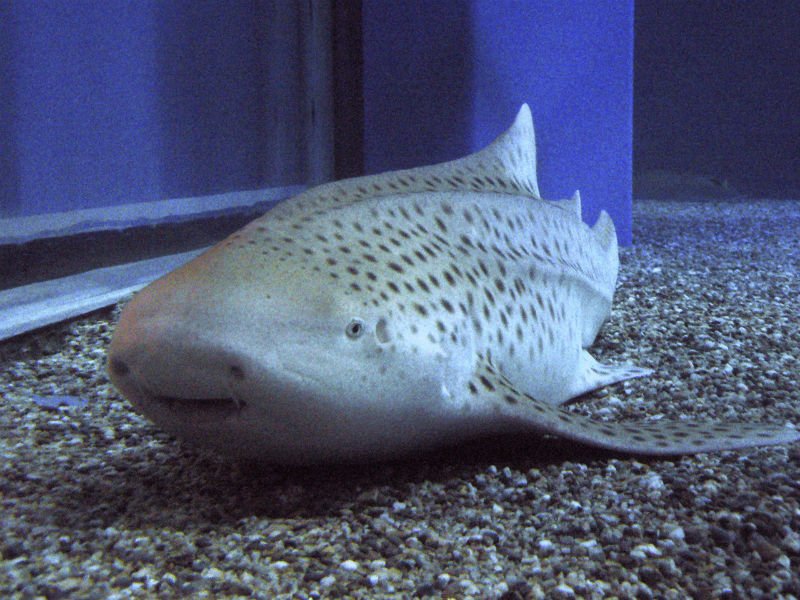
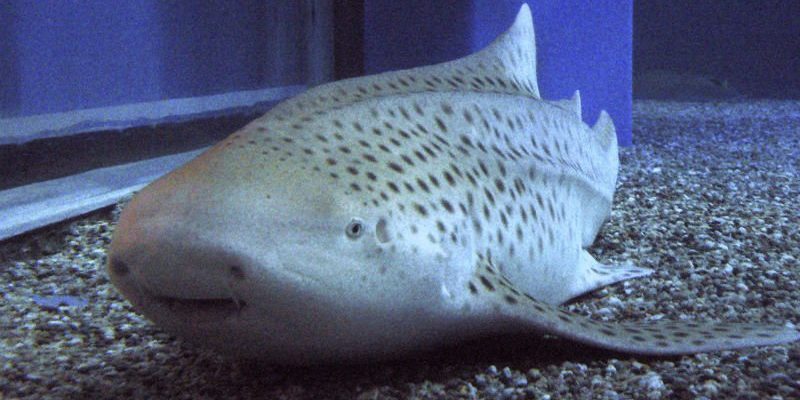
Zebra sharks, known scientifically as *Stegostoma fasciatum*, are often found in tropical waters, gracefully cruising along the ocean floor. Their distinct pattern of stripes and spots resembles that of a zebra, which is how they got their name. These sharks are unique because they exhibit a different kind of reproductive strategy compared to many other shark species. So, let’s dive in and explore the world of zebra shark reproduction and breeding—after all, it’s not just about how they reproduce, but also why it matters for their species and the ocean ecosystem.
Understanding Zebra Shark Reproduction
Zebra sharks are oviparous, which means they lay eggs rather than giving live birth. This is a bit of a twist compared to what many people expect when they think of sharks. Think of it like the difference between a chicken laying eggs versus a cat giving birth to kittens. During the breeding season, which typically occurs between late spring and early summer, the females start to prepare for the process of laying their eggs.
Female zebra sharks can lay up to 50 to 100 eggs at a time. These eggs are encased in tough, leathery capsules that look like little gelatinous pouches. They often attach themselves to the ocean floor, hiding in crevices or under rocks, providing some protection from predators. This strategic placement is essential, as it increases the chances of survival for the developing embryos inside.
Mating Behavior
Before the eggs are laid, mating rituals take place. During this time, you might see a female zebra shark swimming alongside a male. They’ll engage in a series of dances, which can be quite a sight. The male often grasps the female’s fin with his mouth, showing off his strength and determination. This courtship can last several hours, and it’s a critical step in ensuring proper fertilization of the eggs.
You might be wondering why zebra sharks have such intricate mating behaviors. Well, these patterns help ensure that the right mates come together. After all, the ocean is a vast place, and finding a partner isn’t always easy!
Egg Development and Hatching
Once the eggs are laid, the real wait begins. The embryos develop inside their protective casings for about 3 to 6 months, depending on water temperature and environmental conditions. Warmer water tends to speed up development, while cooler conditions can slow it down.
Inside those egg cases, the baby zebra sharks are growing and getting ready to hatch. When they’re finally ready, the young sharks use a specialized structure called an “egg tooth” to break free from their capsules. It’s like having a built-in tool for their grand entrance into the world. Once hatched, they are on their own, swimming away to navigate the ocean.
Survival Challenges for Hatchlings
As you can imagine, life isn’t easy for these young sharks. Right after hatching, they are vulnerable to a host of predators, including larger fish, birds, and even other sharks. Their size—around 12 to 14 inches—makes them an easy snack. This is why the choice of breeding location is so crucial; the more concealed they can be, the better chance they have.
Hatchlings are also responsible for finding their own food. They typically feed on small fish, crustaceans, and mollusks. As they grow, their hunting skills sharpen, but the initial phase of survival is certainly challenging.
The Role of Breeding in Conservation
The reproductive success of zebra sharks is vital for their population health. Unfortunately, these sharks face threats from habitat loss and overfishing. Conservation efforts focus not only on protecting their habitats but also on understanding their breeding habits.
By studying zebra shark reproduction, scientists can assess their population health and develop strategies to ensure their survival. For example, if we know when and where they breed, we can create marine protected areas to safeguard these vital locations.
Here’s the thing: protecting one species like the zebra shark also helps the entire marine ecosystem. Healthy shark populations mean better regulation of fish populations, which contributes to a balanced ocean environment.
Current Conservation Efforts
Several organizations are currently working to protect zebra sharks, including marine sanctuaries and aquariums that focus on education and breeding programs. These efforts aim to raise awareness about the importance of zebra sharks and their role in the ecosystem.
Aquarium breeding programs are particularly interesting. They mimic natural breeding conditions and aim to produce viable eggs for future generations. By doing this, they not only help the zebra shark population but also educate the public about the importance of marine conservation.
Breeding and reproduction of the zebra shark are more than just a biological process; they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ocean ecosystems. From their unique mating rituals to the challenges faced by hatchlings, these sharks exemplify the wonders of marine life.
As we continue to conserve and protect zebra sharks and their habitats, we also safeguard the health of our oceans. Honestly, it’s a win-win situation. Every effort counts towards ensuring these striking creatures thrive for generations to come. So next time you think of sharks, remember the zebra shark and their impressive journey of reproduction!