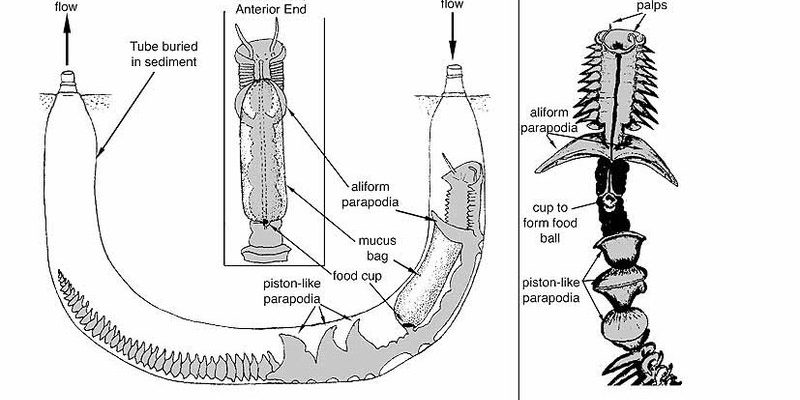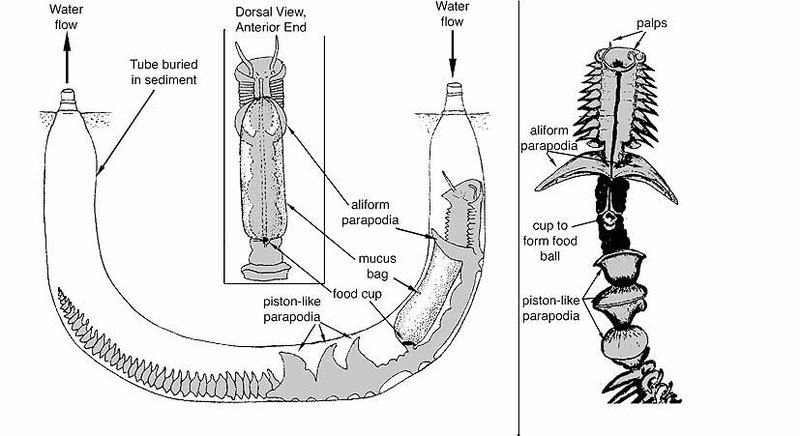
You might be surprised to learn that there are over 10,000 known species of marine polychaetes, and they come in all shapes and sizes. Some are tiny and hardly noticeable, while others can grow to be several feet long! With such variety, their feeding strategies are quite different, adapting to their specific environments. From scavenging to predation, understanding how these creatures catch their meals can give us insight into the intricate web of life beneath the waves.
What Are Marine Polychaetes?
Before diving into their feeding mechanisms, it’s essential to know a bit about what polychaetes are. These worms belong to the class Polychaeta within the phylum Annelida. They live mostly in marine environments, from tidal pools to the deep sea. Their distinguishing features include a segmented body and parapodia—little, fleshy appendages that often have bristles called chaetae.
Many of these worms are burrowers. They can dig into the ocean floor, creating intricate tunnels. Others prefer to hang out on rocks or coral, where they can catch drifting food particles. Their adaptations to different lifestyles make them a highly successful group in marine ecosystems.
In terms of reproduction, polychaetes can be quite fascinating. Most of them have a complex life cycle that includes both a larval stage and a reproductive phase, where they often have spectacular swarming events. But let’s focus on what brings us here today: their feeding mechanisms!
How Do Marine Polychaetes Feed?
Marine polychaetes have evolved various methods for feeding depending on their habitat and lifestyle. Here are some of the primary feeding strategies you might encounter:
- Suspension Feeding: Some polychaetes, like feather duster worms, have specialized structures called tentacles that filter tiny particles from the water. They wave these tentacles back and forth to catch plankton and detritus.
- Deposit Feeding: Other species, such as certain types of lugworms, consume organic matter found on or within the sediment. They ingest substrate and extract nutrients, leaving behind burrows enriched with waste.
- Carnivorous Feeding: Some polychaetes are active predators. They have elongated jaws or hooks to catch prey. For example, the infamous bristle worm can grab small fish or other invertebrates, making it quite the underwater hunter.
Each of these strategies showcases how polychaetes have adapted to their environments and available food sources. Their flexibility in feeding methods is one reason they can thrive in diverse habitats.
Understanding Suspension Feeding
Let’s dig a little deeper into suspension feeding since it’s one of the most visually striking methods. Suspension feeders often create elaborate structures to maximize their food capture. Imagine a tree with branches reaching wide into the air—this is similar to how some polychaetes, like the Christmas tree worm, display their tentacles.
Here’s how it typically works:
1. Tentacle Movement: The worm extends its tentacles into the water column. These tentacles have tiny, hair-like structures that trap microscopic food particles, like phytoplankton.
2. Mucus Production: Many polychaetes secrete mucus to help capture food. The gelatinous threads increase the chances of food sticking to their feeding apparatus.
3. Transporting Food: Once food is captured, it’s drawn back toward the mouth, where it’s ingested. This process can resemble a delicate dance, as the worm must ensure its tentacles remain in the right position to catch drifting food.
Suspension feeding is particularly efficient in nutrient-rich waters, often found in coastal areas where currents bring in an abundance of plankton.
Diving Into Deposit Feeding
Deposit feeding is another common strategy used by many polychaetes, especially those that burrow in sediment. Here’s how these worms get their meals:
1. Tunneling: These polychaetes dig into the ocean floor, creating burrows where they can hide and feed. They constantly ingest sediment, which may sound a bit strange!
2. Nutrient Extraction: As they consume soil or sediment, they extract organic matter like decaying plant and animal material. It’s like they’re sifting through a compost pile, finding the good stuff.
3. Waste Production: The leftover material is excreted, which helps recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem. This process is crucial for maintaining the health of marine environments, as it enriches the soil for other organisms.
By being efficient deposit feeders, these worms play a vital role in shaping sediment structures and promoting biodiversity.
The Role of Carnivorous Polychaetes
When you think of hungry creatures in the ocean, carnivorous polychaetes might not come to mind right away. However, their role as predators is just as fascinating. Here’s how they operate:
1. Hunting Techniques: These polychaetes often have sharp jaws or hooks, making them effective hunters. Some can even extend their bodies to lunge at prey, grabbing fish or other invertebrates with surprising speed.
2. Camouflage and Ambush: Many carnivorous polychaetes blend into their surroundings, using camouflage to surprise unsuspecting prey. They might even hide in crevices or under debris, waiting patiently.
3. Feeding on Prey: Once they’ve captured their food, they use their strong jaws to consume it, often tearing it apart. Some species can even digest prey outside their bodies, releasing enzymes to break it down before ingesting it.
This predatory behavior not only highlights their adaptability but also unveils the complex relationships these creatures have with other marine life.
Why the Feeding Mechanism Matters
Understanding the feeding mechanisms of marine polychaetes can give us valuable insights into marine ecosystems. Here are a few reasons why it’s essential:
1. Ecosystem Health: By examining how polychaetes feed and interact with their environment, scientists can better understand the overall health of marine ecosystems. Their roles as both prey and predators help maintain balanced food webs.
2. Biodiversity Indicators: Polychaete populations can indicate environmental changes. For instance, a decline in certain polychaete species might signal problems like pollution or habitat loss.
3. Nutrient Cycling: As deposit feeders, polychaetes contribute to nutrient cycling. Their feeding habits help enrich sediments, benefiting other organisms and promoting biodiversity.
Recognizing how these worms feed lays a foundation for deeper ecological studies and conservation efforts.
The feeding mechanisms of marine polychaetes showcase the remarkable adaptability of these creatures. From suspension feeding and deposit feeding to carnivorous hunting, polychaetes have evolved unique methods to thrive in diverse environments. Understanding these strategies is like unlocking a secret door to the ocean’s hidden world, revealing how life is interconnected and how each organism plays a role in the broader ecosystem.
This knowledge is not just academic; it can inform conservation efforts and help us appreciate the complexity of marine life. So next time you think about the wonders of the ocean, remember the humble polychaete worm and their vital contributions beneath the waves.