds and prefer to live alone, only coming together during mating season.
What is the average lifespan of a Dumbo Octopus?
The average lifespan of a Dumbo Octopus is about three to five years. Despite their short lives, they make significant contributions to the deep-sea ecosystem during their time in the ocean.
How do Dumbo Octopuses protect themselves from predators?
While Dumbo Octopuses are not aggressive and prefer to flee from threats, they can use their ability to change color to blend in with their surroundings, helping them avoid detection by predators.
Why are Dumbo Octopuses important to the ecosystem?
Dumbo Octopuses play a crucial role in the deep-sea ecosystem as both predators and prey. They help maintain the balance of marine life, contributing to the overall health of the ocean.
Can Dumbo Octopuses be kept in aquariums?
Keeping Dumbo Octopuses in aquariums can be challenging due to their specific habitat needs and dietary requirements. They thrive in deep-sea conditions that are difficult to replicate in captivity.
What threats do Dumbo Octopuses face?
Dumbo Octopuses face several threats, including habitat destruction from deep-sea mining, pollution, and climate change affecting ocean temperatures. Conservation efforts are important to ensure their survival.
How do scientists study Dumbo Octopuses?
Scientists study Dumbo Octopuses using submersibles and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) to observe their behavior and habitat in their natural environment. This research helps us learn more about their biology and ecology.

