Picture yourself strolling near a body of water, curious about the tiny organisms that thrive just beneath the surface. Understanding more about trematodes could help you appreciate the complexity and interconnectivity of nature. Identifying these creatures in their natural habitat may seem tricky at first, but don’t worry. With some guidance and keen observation, you’ll see that it’s easier than it looks. So, let’s dive in!
Understanding Trematodes: The Basics
Trematodes are more than just slimy little worms. They belong to a class of flatworms known as Trematoda. These creatures are typically parasitic, meaning they rely on hosts—like fish, amphibians, and even mammals—to survive and reproduce. What’s interesting is that they often go through multiple stages in their life cycles, sometimes involving different hosts altogether.
One crucial thing to note is that trematodes have a soft, flat body, which can make them look similar to leeches at first glance. Depending on the species, they can vary in color and size, ranging from tiny specks to a few centimeters long. Understanding what makes them tick can help you identify them more easily when you spot them in their natural habitats.
You might also be wondering how these creatures impact their environment. Some trematodes are known to help control host populations, while others can cause diseases in their hosts. This dynamic interplay emphasizes the importance of understanding these organisms further.
Where to Find Trematodes
Trematodes thrive primarily in aquatic habitats, but not all water bodies are created equal. They can typically be found in:
- Freshwater lakes and ponds
- Slow-moving streams
- Brackish water environments
- Coastal areas
While they can be tricky to spot, a good starting point is to look for organisms that often host trematodes, such as fish or snails. These hosts play a role in the trematode life cycle, so observing them can give you clues about the presence of trematodes nearby.
Finding the right environment is essential. Look for areas with plenty of vegetation, as this is where snails—the first host in many trematode life cycles—tend to hang out. You might find them hiding among the weeds or stuck to rocks, patiently waiting to be discovered.
Identifying Trematodes: What to Look For
Identifying trematodes in their natural habitat involves paying attention to several key features. First and foremost, these creatures generally have a unique, flat, and leaf-like shape. You’ll want to keep an eye out for their characteristic body structure, which can help differentiate them from other similar organisms.
Another vital feature to consider is their coloration. Trematodes may vary from shades of brown to green or even yellowish tones. Depending on their environment, they might blend in with surrounding algae or plant life, making them harder to spot.
When observing potential trematode hosts, look for signs of infection or abnormal behavior. For example, if fish appear sluggish or unwell, it may indicate the presence of trematodes. Additionally, note any changes in the host’s appearance, such as lesions or unusual growths, which can signal the presence of these parasitic worms.
Examining Worm Characteristics Under a Microscope
To get a closer look at trematodes, you may need a microscope. This is where the real fun begins! If you’ve collected some samples from water bodies or potential host organisms, take the time to examine them carefully.
You’ll want to look for:
- Size: Trematodes can vary widely in size, but often they are small enough to be difficult to see with the naked eye.
- Body Structure: The flat, leaf-like shape is a signature trait. Look for the oral sucker, which helps them attach to their host, and the ventral sucker that provides additional support during feeding.
- Movement: Observing how they move, if visible, can help identify their species. Some trematodes are more mobile than others, while some might appear inactive when separated from their host.
Using a microscope can be a game-changer in identifying these fascinating creatures. You might discover details you never noticed before, like the reproductive organs or the movement patterns that characterize different trematode species.
Common Trematode Species and Their Hosts
There are various species of trematodes, each with its specific host preference. Here are three common types you might encounter:
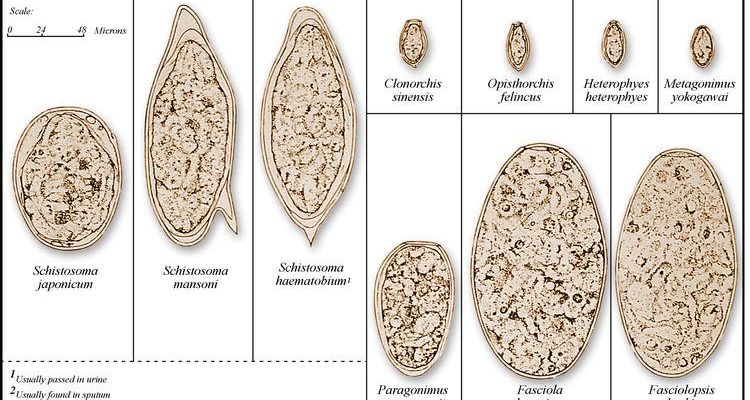
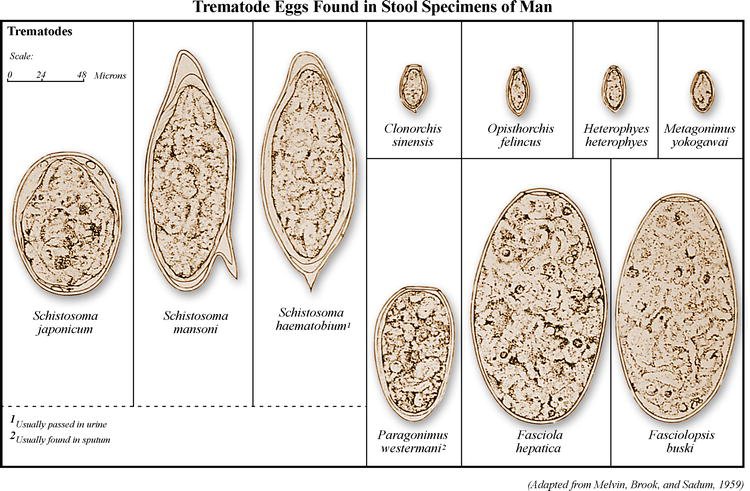
- Fasciola hepatica: Also known as the liver fluke, this species typically infects sheep and cattle. They can cause significant health issues in these livestock, leading to economic losses.
- Schistosoma: This genus includes the blood flukes, which can infect humans, causing the disease schistosomiasis. They are often found in stagnant water bodies where they can penetrate the skin of unsuspecting swimmers.
- Clonorchis sinensis: Known as the Chinese liver fluke, this trematode primarily infects fish-eating mammals, including humans who consume raw or undercooked fish.
Understanding which hosts are involved with different trematodes helps paint a broader picture of their ecological roles. If you spot any infected hosts, it’s a good idea to investigate further.
The Role of Trematodes in the Ecosystem
Even though trematodes are often cast in a negative light due to their parasitic nature, they serve essential roles in their ecosystems. For one, they help regulate host populations, which can be critical in maintaining balance within habitats. If a specific species becomes too dominant, trematodes can act as a natural control mechanism.
Additionally, trematodes can be indicators of environmental health. Changes in their populations might signal shifts in ecosystem dynamics, such as pollution or habitat destruction. By studying these creatures, researchers gain insights into the broader picture of aquatic health.
Understanding the ecological roles of trematodes can foster a deeper appreciation for these often-overlooked creatures. Though small, they play big roles in maintaining the balance of life around them.
Final Thoughts on Identifying Trematodes
Identifying trematodes in their natural habitat can be a fascinating adventure. With a little curiosity and the right knowledge, you can uncover these hidden creatures and understand their roles in the ecosystem. From their unique shapes and colors to their relationships with various hosts, there’s so much to explore.
As you embark on your journey to identify trematodes, remember to stay patient and observant. Nature often rewards those who take the time to look closely. So grab your gear, head to a nearby water source, and start your exploration—you never know what you might discover!
In the end, the world of trematodes is just a reflection of the beauty and complexity of nature itself. Embrace your curiosity, and delve deeper into the wonders that lie below the surface!