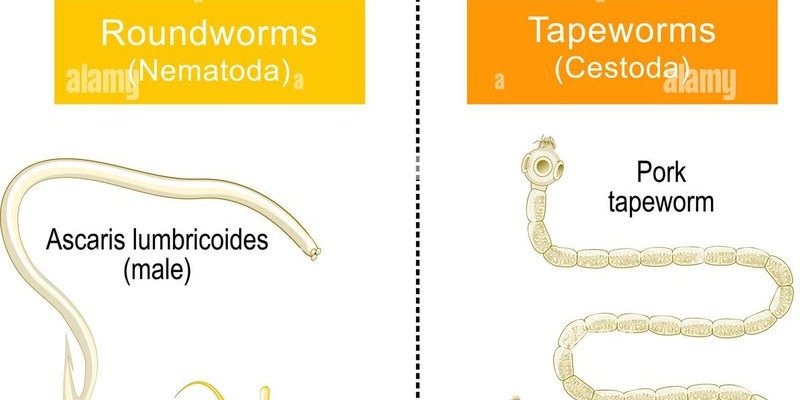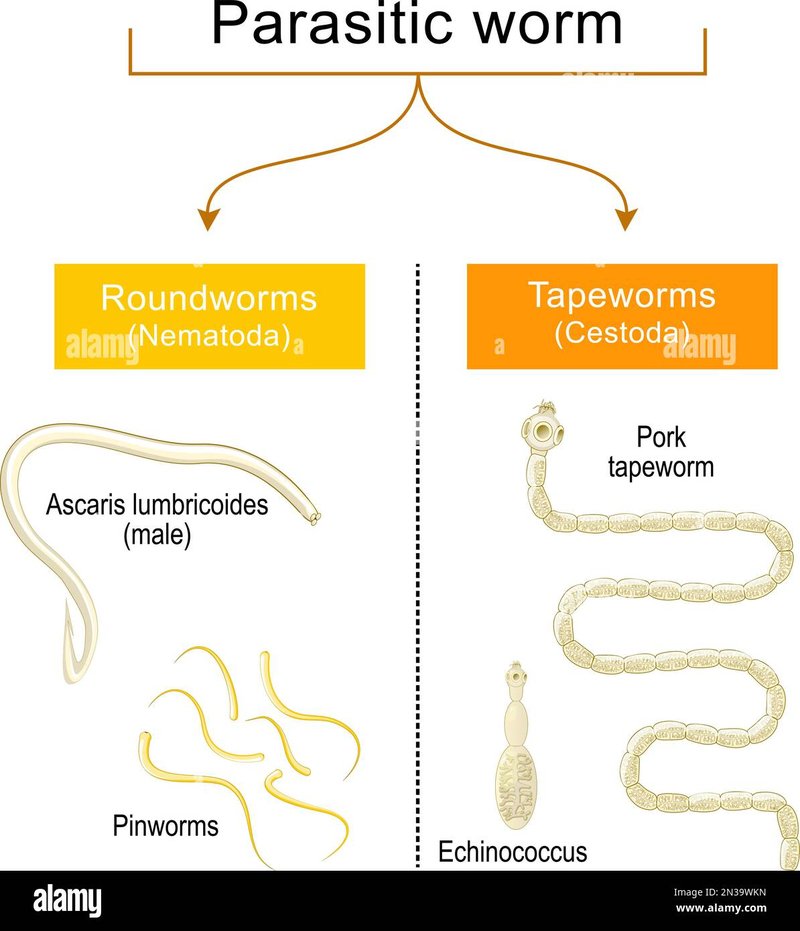
Tapeworms are fascinating because of their unique way of life. They have a long, flat body that’s made up of many segments. This allows them to easily attach to the intestinal walls of their hosts, which can include humans, dogs, and many other animals. But before you get too squeamish, let’s take a moment to explore how these little guys stack up against their relatives in the worm world. You might be wondering why this matters, and the answer is simple: understanding these differences can help us tackle issues like parasitic infections and improve our overall health.
What is a Tapeworm?
Tapeworms belong to a group called cestodes. They are flat, segmented worms, typically found in the intestines of their hosts. One of the most interesting things about tapeworms is their ability to have multiple segments, known as proglottids. Each of these segments can produce eggs, which contributes to their prolific nature.
These worms have a unique lifecycle. They start as eggs, which are usually ingested by an intermediate host, like a cow or pig. Once inside, they grow into larvae and eventually become the adult tapeworm we all love to hate. They can grow quite large, sometimes reaching lengths of over 30 feet!
You might be thinking, “How do they survive inside a host?” Well, tapeworms don’t have a mouth or digestive system. Instead, they rely on their skin to absorb nutrients directly from the host’s intestine. It’s like being the ultimate freeloader at a buffet—just sitting there and eating while someone else does all the work!
Exploring Roundworms
Next up, we have roundworms, or nematodes. These guys differ quite a bit from tapeworms and are more common than you might think. They can be found in soil, in our gardens, and even in our own bodies! Roundworms have a cylindrical shape, which is quite different from the flat body of tapeworms.
While some roundworms are harmless, others can be quite harmful to humans and animals. For instance, the ascaris roundworm can cause serious health issues in humans, including malnutrition and respiratory problems. Unlike tapeworms, roundworms have a complete digestive system, meaning they have both a mouth and an anus. This allows them to eat and excrete waste efficiently.
This leads us to a crucial point: while tapeworms thrive off a host’s nutrients without giving much in return, roundworms often impact their host’s health significantly, sometimes leading to chronic issues. So, if you’re ever concerned about parasitic worms, understanding the differences between these two can help you figure out the best steps to take.
Flatworms: The Lesser-Known Cousins
Now let’s talk about flatworms. While tapeworms are a type of flatworm, not all flatworms are tapeworms. Flatworms are a diverse group that can be found both in aquatic environments and on land. They tend to have more complex lifestyles, with some being free-living and others parasitic.
Free-living flatworms, like planarians, are fascinating because they have the ability to regenerate lost body parts. Imagine losing your arm and growing it back! Parasitic flatworms, aside from tapeworms, often infect fish or other aquatic animals, leading to various health problems.
The key takeaway here is that while tapeworms are specialized parasitic flatworms, other flatworms show a wide range of lifestyles, some of which can be beneficial to their environments. Think of flatworms as the diverse family members that each bring something unique to the table.
Comparing Lifecycles and Habitats
When comparing these worms, it’s important to consider their lifecycles and habitats. Tapeworms need a host to survive, often going through several life stages that involve different hosts. Their eggs are typically excreted with the host’s feces, which then find their way into the environment, ready for new hosts to consume.
In contrast, roundworms can be more versatile. Depending on the species, they can live in soil or infect various animals, including humans. Their lifecycle can vary significantly, with some needing just one host, while others might require multiple.
Flatworms also show diverse lifecycles. Free-living flatworms can reproduce asexually, while parasitic ones often need to go through multiple hosts, similar to tapeworms. Habitat-wise, flatworms can thrive in both freshwater and saltwater, showcasing their adaptability.
Understanding these differences in lifecycles and habitats helps us appreciate the ecological roles these worms play, and how they interact with their environments and hosts.
Health Risks and Treatments
Health concerns associated with these worms also vary greatly. Tapeworm infections can lead to symptoms like abdominal pain, nausea, and weight loss. Treating a tapeworm infection typically involves medication, like praziquantel, which is effective at eliminating the worm from the intestines.
Roundworms can cause a variety of symptoms, depending on the species. In some cases, they might not show any symptoms at all, while in others they can lead to serious health issues. Treatment often involves anti-parasitic medications, which can effectively kill the worms and relieve symptoms.
Flatworms, especially the free-living varieties, generally don’t pose a risk to humans. However, those that are parasitic can cause various health problems similar to tapeworms and roundworms. Prevention is key here, often revolving around good hygiene practices and proper cooking of food.
In short, while these worms share a similar habitat, the health risks they pose and the treatments available can vary significantly.
Final Thoughts: Why This Matters
So, why should we care about tapeworms and their relatives? Understanding these different worm species helps us better grasp their roles in our ecosystems and their impacts on our health. It’s like getting to know the characters in your favorite book; they all have their quirks and stories that shape the bigger picture.
By learning about their similarities and differences, we can take steps to minimize risks associated with parasitic infections. This knowledge promotes better health practices, whether it’s through improved food safety or awareness of the environments that harbor these creatures.
Remember, the world of worms is much more than meets the eye. By comparing tapeworms to similar worm species, we unveil a complex and intriguing ecosystem that deserves our attention, whether we’re gardening, raising pets, or simply enjoying nature.