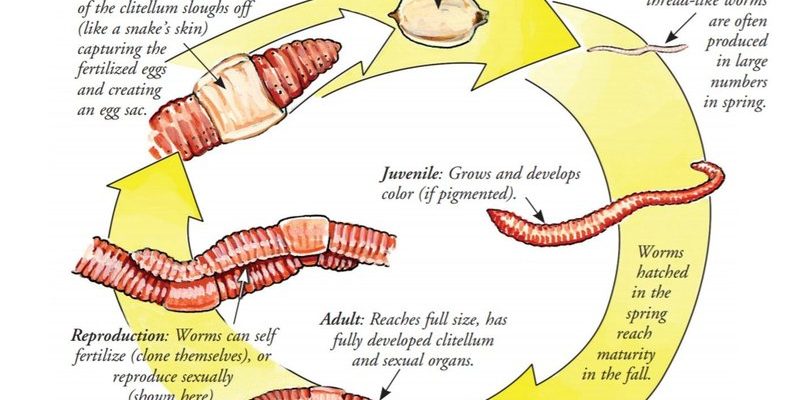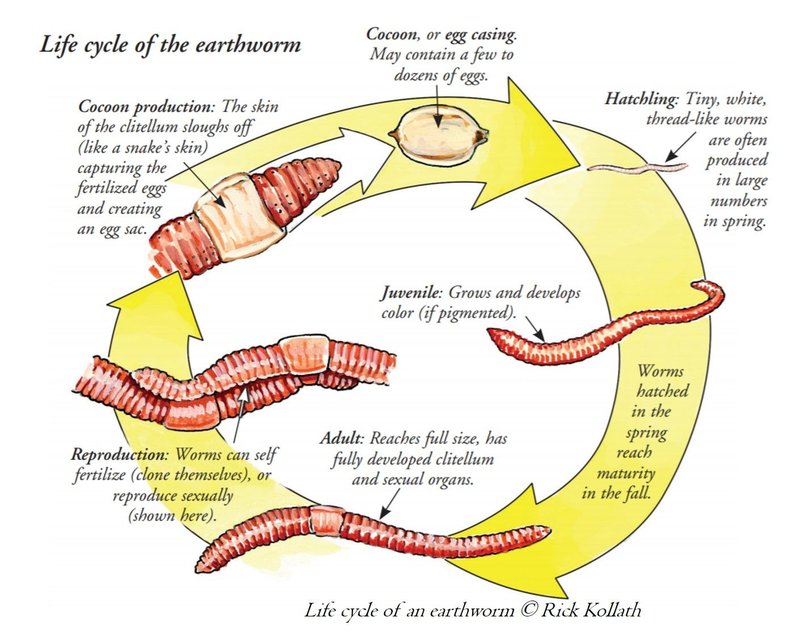
To understand this remarkable earthworm, let’s take a walk through its life cycle, from its humble beginnings as an egg to its emergence as a full-grown adult. We’ll dive into its behaviors, habitats, and the crucial roles it plays in its ecosystem. So grab a cup of coffee, and let’s dig in!
Stage 1: Egg Development
The life of a Giant Palouse Earthworm begins in the form of tiny eggs. These eggs are often laid in the soil, sheltered from predator eyes, making them a bit like buried treasure. Female earthworms can lay around 10 to 20 eggs at a time, which are encased in a protective cocoon.
These cocoons are about the size of a small bead and are made up of a gelatinous substance. The eggs take several weeks to hatch, depending on the temperature and moisture levels in the soil. Here’s the thing: the conditions must be just right. If it gets too dry or too cold, the eggs might not survive, making the right environmental factors crucial.
Once the eggs hatch, tiny worms emerge, ready to start their journey. Much like human babies, they are not fully developed at this stage. Instead, they’re small, soft-bodied, and a bit wiggly as they begin to burrow into the soil.
Stage 2: Juvenile Growth
After hatching, the Giant Palouse Earthworms enter a juvenile phase. During this stage, they start to grow and develop, feeding on organic matter like decaying leaves and plant roots. This diet not only helps them gain size but also plays a significant role in nutrient cycling in the soil.
Juveniles are often less than a few inches long when they first start growing, but they can reach impressive lengths as they mature. Honestly, their growth can be quite rapid under ideal conditions. As they consume organic material, they also contribute to breaking it down and enriching the soil with nutrients, which benefits the plants around them.
During this time, they stay underground, which protects them from predators and helps them conserve moisture. But they’re not completely alone—there are other microorganisms and fellow earthworms nearby, creating a bustling community in the soil.
Stage 3: Adult Maturity
As the Giant Palouse Earthworms grow larger, they eventually reach adulthood. This phase can take several years, sometimes up to three to five years, before they fully mature. At this point, they can stretch to about 3 feet long—impressive, right?
Adult earthworms are crucial for soil health. They continue to eat organic matter, but they also begin the reproductive cycle. During mating, two earthworms will exchange sperm, which is stored for future use. The pairing process can be fascinating, as they engage in a sort of “dance” to align their bodies.
Once they mate, they will produce cocoons and the cycle starts anew. Adult earthworms spend most of their time underground but will surface occasionally, particularly after rain, which helps them breathe more easily. Picture them emerging like little submarines surfacing for air!
Behavior and Adaptations
Giant Palouse Earthworms have some unique behaviors and adaptations that help them thrive. For one, they’re primarily nocturnal, meaning they’re most active at night. This behavior reduces their chances of being spotted by predators like birds and toads.
They also have a remarkable ability to burrow deep into the soil, creating extensive tunnels. This activity aerates the soil, promoting healthy plant growth. Additionally, these burrows help with water drainage, preventing flooding during heavy rains.
You might be wondering how they do this. Well, their bodies are built for it! They have strong, muscular bodies that allow them to push through the soil with ease, alongside a slimy coating that helps them glide smoothly underground. This adaptation is crucial for their survival and for maintaining the health of their ecosystem.
The Environmental Importance of Giant Palouse Earthworms
Giant Palouse Earthworms aren’t just interesting; they’re vital to their environment. By breaking down organic matter, they play a key role in soil fertility. Their burrowing actions help aerate the soil, making it easier for plant roots to grow and absorb nutrients and water.
Furthermore, they contribute to the overall health of the Palouse ecosystem. The nutrients they release into the soil enhance plant growth, which in turn supports various wildlife species. It’s like a cycle of life where each part plays an indispensable role in the big picture.
Without these worms, the soil could become compacted and less fertile, leading to poor plant growth. That’s why the survival of the Giant Palouse Earthworm is so important—not just for its species but for the entire ecosystem.
Conservation and Threats
Despite their importance, the Giant Palouse Earthworm faces several threats. Habitat destruction, primarily due to agricultural development, poses a significant risk. As farmers convert land for crops, the natural environment of these earthworms is disturbed, making it harder for them to survive.
Other threats include pollution and climate change. Changes in temperature and moisture can impact their development and reproductive cycles, potentially leading to population declines. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these unique creatures and their habitats.
Organizations are working to raise awareness about the importance of the Giant Palouse Earthworm and advocating for measures to preserve their natural environment. If we want to keep the environment balanced, we need to pay attention to these unsung heroes in the soil!
The life cycle of the Giant Palouse Earthworm is a beautiful example of nature’s intricacy and interdependence. Each stage, from egg to adult, showcases their unique adaptations and behaviors, emphasizing their role in maintaining soil health and supporting the wider ecosystem.
Understanding their life cycle helps us appreciate these remarkable creatures. Protecting them means supporting the delicate balance of the ecosystems they inhabit. So next time you think about soil health, remember the unseen giants working diligently beneath our feet. They may be small in stature, but their impact is anything but!