The peanut worm might not be the first thing that comes to mind when you think about the natural world, but that’s part of what makes them so fascinating. They’re like the hidden gems of the animal kingdom, living in habitats that might seem unwelcoming to other species. So, if you’re curious about where they call home, what factors influence their distribution, and how they manage to survive in such varied conditions, you’re in the right place. Let’s dig deeper into the world of peanut worms.
What Are Peanut Worms?
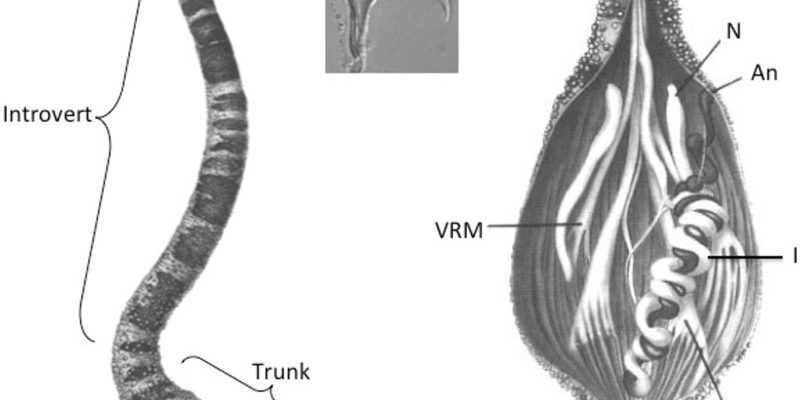
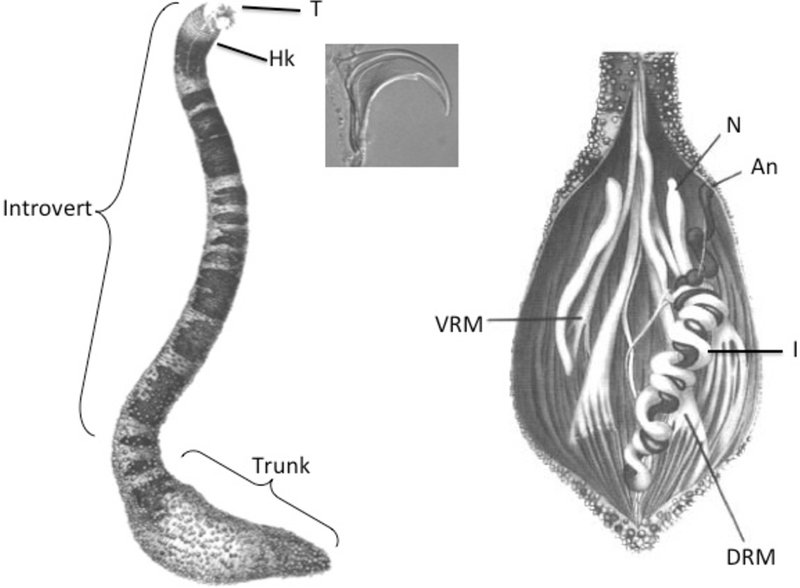
Peanut worms belong to the phylum Sipuncula, which is a group of marine worms. They’re not actually related to earthworms, so don’t let the name fool you! Imagine a squishy little creature that resembles a peanut in its burrow, curled up and waiting for the right moment to stretch out and feed. These worms can be found in various marine environments, including sandy seafloors and muddy bottoms, mainly in shallow waters.
One of the most intriguing aspects of peanut worms is their unique body structure. They possess a retractable proboscis, which can extend outward to capture food particles. This feature is much like how an octopus reaches out with its tentacles to snag prey. Simply put, peanut worms have evolved to become adept at surviving and foraging in their habitats.
Global Distribution of Peanut Worms
When we talk about the geographical spread of peanut worms, we’re diving into a story that spans oceans and continents. These worms can be found in various parts of the world, from the warm waters of the tropics to the cooler regions near the poles. As adaptable as they are, they primarily inhabit coastal areas, preferring the soft substrates found in sandy and muddy environments.
You might find peanut worms lurking in places like the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico, and along the coasts of Southeast Asia. The distribution isn’t uniform—some areas are teeming with peanut worms, while others might have sparse populations. This variability can be due to factors like water temperature, salinity, and the availability of food sources.
Factors Influencing Their Distribution
Peanut worms don’t just settle wherever they please; several environmental factors play a role in where they thrive. Water temperature is crucial—most peanut worms prefer warmer waters, which often leads them to tropical and subtropical regions. Like Goldilocks, they need their habitat to be “just right” to flourish.
Salinity is another key factor. Peanut worms often prefer brackish waters, which are less salty than sea water but saltier than fresh water. This makes estuaries and coastal lagoons prime spots for them. The availability of organic matter on the sea floor is also essential, as it provides nourishment for these creatures. Areas with a rich supply of detritus, which is essentially decaying organic material, can support larger populations.
Adaptation and Survival Strategies
The adaptability of peanut worms is quite impressive. They employ several survival strategies that allow them to cope with changes in their environment. For instance, they can retract into their burrows when threatened. This ability to “hide out” helps them avoid predators and changes in water conditions, much like how a turtle pulls its head back into its shell.
During times of stress, whether it’s due to pollutants or changes in temperature, peanut worms can alter their reproductive strategies. In some cases, they can switch from sexual reproduction to a form of asexual reproduction, allowing them to reproduce more quickly when conditions are less than ideal. It’s a clever workaround that speaks to their resilience.
Importance of Peanut Worms in Ecosystems
You might be wondering why anyone should care about peanut worms. Well, they play an essential role in their ecosystems. As filter feeders, they help clean the water by consuming organic matter and sediments. This process contributes significantly to nutrient cycling in marine environments, which supports various other forms of marine life.
Additionally, peanut worms serve as a food source for various animals, including fish and seabirds. They’re like tiny links in a vast food chain, ensuring that larger creatures thrive while also keeping the ecosystem balanced. A healthy population of peanut worms can indicate a thriving marine environment, making them important indicators of ecological health.
Research and Conservation Efforts
Despite their low profile, there’s a growing interest in studying peanut worms. Researchers are beginning to uncover more about their biology, behavior, and interactions with their environment. Understanding their distribution is crucial, especially as climate change and human activities continue to impact marine ecosystems.
Conservation efforts are vital for ensuring that peanut worms and their habitats remain protected. Preserving coastal regions, reducing pollution, and managing fishing practices can go a long way in safeguarding these little critters. After all, maintaining the health of our oceans benefits not only peanut worms but countless other marine species as well.
Peanut worms may be small, but their impact on the marine ecosystems they inhabit is anything but insignificant. From their fascinating adaptability to their essential role in nutrient cycling, understanding their documented range and distribution is vital for appreciating the complexity of our oceans.
So, next time you think about marine life, don’t forget these quirky worms that are quietly playing their part beneath the waves. Their story is a reminder of how interconnected our world is and how each creature, no matter how small, contributes to the bigger picture. By learning about and protecting these remarkable organisms, we take a step towards a healthier planet for all its inhabitants.