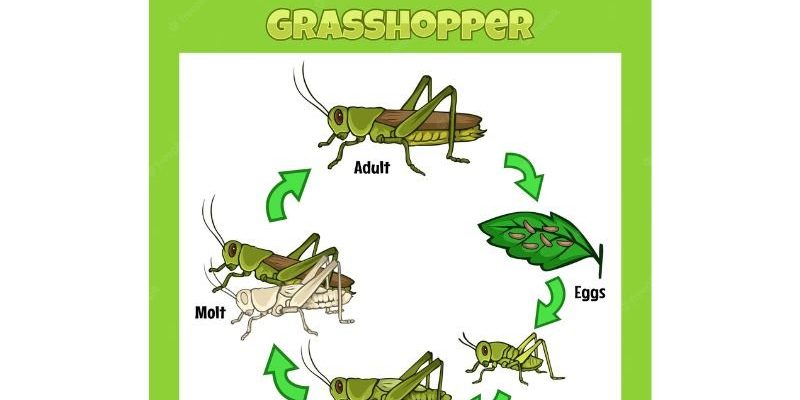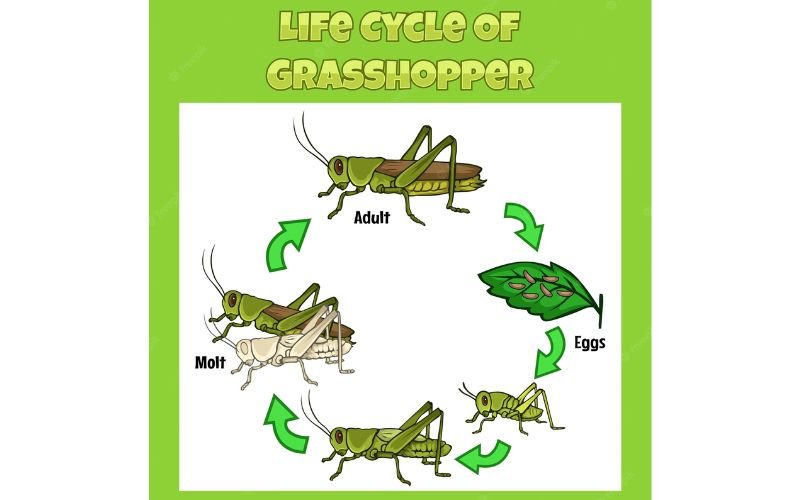
Imagine for a second that a grasshopper’s life is like a great adventure, taking it from a small egg nestled in the ground to a vibrant creature worthy of hopping through fields. This journey unfolds in several stages: egg, nymph, and adult. Each of these stages is essential and plays a crucial role in the grasshopper’s overall development. So, grab your favorite drink, and let’s hop into the incredible world of grasshoppers!
Stage 1: The Egg
The lifecycle of a grasshopper begins with the egg. Typically, a female grasshopper lays her eggs in the late summer or early fall, placing them in clusters called pods. These pods often look like tiny grains of rice and can hold anywhere from 20 to even 100 eggs, depending on the species. Isn’t that wild?
Once laid, these eggs are protected from harsh weather and predators by a tough outer shell. They will spend the winter buried in the soil, waiting for the right conditions to emerge. During the chilly months, they’re like little time capsules, quietly developing inside until the warmth of spring arrives.
When spring finally rolls around, the eggs hatch and tiny grasshopper nymphs, resembling miniature versions of adults, emerge. You might be wondering, “How do they find their way out?” Well, the nymphs use a combination of instinct and environmental cues to break free from their eggs, ready to take on the world.
Stage 2: The Nymph
After hatching, grasshopper nymphs enter the next stage of their journey. Unlike adults, they don’t have fully developed wings or reproductive organs. Instead, they’re just small versions of their future selves. This stage can last several weeks to a few months, depending on the species and environmental conditions.
During this time, nymphs go through a process called molting. Basically, this means they shed their exoskeleton multiple times as they grow. Each time they molt, they become slightly larger and more like adults. Picture it like outgrowing your favorite pair of shoes—eventually, you need to trade them in for a bigger size!
Nymphs are extremely hungry, munching on grass and leaves to fuel their growth. They can be seen scampering around, trying to avoid predators while searching for food. If you’ve ever seen a grasshopper hop away quickly, you’ve witnessed their survival instinct in action!
Stage 3: Maturation
As nymphs continue to grow and molt, they are getting closer to becoming adults. This stage is crucial; the grasshopper must prepare for its transformation. During the final molts, you’ll notice they start developing wings and reproductive organs. It’s like watching a caterpillar turn into a butterfly—exciting and full of potential!
Adult grasshoppers are often vibrant and colorful, showcasing various patterns depending on their species. Once they reach maturity, they are ready to take on new challenges: finding food, escaping predators, and, most importantly, reproducing. At this point, they can also be seen making distinctive sounds, often referred to as “stridulation,” by rubbing their wings together. It’s their way of singing out to attract mates!
This maturation phase is vital not just for the individual grasshopper but for sustaining the species as a whole. A healthy population of grasshoppers contributes to the ecosystem by serving as food for various predators, including birds and small mammals.
Stage 4: The Adult
Now, let’s talk about the final stage: adulthood. An adult grasshopper is a magnificent creature, capable of jumping great distances and flying short bursts. Typically, they live for several months to a year, depending on various factors such as climate, food availability, and threats from predators.
In this stage, it’s all about survival and reproduction. Adult grasshoppers seek out mates to ensure the next generation continues the cycle. Once they find a partner, the female will go on to lay eggs, starting the whole process over again. You can see how the lifecycle of a grasshopper is a continuous loop, one feeding into the next.
Interestingly, during this stage, grasshoppers play an essential role in the ecosystem. They help to control plant populations by consuming leaves and stems, which influences the growth of various plant species. Plus, think about all the animals that rely on them for food—grasshoppers are a key link in the food chain!
The Importance Of Grasshoppers In Our Ecosystem
Grasshoppers might seem like simple insects darting around, but they’re crucial to our ecosystem. They contribute to the health of various habitats by aiding in plant growth and serving as a food source for many animals. Without them, there would be a significant impact on the food chain.
Moreover, grasshoppers help recycle nutrients back into the soil. As they munch on plants, they produce waste that decomposes and enriches the earth. This natural fertilization process benefits countless other creatures and plants. It’s a lovely reminder of how interconnected everything is, isn’t it?
Grasshoppers also show us a lot about environmental changes. For instance, if their population decreases significantly, it can indicate an imbalance in their habitat. Scientists often study these insects to understand the health of ecosystems better.
The lifecycle of a grasshopper, from egg to adult, is truly a remarkable journey. It teaches us about resilience, growth, and the cycles of life that we often take for granted. Each stage, from the tiny egg nestled in the soil to the leaping adult, is a celebration of nature’s wonders.
So, the next time you spot a grasshopper in your garden or park, take a moment to appreciate its story. It’s not just a bug; it’s a small marvel of nature, linking many different parts of the ecosystem together. And who knows? Maybe you’ll feel inspired to learn even more about the incredible insects that share our world!