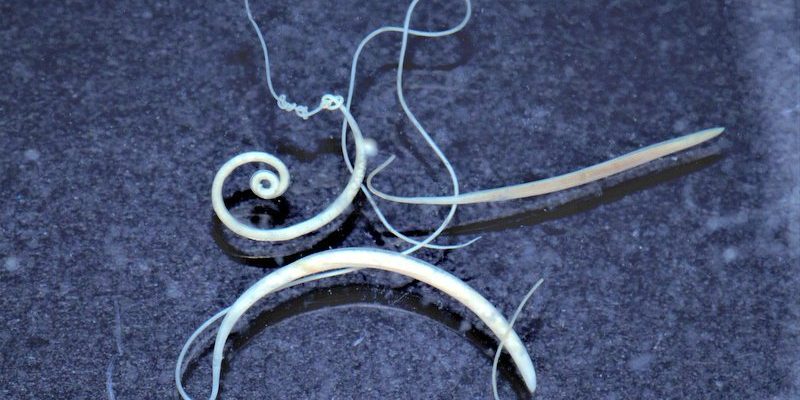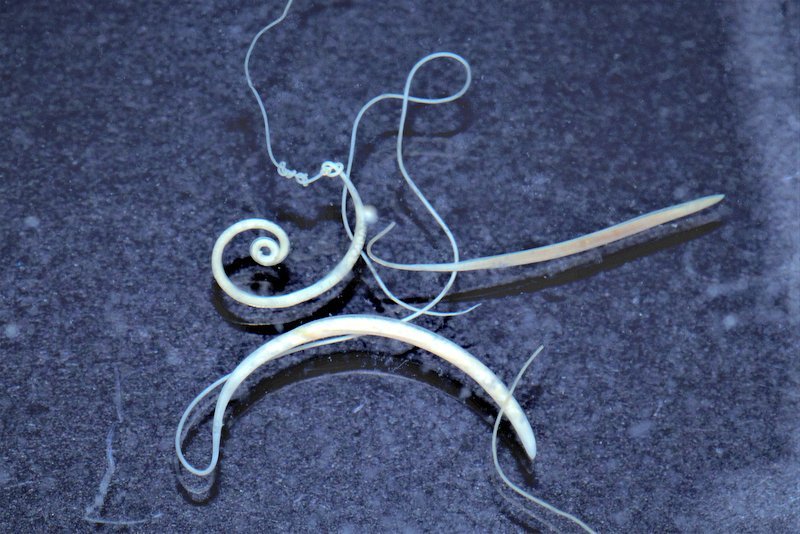
To put it simply, whipworms are parasites that feed off their hosts, primarily living in the intestines. They’re named for their whip-like shape, which actually looks a bit like a tiny piece of spaghetti! Despite their somewhat scary reputation, whipworms often go unnoticed until they cause trouble, which often leads to various health issues for their hosts. So, let’s dive into the world of whipworms, understanding their anatomy, life cycle, and the impact they have on their hosts and the environment.
Understanding Whipworms: Anatomy and Life Cycle
Whipworms belong to the genus *Trichuris*, and their anatomy is quite unique. Unlike many other worms, whipworms have a whip-like appearance that helps them anchor themselves into the intestinal lining of their host. Their body is thin at one end and thicker at the other, which is essential for their survival. This design allows them to effectively burrow into the intestine, where they can feed off the nutrients of their host.
Here’s the thing: whipworms have a fascinating life cycle that consists of several stages. It starts when the female whipworm lays eggs in the intestine. These eggs are then expelled into the environment through the host’s feces. Once in the soil, the eggs need the right conditions—like warmth and moisture—to mature. After a week or two, the eggs become infectious larvae. If another host ingests these larvae through contaminated food or water, it’s a perfect setup for a new whipworm infection.
Life Cycle Stages of Whipworms
1. Egg Production: Adult whipworms produce eggs that are expelled into the environment.
2. Environmental Maturation: Eggs develop in the soil under suitable conditions.
3. Infection: New hosts ingest the larvae through contaminated food or water.
4. Maturation in Host: Once ingested, the larvae develop into adult whipworms in the intestines.
Understanding this life cycle is critical, especially when discussing the impact whipworms can have on both animals and humans.
Whipworms and Their Hosts: A Complex Relationship
Whipworms primarily infect mammals, including both pets and humans. In particular, humans can be affected by *Trichuris trichiura*, the species of whipworm that causes infections. Here’s the kicker: while whipworms can cause various health problems, their relationship with their hosts is complex and somewhat interconnected.
Infected hosts sometimes experience symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and even anemia. This happens because whipworms feed on the nutrient-rich lining of the intestines, stealing vital resources from their hosts. However, the presence of whipworms can sometimes lead to a unique balance in the gut ecosystem. This balance can affect everything from digestion to immune response.
Common Symptoms of Whipworm Infection
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Anemia
- Weight loss
It’s important to remember that not all hosts will show symptoms. Some may carry the whipworms without ever knowing it, which raises questions about their overall health and well-being.
How Whipworms Impact Ecosystems
Despite being parasites, whipworms play an essential role in their ecosystems. They contribute to the nutrient cycling in the environments they inhabit. When whipworms consume the intestinal lining of their hosts, they help regulate the host’s nutrient intake. This, in turn, has broader implications for the host’s health and can influence overall ecosystem dynamics.
Moreover, whipworms can serve as indicators of environmental health. A high prevalence of whipworm infections may point towards unsanitary conditions, as they thrive where sanitation is poor. By studying whipworms and their impacts, scientists can gain insights into various environmental factors, including soil quality and water safety.
Whipworms as Environmental Indicators
1. Sanitation Indicators: High rates of whipworm infections can suggest unsanitary conditions in specific areas.
2. Ecosystem Health: Understanding the balance of whipworm populations can offer valuable information about the overall health of the environment.
So, while they may seem like nuisances, whipworms can tell us a lot about the state of our ecosystems.
Preventing Whipworm Infections
While whipworm infections may not be a hot topic at your next dinner party, knowing how to prevent them can be crucial, especially if you have pets or children. The best way to avoid these pesky parasites is through good hygiene practices and proper sanitation.
Here are some effective prevention tips:
- Wash your hands regularly, especially after using the bathroom or handling pets.
- Avoid drinking contaminated water or eating foods that might be contaminated.
- Regularly deworm pets to help keep them free from whipworms and other parasites.
- Ensure proper sanitation in areas where food is prepared and consumed.
Making these habits part of your daily routine can significantly reduce the risk of whipworm infections.
Why Does Prevention Matter?
Preventing whipworm infections isn’t just about individual health; it’s about the bigger picture. When we prioritize hygiene and sanitation, we contribute to community health and well-being. Plus, it helps maintain a balance in the ecosystem, minimizing disruptions caused by parasites.
Whipworms in Veterinary Medicine
If you have pets, you might be concerned about whipworms and their impact on your furry friends. Whipworm infections can be particularly problematic for dogs, leading to health issues if left untreated. In veterinary medicine, it’s crucial to tackle whipworm infections promptly.
Routine veterinary check-ups can help identify whipworm infections early. If your vet suspects a whipworm infestation, they may recommend specific deworming treatments tailored to your pet’s needs. Here’s how you can be proactive:
- Schedule regular vet check-ups.
- Discuss deworming options with your veterinarian.
- Keep your pet’s living area clean and free of waste.
By staying ahead of possible infections, you can help ensure that your pets lead happy and healthy lives.
Common Vet Treatments for Whipworm Infections
1. Deworming Medications: Your vet may prescribe specific medications to eliminate whipworms.
2. Follow-Up Testing: After treatment, follow-up tests can confirm that the infection has been cleared.
Working closely with your veterinarian can make a world of difference in your pet’s health and well-being.
While whipworms might not be the most glamorous creatures, they hold a unique place in nature. Understanding what whipworms are and how they interact with their hosts can shed light on broader ecological issues. Whether you’re looking to protect yourself, your family, or your pets, knowledge is key.
So next time you hear the term “whipworm,” you can appreciate the complexities of these tiny parasites and the role they play in the grand scheme of life. Nature is full of surprises, and even the smallest creatures can have big impacts. Armed with this knowledge, you can help prevent whipworm infections and contribute to a healthier environment for all.