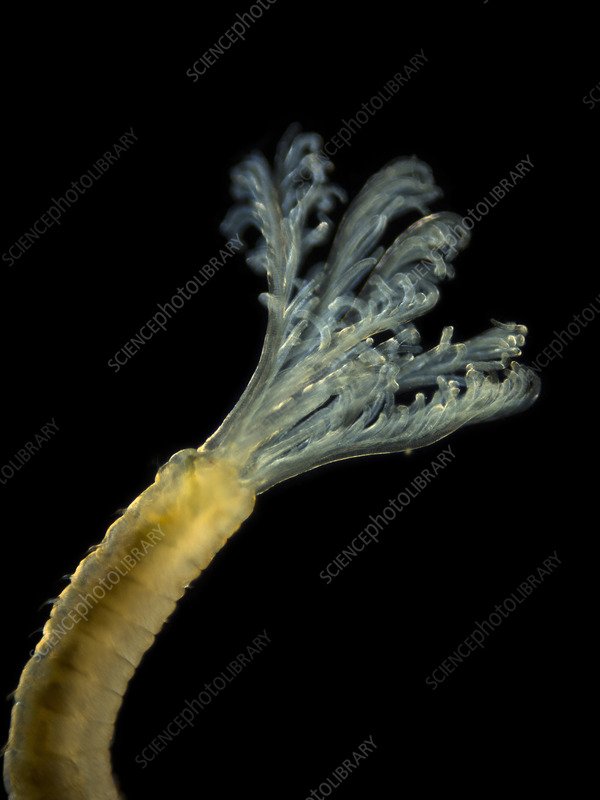
When we talk about “monitoring marine polychaete activity,” it’s like keeping track of the rhythm of a band. Their activity varies with the seasons, influenced by factors such as temperature, salinity, and food availability. To better understand how these worms thrive, scientists often use tools like remote sensors. One popular choice is the versatile Oceanographic Remote Data Logger, which helps researchers get an accurate picture of polychaete behavior without disrupting their habitat.
What Are Marine Polychaetes?
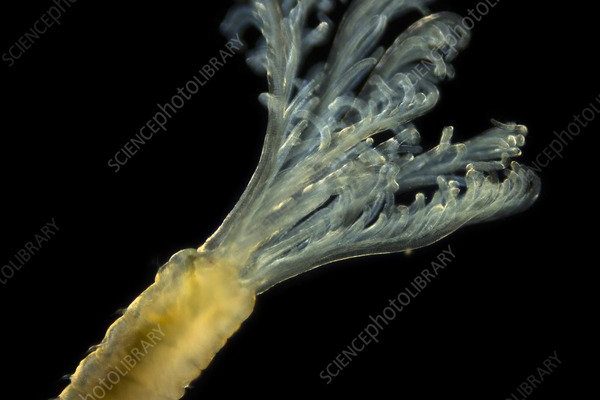
Marine polychaetes are a class of annelid worms, distinguished by their segmented bodies and bristle-like appendages called *chaetae*. You might think of them as the unsung heroes of the seafloor. These worms can range in size from a few millimeters to impressive lengths of over a meter. They play essential roles in the ecosystem, such as breaking down organic matter and serving as food for a variety of marine animals.
There are two main groups of polychaetes: sedentary and errant worms. Sedentary polychaetes often build tubes or burrows where they remain, while errant types are more mobile and actively hunt for food. This distinction is important because their behavior can greatly affect their interaction with the environment. For example, sedentary worms can help aerate the sediment, promoting healthier ecosystems, while errant worms contribute to nutrient cycling.
By understanding the diversity of marine polychaetes, we can appreciate their ecological roles. Think of them as nature’s recyclers, working tirelessly to maintain the balance in marine environments.
Why Monitor Polychaete Activity?
Monitoring the activity of marine polychaetes is crucial for several reasons. First, these worms are indicators of ecosystem health. Changes in their population or behavior can signal problems, such as pollution or climate change. For instance, if polychaete numbers decline, it might suggest that their habitat is becoming unlivable.
Moreover, tracking polychaete activity helps scientists understand larger ecological shifts. For example, if a region experiences a temperature increase, polychaetes may migrate or change their feeding habits. This data can help researchers predict broader changes in marine environments, similar to how early weather patterns can forecast a storm.
Lastly, polychaetes are essential to many marine food webs. By monitoring their activity, we gain insight into the health and stability of the entire ecosystem. Just like keeping an eye on the small plants in a garden can indicate the overall health of the environment, watching polychaetes can provide valuable information about oceanic changes.
Seasonal Changes Impacting Polychaete Activity
Marine polychaetes are heavily influenced by seasonal changes. As temperatures rise in spring and summer, polychaete populations often explode, taking advantage of abundant food sources. This is a time when they reproduce and grow, similar to how flowers bloom in spring. The warmer waters can also lead to a higher rate of organic matter decomposition, providing more nutrients for these creatures.
On the other hand, during fall and winter, many polychaete species slow down. Cooler temperatures can lead to decreased metabolic rates, meaning they become less active and may enter a sort of dormancy. This seasonal rhythm of activity highlights their adaptability, allowing them to survive in varying environmental conditions.
Additionally, factors like salinity and nutrient availability fluctuate with the changing seasons, also influencing polychaete behavior. For example, a heavy rain can dilute seawater salinity, which may stress some species while benefiting others. Understanding these seasonal dynamics helps scientists predict how polychaetes—and, by extension, marine ecosystems—will respond to climate change.
How Scientists Monitor Polychaete Activity
Monitoring marine polychaete activity involves a variety of methods. One common approach is using remote sensors that keep track of environmental variables like temperature, salinity, and oxygen levels. These devices can gather data over long periods without the need for constant human presence, allowing for a more accurate understanding of polychaete behavior. Think of it like setting up a camera to catch glimpses of wildlife in action without disturbing them.
Research teams may also conduct field sampling, where they collect polychaetes from different locations and analyze their population structures and sizes. This hands-on approach can reveal insights into how different species adapt to their environments, similar to how scientists study various plant species to see which ones thrive in different climates.
Diving deeper, genetic studies can provide a clearer picture of polychaete diversity. By analyzing genetic material, researchers can identify undiscovered species and track changes in population dynamics over time. This comprehensive monitoring helps create a fuller picture of how polychaetes interact with their environment.
The Role of Technology in Monitoring
Technological advancements have significantly enhanced our ability to monitor marine polychaete activity. Remote sensors, equipped with various tools like cameras and environmental probes, have become essential. The data collected helps researchers understand polychaete behavior in real time, much like how a fitness tracker monitors our health indicators.
Innovations like underwater drones and autonomous vehicles allow scientists to explore previously unreachable areas of the ocean. These technologies gather high-resolution images and data, shedding light on polychaete behavior that was once difficult to study. They offer a window into the hidden life of the ocean floor.
Another exciting advancement is the integration of machine learning in data analysis. By using algorithms, researchers can quickly identify patterns and anomalies in polychaete populations. This technology not only saves time but also improves the accuracy of predictions regarding marine ecosystem health.
Challenges in Monitoring Marine Polychaetes
While monitoring marine polychaete activity is vital, it comes with its challenges. One major obstacle is the sheer diversity of polychaete species and their habitats. Different species can occupy a range of environments, from deep sea trenches to shallow coastal waters. This variability makes it difficult to establish standardized monitoring methods that apply universally.
Additionally, environmental factors such as pollution and climate change can complicate observations. Changes in water quality can lead to shifts in polychaete populations, making it harder to draw clear conclusions. Moreover, human activities like overfishing can disrupt their habitats, adding another layer of complexity.
Finally, funding and resources often limit the scope and duration of monitoring projects. Long-term studies offer the best insights into polychaete behavior, yet securing consistent funding can be challenging. Despite these obstacles, ongoing research in marine biology continues to uncover important data, paving the way for better protection of these crucial organisms.
Monitoring marine polychaete activity across seasons is not just an academic exercise; it’s essential for the health of our oceans. By understanding the seasonal rhythms of these remarkable worms, we can glean insights into the broader state of marine ecosystems. It’s like reading the ocean’s pulse, helping us detect changes and address challenges before they escalate.
With advancements in technology and ongoing research, we are better equipped than ever to study these wormy wonders. As we face global environmental changes, keeping an eye on polychaetes can serve as a bellwether for the health of marine life. Ultimately, every little piece of research adds to our understanding of the ocean, reminding us of the delicate balance necessary to sustain life beneath the waves.