Think of the life cycle of a pinworm like a mini soap opera, complete with twists, turns, and some unexpected characters along the way. These worms have a pretty interesting journey, starting from eggs and leading to adult worms. The whole process is fascinating, and once you get to know it, you’ll have a better grip on how to avoid these unwanted house guests.
In this article, we’ll break down the life cycle of the pinworm, focusing on each stage and how they behave. By understanding how they operate, you can better protect yourself and your family. Let’s dive in!
What Are Pinworms?
Before we jump into the life cycle, it’s essential to understand what pinworms really are. Pinworms, scientifically known as *Enterobius vermicularis*, are small, white, threadlike worms that typically live in the human intestines. They’re notorious for causing itching around the anus, particularly at night when the female pinworms come out to lay eggs.
These worms are spread easily, especially in crowded settings like schools or daycare centers. When an infected person scratches the itchy area, they can transfer the eggs to their hands and other surfaces, making it super easy for others to pick them up. Honestly, it’s a bit like a game of tag, but not the fun kind.
So, why do we need to care about pinworms? Well, while they don’t usually cause serious health issues, they can lead to discomfort and, in some cases, secondary infections from scratching. Understanding how they work can help keep you and your loved ones safe.
The Life Cycle of the Pinworm
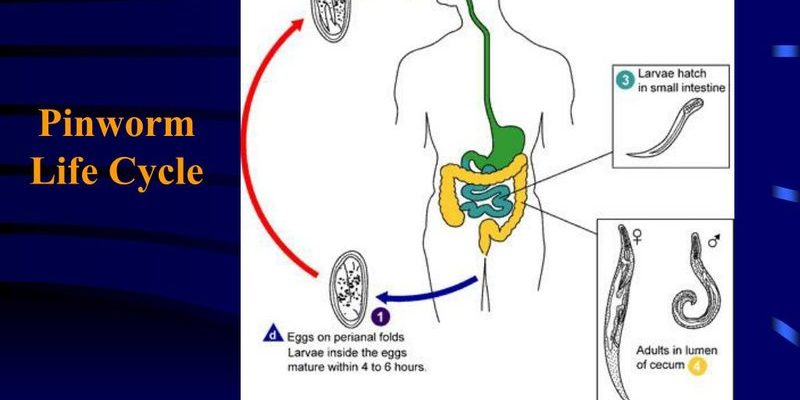
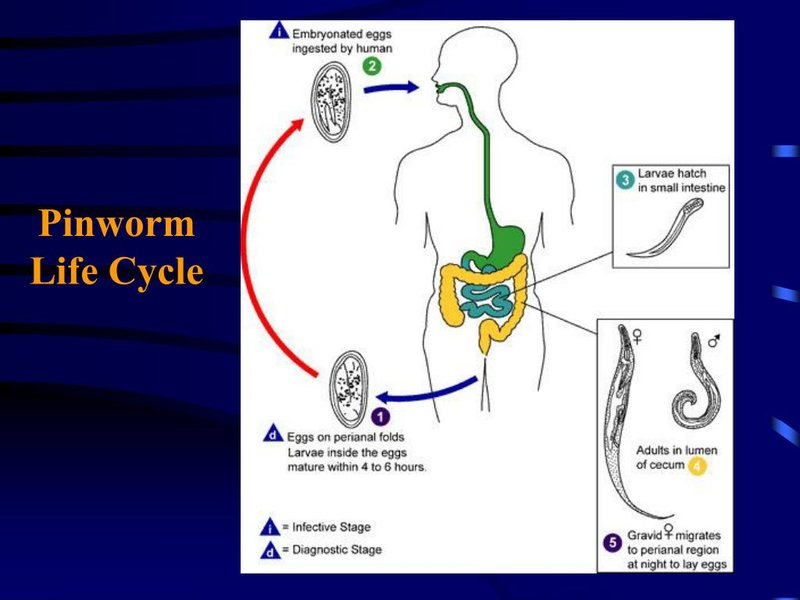
The life cycle of a pinworm can be divided into several key stages: egg, larva, adult, and re-infection. Each stage has its own unique characteristics and behaviors, which we’ll explore below.
1. The Egg Stage
The life cycle kicks off with the egg stage, which is where it all begins. Female pinworms lay their eggs in the folds of the skin around the anus, typically at night. These eggs are microscopic and can survive on surfaces for several weeks, waiting for a new host. It’s a bit like they have a little survival kit just to hang around.
You might be wondering why the eggs are laid at night. It’s because the itching promotes scratching, which can spread the eggs onto hands, bed sheets, and even into the air. Imagine tossing and turning at night and unintentionally sending tiny pinworm eggs flying into the world. Not exactly the peaceful night’s sleep you’d hope for, right?
In this stage, eggs can be ingested or transferred to surfaces. Children, in particular, can easily pick them up by touching contaminated surfaces and then putting their hands in their mouths. A classic case of “you didn’t wash your hands well enough.”
2. The Larva Stage
Once ingested, the eggs hatch in the intestines, leading to the larva stage. The larvae mature into adult pinworms over about four to six weeks. Picture it like an intense transformation, similar to a caterpillar turning into a butterfly, but a whole lot less glamorous.
As they grow, these tiny larvae start to make themselves comfortable in the intestines. They feed off the nutrients in the intestines and thrive in this warm environment. Here’s the thing: during this stage, they aren’t just biding their time. They’re actively preparing to reproduce.
This is also when symptoms may start to appear. You might feel mild abdominal discomfort or get that infamous itch. If you notice any of these signs, it might be time to check in with your healthcare provider.
3. The Adult Stage
The adult stage is when pinworms really show their true colors. Adult pinworms can measure up to half an inch long—about the size of a staple—and they’re often males or females. The females are the primary culprits when it comes to irritation since they’re the ones laying eggs at night.
Once they’re fully grown, adult pinworms will migrate to the anal area at night to lay their eggs. This nocturnal behavior is what causes the itchy feeling during the night. It’s almost like a little midnight party that no one invited you to!
During this stage, the cycle can keep repeating itself. If proper hygiene practices aren’t in place, the eggs can infect the same person or others in close contact. It’s why pinworms tend to spread so rapidly, making effective treatment essential.
4. Re-infection: A Never-Ending Cycle
One of the trickiest parts of dealing with pinworms is the re-infection stage. This means once you’ve removed the adult worms, it’s crucial to avoid re-infestation. As many as 90% of people can experience re-infection if they don’t take precautions, mainly because pinworm eggs can remain in the environment for weeks.
So, how does someone fall back into the cycle? It can happen through several means:
- Touching contaminated surfaces, like bedding or clothing.
- Not washing hands thoroughly after using the bathroom.
- Eating food that’s been prepared on contaminated surfaces.
To combat this, it’s important to practice good hygiene. Washing hands regularly, keeping fingernails short, and washing bed linens frequently can help break the cycle.
Symptoms of Pinworm Infection
Knowing the symptoms of pinworm infection is crucial for addressing the issue quickly. The most common symptom is a distinctive itch around the anus, especially at night. This is due to the female pinworm laying her eggs.
Other symptoms may include:
- Restlessness or trouble sleeping due to itching.
- Skin irritation or infections from scratching.
- Occasional stomach pain or discomfort.
- Visible worms in stool or around the anal area.
If you or your child are experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s a good idea to consult your healthcare provider for advice. They can confirm if pinworm infection is the issue and recommend the best treatment options.
Treatment Options for Pinworm Infection
Treating pinworm infections is typically straightforward. Over-the-counter medications can effectively eliminate pinworms in just one or two doses. Common treatments contain antiparasitic agents, such as mebendazole or pyrantel pamoate.
Here’s a basic outline of what treatment might involve:
- Take the recommended medication, usually in one dose.
- Re-take the medication after two weeks to eliminate any new hatching eggs.
- Practice good hygiene to prevent re-infection.
In addition to medication, educating everyone in the household about hygiene practices is vital. Make sure everyone is washing their hands regularly, especially before meals and after using the bathroom.
Prevention: Keeping Pinworms at Bay
Preventing a pinworm infection is often easier than treating one. Here are some effective methods to help keep these pesky parasites away:
- Wash hands regularly: Teach kids to wash their hands with soap and water, especially after using the bathroom.
- Keep fingernails short: This helps reduce the chance of transferring eggs to your mouth.
- Wash bed linens and clothing: Regularly cleaning can help remove any lingering eggs.
- Avoid sharing personal items: Keep towels, combs, and other personal items separate.
By taking these simple steps, you can help protect yourself and your family from pinworm infections. It’s all about creating a clean environment and good habits.
Wrapping It Up
Understanding the life cycle of the pinworm can empower you to tackle any potential infestations with confidence. From their egg stage to their adult lives, these worms have a complicated routine that can disrupt daily life. Luckily, with proper hygiene and treatment, keeping pinworms at bay is entirely possible.
If you or someone in your home is dealing with symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek help from a healthcare provider. With the right knowledge and practices, you can ensure that your household stays happy and healthy—without any uninvited tiny guests!