So, let’s dive in. With their unique features and lifestyles, ribbon worms and annelid worms present some pretty interesting contrasts. Whether you’re simply curious or you’re preparing for a biology class, this comparison will help clarify what sets these two groups apart. Grab a coffee, and let’s explore the world of worms together.
What are Ribbon Worms?
Ribbon worms, or **Nemerteans**, are quite the fascinating bunch. Picture a long, slender noodle, often with a vibrant, often striking coloration. They can stretch out to impressive lengths—some species reach over 30 feet! Despite their lengthy appearance, many are quite thin, almost ribbon-like, hence the name.
These worms are primarily marine creatures, living in oceans and seas around the globe. While some prefer shallow waters, others can be found in the deeper, darker parts. They thrive in various environments, including sandy or muddy substrates. You might be wondering how they catch their meals. Ribbon worms have a unique feeding method involving a **proboscis**, a tubular structure that can extend rapidly to ensnare prey, which often includes small fish and invertebrates.
The way ribbon worms move is another area where they truly shine. They can glide along surfaces or burrow into sediment, showcasing an impressive level of mobility. Honestly, if you ever get the chance to observe them, you’ll see them coil and uncoil with remarkable grace.
What are Annelid Worms?
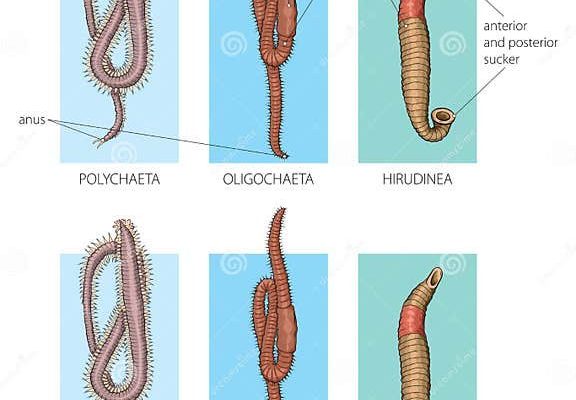
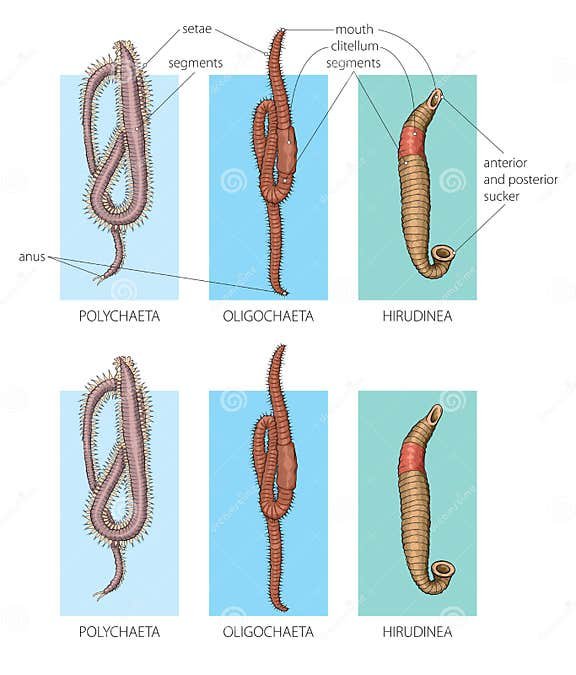
Now let’s shift our focus to annelid worms, the members of the **Annelida** phylum. They’re more commonly known as segmented worms and include familiar faces like earthworms and leeches. Their bodies are divided into segments, which give them a distinctive look, sort of like a living, breathing caterpillar.
Annelid worms are found both in **marine** and **terrestrial** environments. You know that satisfying feeling when you dig up some earthworms while gardening? You’re encountering annelids! They play a crucial role in soil health, helping to aerate and break down organic matter. Their presence contributes to the overall ecosystem, making them essential for garden lovers.
Unlike ribbon worms, annelid worms breathe through their skin and have a **closed circulatory system**. This means their blood is contained within vessels, allowing for more efficient oxygen transport. So, when you think about how each type of worm interacts with its environment, annelid worms set a strong example of nature’s ingenuity.
Key Differences Between Ribbon Worms and Annelid Worms
Let’s take a closer look at what separates these two intriguing types of worms. Here’s a breakdown of their **key differences**:
- Body Structure: Ribbon worms have a smooth, elongated body that lacks segmentation, while annelids boast a segmented form. This segmentation in annelids helps with movement and organization of their bodies.
- Feeding Mechanism: Ribbon worms utilize their unique proboscis for capturing prey, whereas annelids generally use a mouth for feeding and can consume a wider range of organic material, including detritus.
- Respiration: Ribbon worms breathe through their skin and must keep it moist, while annelids also utilize their skin for respiration but have adaptations to better manage life in various environments.
- Habitat: Ribbon worms are predominantly marine, living in a variety of oceanic settings. On the other hand, annelids can be found in both saltwater and freshwater, as well as in terrestrial habitats.
- Movement: Ribbon worms can glide and burrow fluidly, while annelids use their segments to move in a crawling motion, aided by bristles called **setae**.
These differences highlight just how diverse the world of worms really is. Each type has evolved to fit perfectly into its niche in nature.
Ecological Roles of Ribbon Worms and Annelid Worms
Both ribbon worms and annelid worms play vital roles in their ecosystems, helping to maintain balance and health. Ribbon worms, with their predatory nature, help control populations of smaller marine animals, ensuring that prey species do not become overly abundant. Their presence keeps the marine food web in check, making them essential for maintaining biodiversity.
Annelid worms, especially earthworms, are often referred to as **nature’s tillers**. They break down organic matter and contribute to soil fertility. With their burrowing habits, they aerate the soil, allowing water and nutrients to reach plant roots more efficiently. This makes them a gardener’s best friend, boosting crop yields and supporting plant health.
Both types of worms, in their unique ways, contribute to nutrient cycling, which is crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems. Here’s the thing: their roles might look different, but the impact on the environment is equally important.
Reproduction in Ribbon Worms and Annelid Worms
Reproduction methods also set these two groups apart. Ribbon worms have a unique way of reproducing. Many species are capable of **asexual reproduction** through fragmentation. When a piece of the worm breaks off, it can regenerate into a complete organism. It’s a bit like a starfish losing an arm and regrowing it!
On the other hand, annelid worms generally reproduce sexually. They typically have both male and female reproductive organs, allowing them to exchange sperm during mating. Earthworms, for example, will form a mucous ring that captures sperm, which they later use to fertilize their eggs.
This contrast in reproduction highlights the adaptability of each worm type. While ribbon worms can regenerate, annelid worms focus on genetic diversity through sexual reproduction.
In our exploration of ribbon worms and annelid worms, we’ve seen how these fascinating creatures differ across various dimensions, from their body structure to their reproductive methods. Understanding these differences isn’t just about curiosity—it’s about appreciating the complexity of life on Earth. Each worm type plays a critical role in its environment, contributing to the health and balance of ecosystems.
So, the next time you find yourself in the garden or by the sea, take a moment to consider these incredible creatures. They may be small, but they have a big impact on our world. Whether it’s the graceful ribbon worm gliding through the water or the hardworking earthworm aerating the soil, there’s a lot more to these worms than meets the eye. Let’s celebrate the diversity of life and the unique contributions of our wormy friends!