If you’ve ever wondered about how fast hornworms grow and what they go through in their short lives, you’re in the right place. Whether you’re an enthusiastic gardener trying to keep pests at bay or a curious nature lover, understanding the growth rate and life cycle of these creatures can be quite enlightening. So, let’s take a deep dive into the world of hornworms and see what makes them tick, or should I say “crawl”?
The Life Cycle of Hornworms
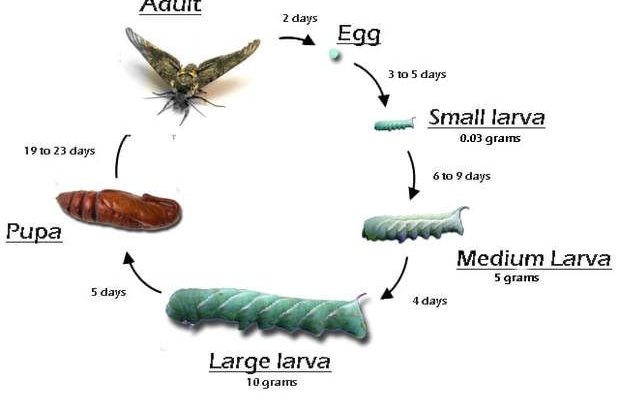
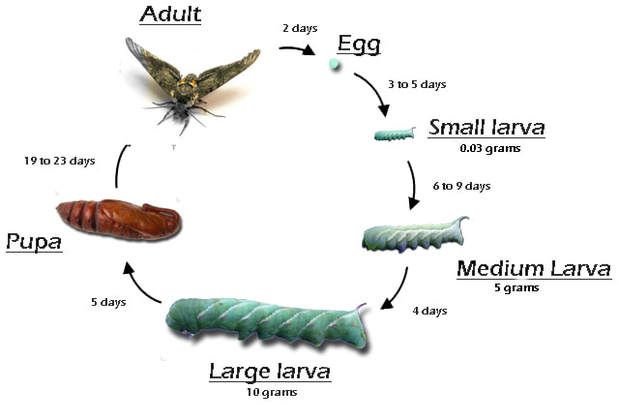
Hornworms belong to the family Sphingidae, and their life cycle consists of four distinct stages: egg, larva (the hornworm itself), pupa, and adult moth. Each stage lasts a different amount of time, leading to the overall speed of their growth.
- Egg Stage: The journey begins when a female moth lays tiny, round eggs on the underside of host plants, typically tomatoes, peppers, or eggplants. These eggs are often a little less than a millimeter in diameter and can hatch in about 3 to 5 days, depending on environmental conditions.
- Larva Stage: Once the eggs hatch, tiny hornworms emerge and begin to munch on the foliage almost immediately. This stage is where they grow the most, and it can last anywhere from 2 to 4 weeks. During this time, they can grow from less than an inch to around 4 inches long!
- Pupa Stage: After the larval stage, hornworms pupate. They usually bury themselves in the soil or create a silk cocoon. This stage can last from 10 days to 2 weeks. They are not active during this stage, but it’s critical for their transformation.
- Adult Moth: Finally, the pupae emerge as adult moths. These moths, typically known as hawk moths or sphinx moths, are often quite large and can have a wingspan of about 4 to 5 inches.
This entire cycle can take just about 30 to 45 days from egg to moth. Isn’t that something?
The Speed of Growth in the Larval Stage
You might be wondering, “How fast do hornworms grow during that larval stage?” Honestly, this is where they really shine. When they first hatch, they are tiny and vulnerable, but by the time they are ready to pupate, they’ve undergone several molts, shedding their skin as they grow.
During this stage, hornworms can consume a staggering amount of foliage—up to 4,000 times their weight! They’ll devour leaves as if they’re at an all-you-can-eat buffet. This rapid growth isn’t just for show; it’s essential for them to store enough energy for their transformation into moths.
On average, a hornworm can grow **1 inch per day** in optimal conditions. Factors like temperature, humidity, and food availability play a significant role in this growth speed. If the weather is warm and the plants are plentiful, hornworms tend to grow faster.
Environmental Factors Affecting Growth
Just like how our moods can change with the weather, hornworms are very sensitive to their environment. The temperature and humidity levels can significantly impact how quickly they grow.
- Temperature: Ideal temperatures for hornworm growth range from 70°F to 85°F. If it gets too hot, they may slow down or even stop eating, while cooler temperatures can also hinder their growth.
- Humidity: Hornworms thrive in moist conditions. If it’s too dry, they can become stressed, affecting their growth. However, if there’s too much moisture, it can lead to fungus or mold, which is harmful.
- Food Supply: The availability and quality of leaves are crucial. Healthy, lush plants provide the best nourishment. If hornworms run out of food, their growth can stall dramatically.
Understanding these factors can help you manage hornworm populations if you’re a gardener or simply appreciate their unique lifecycle.
Why Hornworm Growth Matters
Knowing how fast hornworms grow is essential for gardeners and anyone interested in ecology. These caterpillars can cause significant damage to plants, especially when they’re in the larval stage and hungry. Here’s why it matters:
1. **Pest Management:** Recognizing how quickly they grow can inform your pest control strategies. If you see small hornworms, it might be best to act quickly to prevent them from becoming larger, more destructive pests.
2. **Plant Health:** Understanding hornworm growth helps gardeners assess the health of their plants. If you notice a sudden increase in hornworm activity, it may indicate that your plants are in trouble.
3. **Ecological Balance:** Hornworms are a part of the food web, serving as food for birds and other predators. Knowing their growth cycle helps in understanding their role in the ecosystem.
Physical Characteristics of Hornworms
As hornworms grow, they undergo several distinct physical changes that are fascinating to observe. In their early days, they are small and quite different in appearance compared to their mature selves.
- Color: Young hornworms are usually a pale green color, making them somewhat camouflaged against the green leaves they munch on. As they grow, they become a deeper green, almost blending in completely.
- Size: Starting off at under an inch, mature hornworms can reach impressive lengths of about 4 inches. Their size can be quite shocking if you happen upon one while inspecting your garden!
- Physical Features: Hornworms are distinguished by their characteristic “horn” at the rear end. This horn is not a stinger but is thought to deter predators.
These physical changes not only show their growth rate but also their adaptation to their environment, making them a remarkable study subject.
Dealing with Hornworms in Your Garden
If you’re growing tomatoes or other susceptible plants, chances are you may encounter hornworms. Here are some tips to help manage them effectively:
1. **Regular Inspections:** Check your plants regularly, especially the undersides of leaves. Catching them early can prevent more significant problems.
2. **Natural Predators:** Birds and other wildlife love to snack on hornworms. Encouraging these natural predators can help keep hornworm populations in check.
3. **Manual Removal:** If you find a few hornworms, simply removing them by hand can be effective. Just wear gloves, and throw them in a safe spot away from your garden.
4. **Neem Oil or Insecticidal Soap:** For larger infestations, consider using neem oil or insecticidal soap, which are effective and less toxic options.
By understanding hornworm growth, you can take steps to protect your plants while respecting the role these creatures play in the ecosystem.
Hornworms grow incredibly fast, and their life cycle is a fantastic example of nature’s wonders. From egg to larva to moth, they go through remarkable transformations in just a few weeks. Their growth not only impacts your garden but also provides insight into the ecological balance of the environment.
So, whether you’re a gardener or just someone curious about the life of these hungry little caterpillars, appreciating their growth process can deepen your understanding of nature. The next time you spot a hornworm in your garden, you might just look at it with a newfound respect, knowing the speedy journey it’s on.