Whipworms, specifically the Trichuris trichiura species, are known for their long, whip-like shape. They’re primarily found in humans and some animals, and their reproductive habits are as interesting as their shape. Understanding whipworm reproduction can help us grasp their role in health and disease, especially in areas where sanitation might not be optimal. Like any living thing, they show us the complexity and beauty of life—even if it is a bit icky!
How Whipworms Mate
Whipworms have a unique mating style that might surprise you. When the time is right, male whipworms seek out females to mate with. The males have a slightly different anatomy, often having larger posterior ends that allow them to grasp the female during mating. This process, while not overly romantic, is efficient for their reproduction.
The mating itself can take a while, possibly a few hours, as the male effectively latches onto the female, ensuring he successfully transfers his sperm. After all, in the world of whipworms, it’s a game of survival, and every opportunity counts! Here’s the thing: once mating occurs, the female whipworm doesn’t waste any time.
Egg Production and Characteristics
Once mating is complete, the female whipworm gets to work producing eggs. She can lay hundreds of eggs daily—impressive for such a small creature! The eggs are oval and have a distinctive brown color, often described as “thick-shelled” or “bipolar.” This tough outer layer helps protect the eggs from harsh environmental conditions outside the host’s body.
It’s fascinating how these eggs are designed for survival. To ensure they make it through the digestive system of the host and into the soil, whipworm eggs can survive in various climates. Once they’re out in the environment, they can remain viable for years, waiting for a new host to ingest them. It’s a waiting game, but these eggs are built to last.
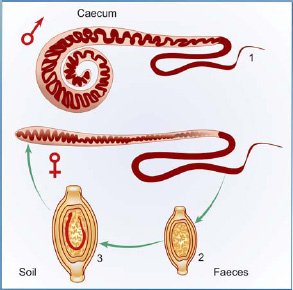
The Life Cycle of Whipworms
The life cycle of whipworms is a truly remarkable journey. After a host ingests the eggs—often through contaminated food or water—the eggs hatch in the intestines, releasing larvae. This is where things get a little wild! These larvae begin to mature and develop into adult whipworms, which can take a few months.
The adult whipworms then attach themselves to the intestinal walls, where they thrive by feeding on nutrients from the host. This can lead to various health issues, especially if the infestation is severe. Symptoms might include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and even anemia. So, you might be wondering, why does understanding this life cycle matter? Well, it’s crucial for public health efforts aimed at controlling whipworm infections.
Understanding Whipworm Eggs
As we’ve touched on, whipworm eggs are quite fascinating. They’re not only unique in their shape and color, but they also have a very specific process for development. After being laid, the eggs need to be in the right environment—moist and warm—to develop properly. This usually happens in the soil, where they mature before they can be ingested by a new host.
The durability of these eggs is key to the whipworm’s survival. They can survive in less-than-ideal conditions, waiting patiently for a suitable host to come along. This adaptability is part of what makes whipworms such successful parasites. If you think about it, it’s a bit like waiting for the right moment to jump in—only these eggs can wait for a very long time!
The Role of Larvae in Development
Once the whipworm eggs hatch, the larvae play a crucial role in the whipworm’s journey to adulthood. After hatching in the host’s intestines, these little larvae begin to grow and eventually make their way to the intestinal walls, where they attach themselves. This transition is vital because it marks the shift from being free-living larvae to becoming adult parasites.
Interestingly, the larvae undergo several stages of development before they fully mature. During this time, they’re feeding and growing, preparing for their role in the ecosystem of the host. The larvae are sort of like teenage whipworms—still growing up, figuring out their place in the world, and getting ready to take on adult responsibilities!
Health Implications of Whipworm Infestations
While whipworms are fascinating creatures, their presence in humans can lead to health problems. Infestations can cause symptoms that range from mild to severe, especially in children. Malnutrition is a particularly serious consequence, as whipworms can consume vital nutrients that the host needs to thrive.
Education on hygiene and sanitation is key in preventing whipworm infections. Proper handwashing, thoroughly cooking food, and ensuring safe drinking water can significantly reduce the risk of ingesting whipworm eggs. It’s a community effort—just like working together to tackle any kind of health issue!
Whipworm reproduction might not be the most glamorous topic, but it offers a peek into the complex and often surprising world of parasitic life. From their unique mating habits to the resilient eggs and larvae that survive in the environment, whipworms show us how life can thrive in unexpected ways.
Understanding these creatures helps raise awareness about the importance of hygiene and public health. The next time someone mentions whipworms, remember the fascinating journey they take from eggs to larvae to adult parasites. It’s a small reminder of the interconnectedness of life—no matter how tiny or slimy that life might be!
